Visit our website at chronoslany.com.
Chronos is a comprehensive developer tool that monitors the health and web traffic for containerized (Docker & Kubernetes) and non-containerized microservices communicated via REST APIs or gRPC, whether hosted locally or on Amazon Web Services (AWS). Use Chronos to see real-time data monitoring and receive automated notifications over Slack or email.
Contributors: Arnold Pinkhasov, Ashley Bisram, Fridchard Chery, Peter Toussaint
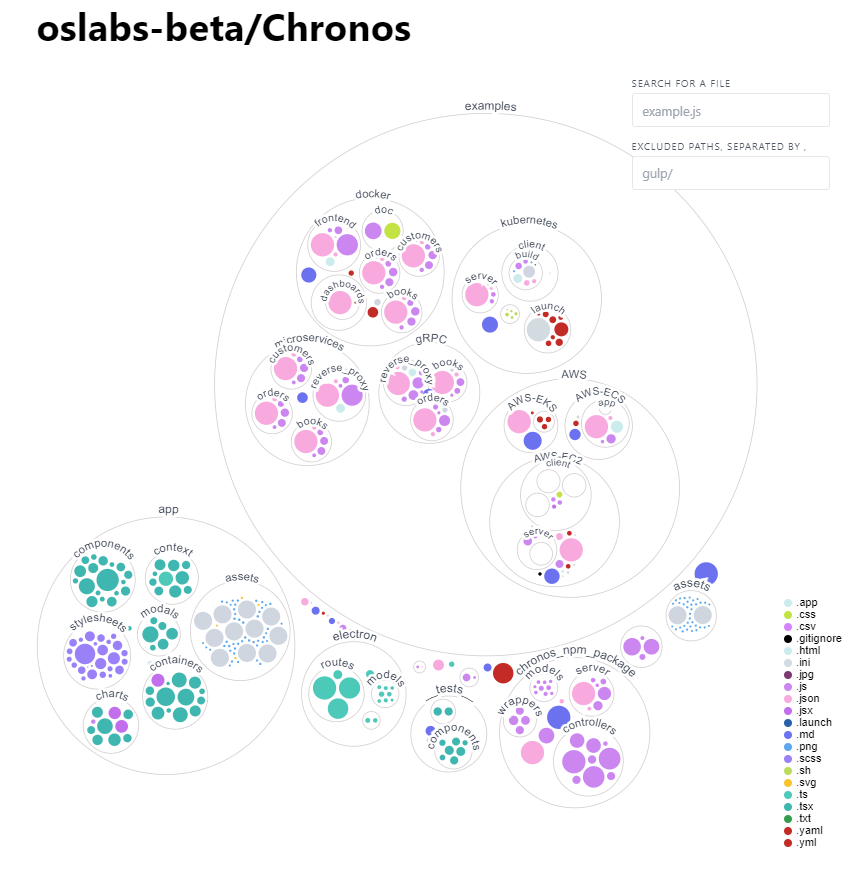
Chronos 14.0
- Implemented a new visualization button (example) to expedite data rendering processes.
- Refactored microservices example, switched over to community version of MongoDB for easier URI implementation.
- Modularized cluttered components into modular units to improve code readability and reusability.
- Optimized startup scripts to reduce application load time and streamline environment configuration.
- Upgraded Material-UI from version 4 to version 5, adapting to new API changes and improving UI responsiveness.
- Refactored portions of the electron app
- Refactored data parsing logic to reduce unnecessary rerenders and improve app performance
- Fixed data bottle necks in the local npm packages, data is now able to flow to microservices for data visualization
Contributors: Michael Tagg, Ted Pham, Sofia Sarhiri, Stephen Yang
Chronos 13.0
- Created new and improved microservices application with updated syntax to better demonstrate Chronos' capabilities
- Dockerized microservices application to demonstrate Chronos within a containerized environment
- Added visulization of Chronos' codebase to illustrate overall structure
- Simplified installation and startup instructions in the root directory README file
- Improved documentation in chronos_npm_package README file for easier on-boarding
Contributors: Elsa Holmgren, Mckenzie Morris, Kelly Chandler, Sean Simpson, Zhongyan Liang
Chronos 12.0
- Grafana charting and visualizer
- Increase in Prometheus and cAdvisor integration span
- Increased testing coverage to include unit testing and Selenium-based, end-to-end testing
- Integrated CI/CD which automates GitHub Action to run testing suites in order and create a publishing action to NPM Registry
Contributors: Haoyu Liu, Edwin Leong, Eisha Kaushal, Tyler Coryell
Chronos 11.0
- Interactive charting which can display and compare metrics in rendered graphs
- Increased user database security with user authorization to connect multiple
- services and databases and have instances persist without having to reconnect
- Improved documentation by adding ReadMes about how to initialize the app, how to use the given examples, and how to update config files
- Updated NPM Package to ‘increase reliability and ease of navigation
- Fixed bugs and improved test coverage
Contributors: Brisa Zhu, Lucie Seidler, Justin Poirier, Jeffrey Na, Kelsi Webb
Chronos 10.0
- Full user authentication integrating with a functional database which enables users to securely save their profile and data
- Updated microservices, gRPC, and Dockerized app examples
Contributors: Brian Lim, Claire Tischuk, Lennon Stewart, Victor Ye,
Chronos 9.0
- Added AWS - Users of Chronos are now able to monitor and visualize containers running in Amazon’s Elastic Kubernetes Service (EKS)~Medium
- Ability to monitor cost metrics through Opencast integration
Contributors: Brian Lim, Claire Tischuk, Lennon Stewart, Victor Ye
Chronos 8.0
- Rewrite microservice in a language with a higher level of support such as GO or Java
- Use packages such as OpenTelementry to record data and export said data to an additional application like Zipkin or Prometheus
- Purchase a license to one of the few monitoring tools that support gRPC and Node.js.
