A Go library for making runnable markdown tutorials, demos and setup scripts. It takes inspiration from the Literate Programming paradigm.
The library is used by the OpenZiti project for tutorials and examples.
runzmd exists to help consolidate scripts and documentation. If you can make a markdown tutorial runnable, then you get the following benefits:
- Testable documentation
- No duplication between the tutorial and the script
- Well documented, easy to read script
- Documentation can be run or viewed in browzer. Browzer view isn't degraded by runnable code portions.
While this library could be used for generalized scripts, it excels when
wrapping a specific tool. The OpenZiti examples mostly use the ziti CLI.
The actions used can be found in the actionz directory.
While this library could be used for generalized scripting it hasn't been optimized for that, and best suited for targeted use cases, like the above.
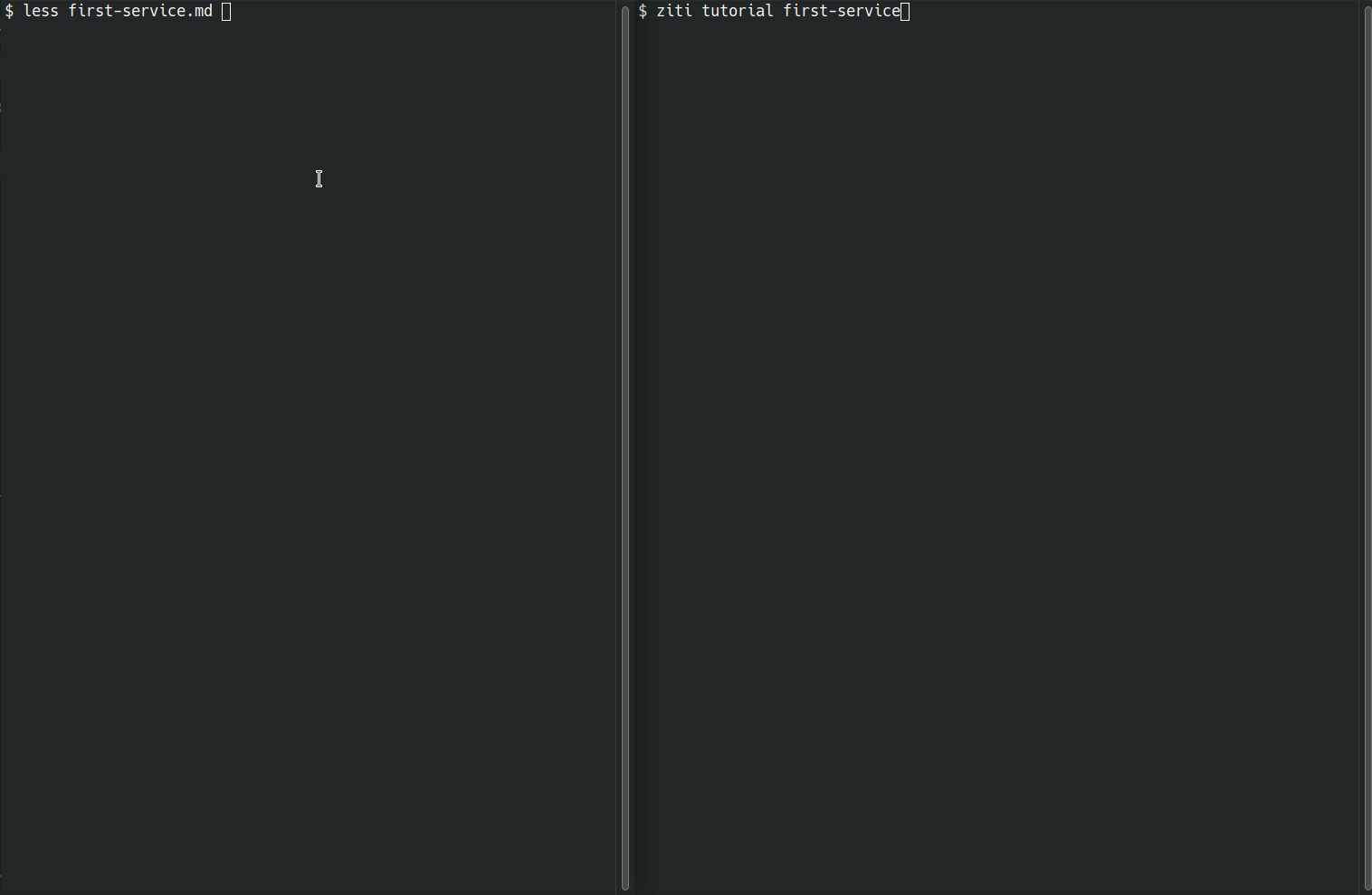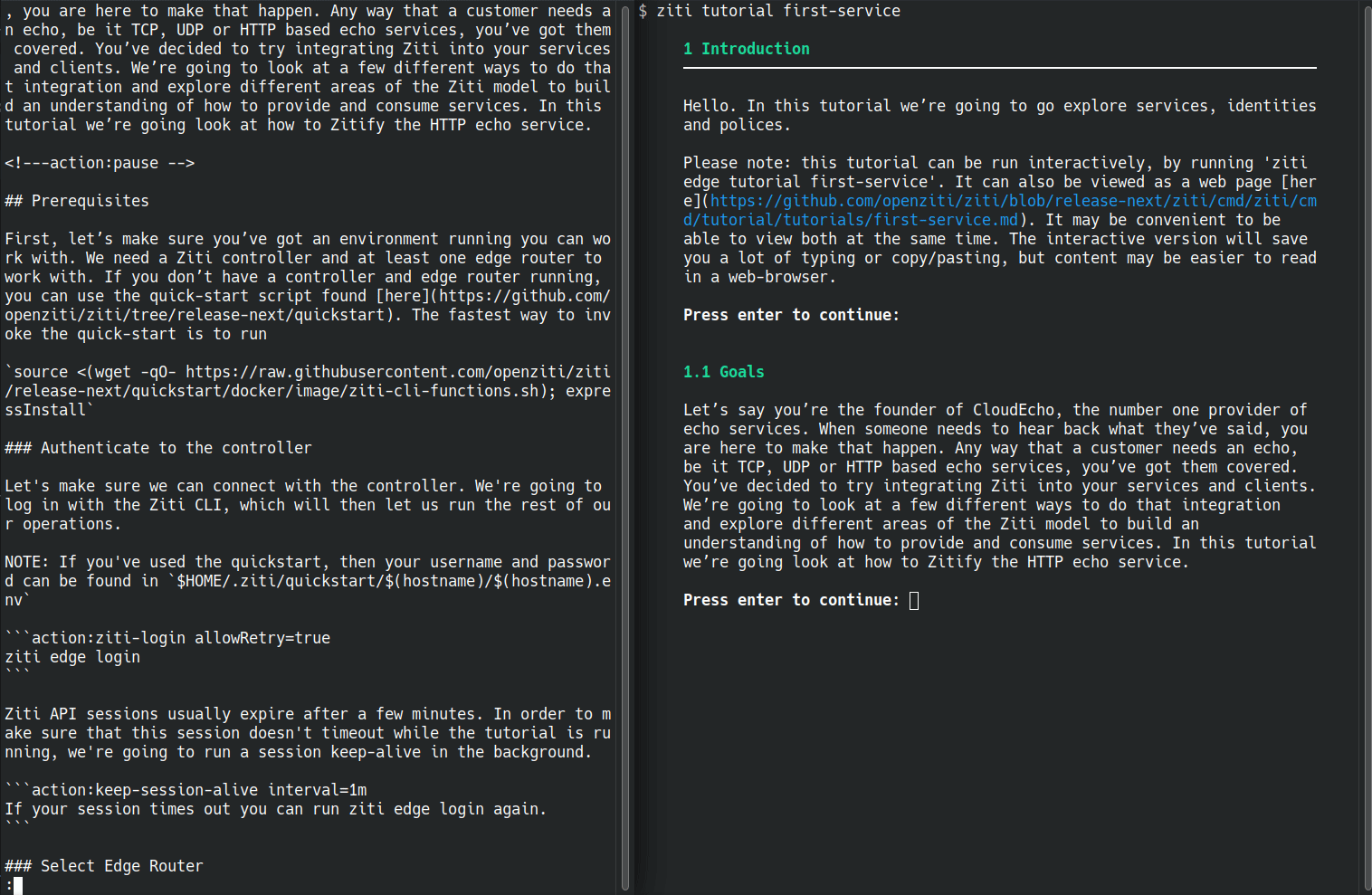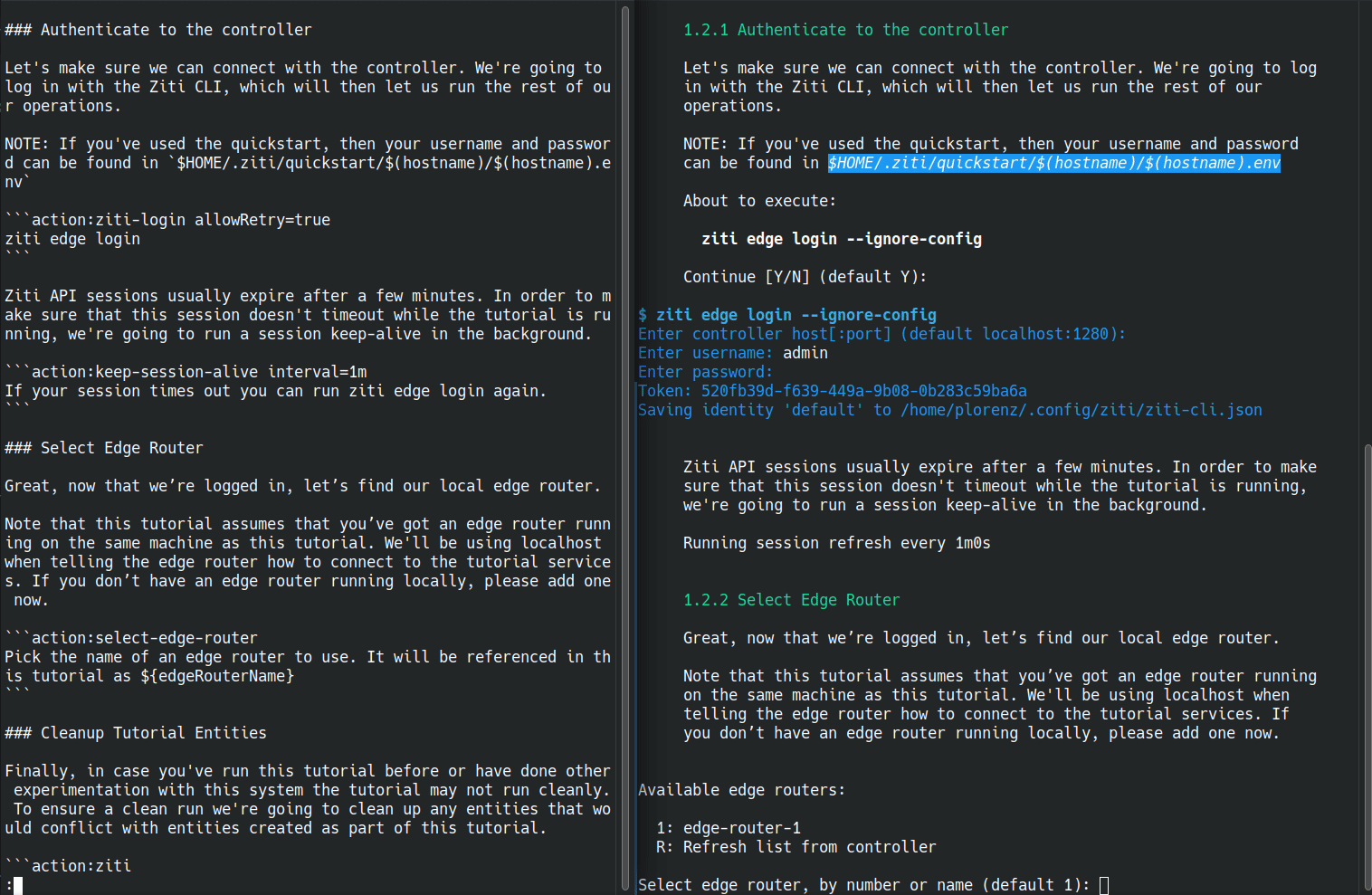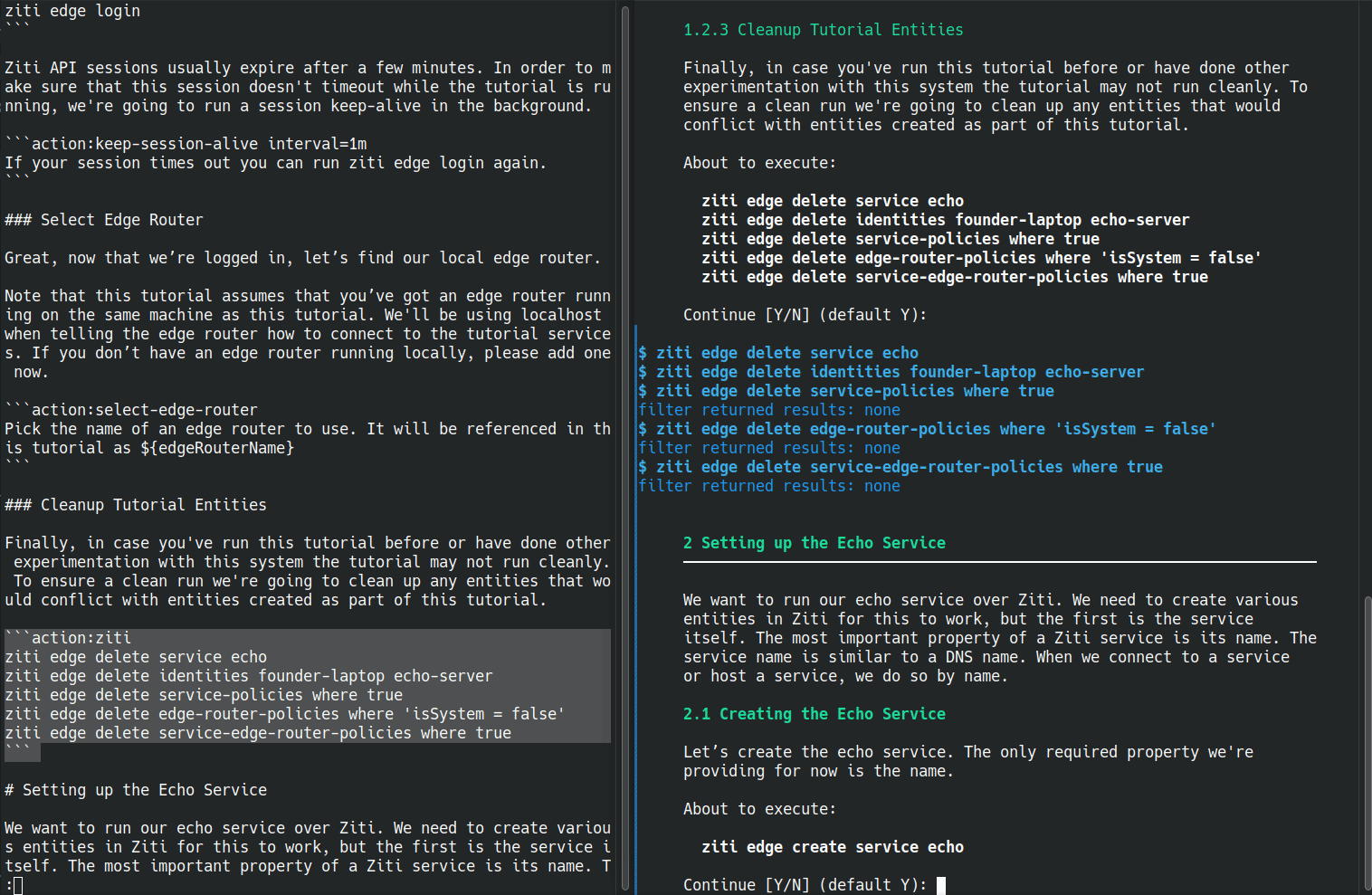
Here's an example of a markdown file being run. This is the creating your first service tutorial for OpenZiti, which is the most involved example I have. Below you can see the original markdown is on the left. On the right is the markdown being executed. The markdown viewed in the browser should still be usable on its own.
runzmd starts with embedded markdown and finds any blockquote sections and comments marked as being executable. Markdown sections between executable blocks are outputted it using the go-term-markdown library. The executable sections are handed off to registered handlers, to executable in whatever manner is appropriate.
There is a small example in the example directory which
just runs the ls command.
It looks like this:
# Example
This is an example
```action:exec
ls
```The go code to run this example markdown, looks like this:
package main
import (
_ "embed"
"fmt"
"github.com/openziti/runzmd"
"time"
)
//go:embed example.md
var scriptSource []byte
func main() {
t := runzmd.NewRunner()
t.NewLinePause = time.Millisecond * 20
t.AssumeDefault = false
t.RegisterActionHandler("exec", &runzmd.ExecActionHandler{})
if err := t.Run(scriptSource); err != nil {
fmt.Printf("failure running example: [%v]\n", err)
}
}The library comes with a few actions.
- ExecActionHandler - supports executing a list of commands
- ShowActionHandler - supports showing some text, usually an embedded file
The library also has a few useful utility functions, which can be used in building custom actions.
Continue- Used for waiting in interactive scriptsExec- Used to execute a commandAskYesNo- Asks a yes/no questionAskYesNoWithDefault- Asks a yes/no question with a default answerAsk- Asks for string response