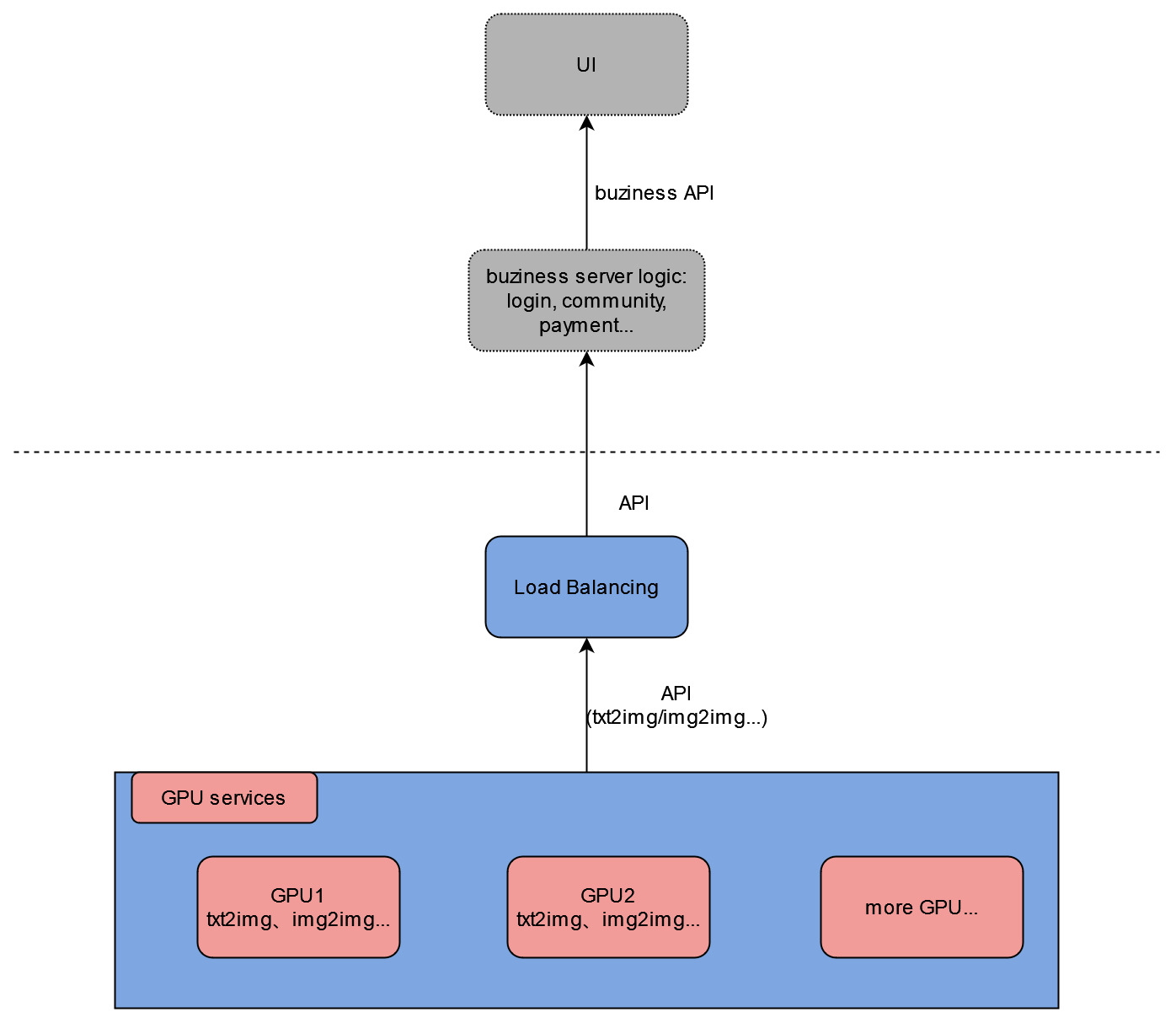
stable diffusion multi-user django server code with multi-GPU load balancing
- a django server that provides stable-diffusion http API, including:
- txt2img
- img2img
- check generating progress
- interrupt generating
- list available models
- change models
- ...
