用最新的Keras當作Tensorflow的front-end可以輕鬆架構出NLP的模型。
例如在BBC news的分類的應用上,要使用第一層為Embedding向量層、第二層為Bidirectional LSTM層、第三層為一般神經元層、第四層為分類總數的softmax層時,只需用以下程式碼即可架構好。[1]
model = tf.keras.Sequential([
tf.keras.layers.Embedding(vocab_size, embedding_dim, input_length=max_length),
tf.keras.layers.Bidirectional(tf.keras.layers.LSTM(embedding_dim)),
tf.keras.layers.Dense(embedding_dim, activation='relu'),
tf.keras.layers.Dense(6, activation='softmax')
])在訓練模型時,可以選擇要一邊訓練同時儲存weights參數或是訓練好後再一次儲存。[2]
需先設定callback並asign到model.fit裡面。
checkpoint_path = "training_1/cp.ckpt"
checkpoint_dir = os.path.dirname(checkpoint_path)
# Create a callback that saves the model's weights
cp_callback = tf.keras.callbacks.ModelCheckpoint(filepath=checkpoint_path, save_weights_only=True, verbose=1)
# Train the model with the new callback
model.fit(train_images,
train_labels,
epochs=10,
validation_data=(test_images,test_labels),
callbacks=[cp_callback]) # Pass callback to training之後同樣架構的模型可以直接讀取參數來用。
# Loads the weights
model.load_weights(checkpoint_path)在訓練好模型後,直接一次儲存所有參數。
# Save the weights
model.save_weights('./checkpoints/my_checkpoint')之後同樣架構的模型可以直接讀取參數來用。
# Restore the weights
model.load_weights('./checkpoints/my_checkpoint')在訓練好模型後,直接儲存整個模型。
儲存的檔案裡面包括全部的weight values、模型架構、optimizer的設定。
# Save the entire model as a SavedModel.
model.save('saved_model/my_model')之後可以直接讀取模型來用。
new_model = tf.keras.models.load_model('saved_model/my_model')混淆矩陣(confusion matrix)常被拿來參考去判定一個分類模型表現的好不好。
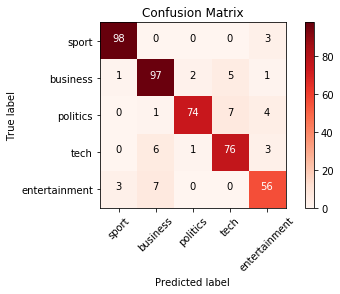
sklearn有提供confusion matrix可直接使用。
from sklearn.metrics import confusion_matrix
cm = confusion_matrix(validation_label_seq, rounded_predictions)
print(cm)[[98 0 0 0 3]
[ 1 97 2 5 1]
[ 0 1 74 7 4]
[ 0 6 1 76 3]
[ 3 7 0 0 56]]
另外可用matplotlib來畫出更容易懂得彩色圖。[3]
import itertools
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
def plot_confusion_matrix(cm, classes, normalize = False, title = 'Confusion matrix', cmap = plt.cm.Reds):
plt.imshow(cm, interpolation = 'nearest', cmap = cmap)
plt.title(title)
plt.colorbar()
tick_marks = np.arange(len(classes))
plt.xticks(tick_marks, classes, rotation = 45)
plt.yticks(tick_marks, classes)
plt.ylim([4.5, -0.5]) # solve squished issue
if normalize:
cm = cm.astype('float') / cm.sum(axis=1)[:,np.newaxis]
print("Normalized confusion matrix!")
else:
print("Confusion matrix, without normalization")
print(cm)
thresh = cm.max()/2
for i, j in itertools.product(range(cm.shape[0]), range(cm.shape[1])):
plt.text(j, i , cm[i, j],
horizontalalignment = "center",
color = "white" if cm[i, j] > thresh else "black")
plt.tight_layout()
plt.ylabel('True label')
plt.xlabel('Predicted label')在做NLP應用時常常會使用別人已經訓練好的辭向量來用,在Keras + TF下只要在Embedding層設定weights為預先處理好的embedding matrix即可。
model = tf.keras.Sequential([
tf.keras.layers.Embedding(vocab_size+1, embedding_dim, input_length=max_length, weights=[embeddings_matrix], trainable=False),
tf.keras.layers.Dropout(0.2),
tf.keras.layers.Conv1D(64, 5, activation='relu'),
tf.keras.layers.MaxPooling1D(pool_size=4),
tf.keras.layers.LSTM(64),
tf.keras.layers.Dense(1, activation='sigmoid')
])[1] https://www.coursera.org/learn/natural-language-processing-tensorflow
[2] https://www.tensorflow.org/tutorials/keras/save_and_load
[3] https://stackoverflow.com/questions/57937751/why-does-this-confusion-matrix-matplotlib-look-squished-in-jupyter-notebook