Contributors: Vince Ho, Matt Giant, Derek Lam, Kit Loong Yee
Chronos 7.0
- Ability to filter out specific metrics using a query tool
- Increased the number of metrics available from 12 to 100+
- Options to filter metrics by category
- Apache Kafka monitoring capabilities
- Bug fixes and UI improvements
Contributors: Yang Song, Giovanni Floreslovo, James Edwards, Alex Kolb
- In our ChroNotes, we have a full overview of all the files in the codebase, and their purpose. Click here to view!
- Cloud-Based Instances:
- Local instances utilitizing
@chronosmicro/trackerNPM package:- Enables distributed tracing enabled across microservices applications
- Displays real-time temperature, speed, latency, and memory statistics for local services
- Displays and compares multiple microservice metrics in a single graph
- Allow Kubernetes and Docker monitoring via Prometheus server and Grafana visualization.
- Compatible with

- Monitor an
 cluster via the JMX Prometheus Exporter
cluster via the JMX Prometheus Exporter - Supports
 and
and  databases
databases
This is for the latest Chronos version 15.0 release.
In order to use Chronos within your own application, you must have the @chronosmicro/tracker dependency installed.
The @chronosmicro/tracker package tracks your application's calls and scrapes metrics from your system.
- NOTE: The Chronos tracker code is included in the chronos_npm_package folder for ease of development, but the published NPM package can be downloaded by running
npm install @chronosmicro/tracker.
For more details on the NPM package and instructions for how to use it, please view the Chronos NPM Package README.
- From the root directory, run
npm install - Run
npm run start:electronto start the electron app. - Run
npm audit fixornpm audit fix --forceif prompted - Refer to
Examplessections below to spin up example applications. (Recommended): If you have mongo community edition running locally just runnpm run start:microservicesto start populating database with server data(more detail in Microservices Example section).
- From the root directory, run
npm run build - Run
npm run package - Find the
chronos.appexecutable inside the newly createdrelease-buildsfolder in the root directory.
NOTE: You must create your own user database for extended features
- Create a MongoDB database in which to store user information and insert it within a root .env file based on .env.example .env.example (.env.example) file.
- This database will privately store user information.
- Once this is set up, you can create new users, log in, and have your data persist between sessions.
We provide eight example applications for you to test out both the Chronos NPM package and the Chronos desktop application:
- AWS
- Docker
- gRPC
- Kubernetes
- Microservices
Additional documentation on how Chronos is used in each example can be found in the Chronos NPM Package README.
The AWS folder includes 3 example applications with instructions on how to deploy them in AWS platforms. Note that using AWS services may cause charges.
- The ECS folder includes an web application ready to be containerized using Docker. The instruction shows how to deploy application to ECS using Docker CLI command, and it will be managed by Fargate services.
- The EC2 folder includes a React/Redux/SQL web application ready to be containerized using Docker. The instruction shows how to deploy application using AWS Beanstalk and connect application to RDS database. Beanstalk service will generate EC2 instance.
- The EKS folder includes a containerized note taking app that uses a Mongo database as its persistent volume. The instructions show how to deploy this application on EKS, how to monitor with Prometheus & Opencost, and how to use Grafana to grab visualizations.
Refer to the EC2 README, ECS README, and EKS README example in the AWS folder for more details.
In the ![]() folder within the
folder within the master branch, we provide a sample dockerized microservices application to test out Chronos and to apply distributed tracing across different containers for your testing convenience.
The docker folder includes individual ![]() files in their respective directories. A docker-compose.yml is in the root directory in case you'd like to deploy all services together.
files in their respective directories. A docker-compose.yml is in the root directory in case you'd like to deploy all services together.
Refer to the Docker README in the docker folder for more details.
The gRPC folder includes an HTML frontend and an Express server backend, as well as proto files necessary to build package definitions and make gRPC calls. The reverse_proxy folder contains the server that requires in the clients, which contain methods and services defined by proto files.
Refer to the gRPC README in the gRPC folder for more details.
The kubernetes folder includes a React frontend and an Express server backend, and the Dockerfiles needed to containerize them for Kubernetes deployment. The launch folder includes the YAML files needed to configure the deployments, services, and configurations of the frontend, backend, Prometheus server, and Grafana.
Refer to the Kubernetes README in the kubernetes folder for more details.
In the microservices folder, we provide a sample microservice application that successfully utilizes Chronos to apply all the powerful, built-in features of our monitoring tool. You can then visualize the data with the ![]() app.
app.
Refer to the microservices README in the microservices folder for more details.
We've created testing suites for Chronos with React Testing, Jest, and Selenium for unit, integration, and end-to-end tests - instructions on running them can be found in the testing README.
Development of Chronos is open source on GitHub through the tech accelerator OS Labs, and we are grateful to the community for contributing bug fixes and improvements.
Read our contributing README to learn how you can take part in improving Chronos.