- supports civitai models and lora, etc.
- supports multi-user queuing
- supports multi-user separately changing models, and won't affect each other
- provides downstream load-balancing server code that automatically do load-balancing among available GPU servers, and ensure that user requests are sent to the same server within one generation cycle
You can build your own UI, community features, account login&payment, etc. based on these functions!
The project can be roughly divided into two parts: django server code, and stable-diffusion-webui code that we use to initialize and run models. And I'll mainly explain the django server part.
In the main project directory:
modules/: stable-diffusion-webui modulesmodels/: stable diffusion modelssd_multi/: the django project nameurls.py: server API path configuration
simple/: the main django codeviews.py: main API processing logiclb_views.py: load-balancing API
requirements.txt: stable diffusion pip requirementssetup.sh: run it with options to setup the server environmentgen_http_conf.py: called insetup.shto setup the apache configuration
- SSH to the GPU server
- clone or download the repository
- cd to the main project directory(that contains
manage.py) - run
sudo bash setup.shwith options(checkout thesetup.shfor options)(recommende order: follow the file order:env,venv,sd_model,apache)- if some downloads are slow, you can always download manually and upload to your server
- if you want to change listening ports: change both
/etc/apache2/ports.confand/etc/apache2/sites-available/sd_multi.conf
- restart apache:
sudo service apache2 restart
/: view the homepage, used to test that apache is configured successfully/txt2img/: try the txt2img with stable diffusion
// demo request
task_id: required string,
model: optional string, // change model with this param
prompt: optional string,
negative_prompt: optional string,
sampler_name: optional string,
steps: optional int, // default=20
cfg_scale: optional int, // default=8
width: optional int, // default=512
height: optional int, // default=768
seed: optional int // default=-1
restore_faces: optional int // default=0
n_iter: optional int // default = 1
// ...
// modify views.py for more optional parameters
// response
images: list<string>, // image base64 data list
parameters: string
/img2img: stable diffusion img2img
// demo request
task_id: required string,
model: optional string, // change model with this param
prompt: optional string,
negative_prompt: optional string,
sampler_name: optional string,
steps: optional int, // default=20
cfg_scale: optional int, // default=8
width: optional int, // default=512
height: optional int, // default=768
seed: optional int // default=-1
restore_faces: optional int // default=0
n_iter: optional int // default = 1
resize_mode: optional int // default=0
denoising_strength: optional double // default=0.75
init_images: optional list<base64 image data>
// ...
// modify views.py for more optional parameters
// response
images: list<string>, // image base64 data list
parameters: string
/progress/: get the generation progress
// request
task_id: required string
// response
progress: float, // progress percentage
eta: float, // eta seconds
/interrupt/: terminate an unfinished generation
// request
task_id: required string
/list_models/: list available models
// response
models: list<string>
- SSH to a CPU server
- clone or download the repository
- cd to the main project directory(that contains
manage.py) - run
sudo bash setup.sh lb - run
mv sd_multi/urls.py sd_multi/urls1.py && mv sd_multi/urls_lb.py sd_multi/urls.py - modify
ip_listvariable with your own server ip+port insimple/lb_views.py - restart apache:
sudo service apache2 restart - to test it, view
ip+port/multi_demo/url path
If you don't want to deploy the load balancing server but still want to test the functions, you can start the load-balancing server on your local computer.
- clone or download the repository
- requirements: python3, django, django-cors-headers, replicate
- modify
ip_listvariable with your own GPU server ip+port insimple/lb_views.py - cd to the main project directory(that contains
manage.py) - run
mv sd_multi/urls.py sd_multi/urls1.py&&mv sd_multi/urls_lb.py sd_multi/urls.py(Rename) - run
python manage.py runserver - click the url that shows up in the terminal, view
/multi_demo/path
Finally, you can call your http API(test it using postman).
see sd-docker-slim