Table of Contents
This is a BOSH release to gather, store and analyze syslog events forwarded by bosh VMs. It currently uses RSyslog which is pre-installed by the stemcell.
Only Linux stemcells are supported at the moment.
Usually, platform logs are sent to ELK stacks which store and index events on-the-fly. Finally, users can build fancy Kibana dashboards by extracting metrics from elasticsearch queries.
With the development of micro-services architectures, the number of emitted logs recently exploded, making these ELKs very hardware and, therefore, money consuming. Even more, these stacks are often built with heavy redundancy and high availability even when most of the emitted events are not critical.
The idea here is having a much more lightweight architecture, providing only the most essential features of log processing:
- midterm storage for debug and production incident analysis
- hardware-efficient generation of metrics
- redundancy and availability matching the actual criticality of the logs
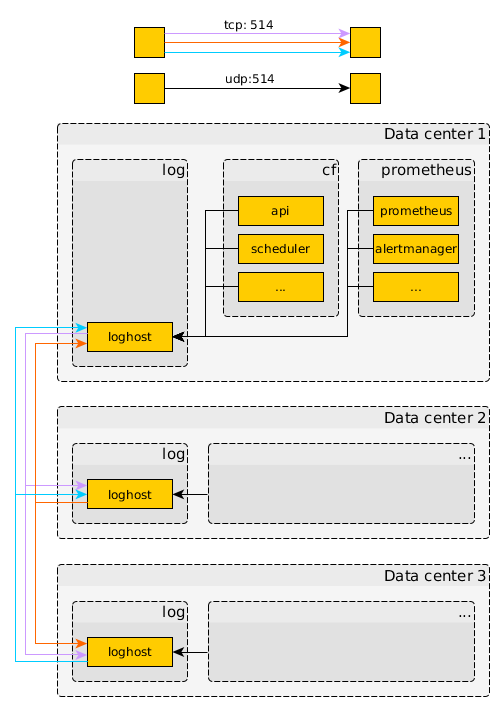
This is achieved by using both good old technologies such as RSyslog and modern tools like Prometheus. The bridge between logs and metrics is provided by a brilliant tool grok_exporter.
The job loghost_concentrator configures local rsyslogd to store received logs to persistent disk.
Only syslog events received in RFC5424 format with instance@47450 in
Structured Data ID are handled. The 47450 private enterprise number is the one
generated by the syslog-release generally used to forward VM log events to a given endpoint.
Received logs are stored on persistent disk in root directory /var/vcap/store/loghost where
{path} depends on parsed Structured Data ID fields of the event.
Assuming logs are forwarded by syslog-release, the parsed fields are:
$.director: the configured name of bosh director$.deployment: the name of deployment from which event was sent$.group: the name of the instance from which event was sent
Finally, logs are stored under /var/vcap/store/loghost/{$.director}/{$.deployment}/{$.group}.log
The job also configures local logrotate in order to rotate and compress logs every hour.
Rotated logs are stored in the same directories with the -%Y%m%d%H.gz suffix.
The number of kept rotations can be configured loghost_concentrator.logrotate.max-hours property
with a default value of 360 (i.e.: 15 days).
The job also provides the possibility to re-forward received syslog event under specified conditions; this can be useful for:
- Clusterize multiple concentrators in order to create a kind of backup across independent BOSH directors
- Forward business or security critical events to an external log handling platform
Forwarding is configured from the loghost_concentrator.syslog.forward property by defined
target objects as follows:
<target-name>:
conditions:
- <condition>
- ...
targets:
- address: hostname
port: port
transport: tcp|udp|relp
- ...Where:
<condition>are valid rainerscript expressions with parenthesis. Multiple conditions can be given, all must be true to trigger the forward<targets>: is a list of syslog endpoints where matching events are forwarded. When multiple targets are defined, matching events will be forwarded to all endpoints
Example:
jobs:
- name: loghost_concentrator
release: loghost
properties:
loghost_concentrator:
syslog:
forward:
my-forward-target:
conditions:
- ($.director isequal "local-director-name")
- ($.deployment isequal "cf")
targets:
- address: target1.hostname.example.com
port: 514
transport: tcp
- address: target2.hostname.example.com
port: 514
transport: tcpAssuming that your deployment uses bosh-dns, the job loghost_dns can be used to define new
aliases.
DNS aliases are configured from the loghost_dns.aliases key with the same syntax as the
aliases key of bosh-dns job.
Example:
jobs:
- name: loghost_dns
release: loghost
properties:
loghost_dns:
aliases:
my.alias.internal:
- 127.0.0.1
my.other.alias.internal:
- '*.collector-z1.default.logsearch.bosh'
- '*.collector-z2.default.logsearch.bosh'The loghost_exporter job installs and configures the grok_exporter. This brilliant program
processes log files and computes Prometheus metrics according to parse rules given in
grok format.
Parsing rules are defined by the loghost_exporter.metrics key with the exact same syntax defined
by the grok_exporter-metrics.
In addition, loghost_exporter.directors and loghost_exporter.deployments keys must be configured
to give the list of logs files that the exported should watch.
Note: A limitation in the grok_exporter implementation forces watched directories to pre-exist at exporter startup. Because rsyslog files are created on the fly when events are received, the job creates required directories in its
pre-startscript.
In addition to user-defined metrics, the exporter provides builtin metrics.
Ops-files provided in the release also provide metrics, as described in the usage section.
The job loghost_alerts defines the following alerts for your prometheus-boshrelease deployment:
LoghostNoLogReceived: triggers if exporter reports no processed logs in the last 15 minutesLoghostDroppedMessages: triggers when there is an increase of "failed to write to target.example.net:6067" in the logs
When loghost_alerts.security.enabled key is set to true (default false), the job also defines
the following alerts:
SecurityTooManySystemAuthFailures: triggers whenaudispdreports too many auth failures.audispdlogs are generated by all virtual machines deployed by boshSecurityTooManyUaaClientFailures: triggers whenuaacomponent reports too many client authentication failuresSecurityTooManyUaaUserFailures: triggers whenuaacomponent reports too many user authentication failuresSecurityTooManyDiegoSshFailures: triggers whenssh_proxycomponent running on (schedulerinstance) reports too many SSH authentication failures to containersSecurityTooManyDiegoSshSuccess: triggers whenssh_proxycomponent running on (schedulerinstance) reports too many SSH authentications to containers
Alert thresholds and evaluation time can be configured from job's spec.
The job loghost_dashboards adds Grafana dashboards for your prometheus-boshrelease
deployment.
-
a global overview giving the system status, number of processed logs per rules, deployments and instances
-
a security dashboard overview giving information on authentications when
loghost_dashboards.security.enabledkey is enabled.
First, you must add loghost instance to the deployment of your choice. You can use the following
ops-files:
manifests/operations/loghost-concentrator-enable.ymlmanifests/operations/loghost-exporter-enable.ymlmanifests/operations/loghost-exporter-enable-security.yml
It will add the instance loghost with basic features enabled:
- received log written to
/var/vcap/store/loghost - grok_exporter reading and generating metrics from received logs
The simplest way to forward all logs at once is to create a runtime-config.yml using the syslog-release.
With file runtime-syslog-forward.yml:
addons:
- exclude:
instance_groups:
- loghost
jobs:
- name: syslog_forwarder
properties:
syslog:
address: q-s0.loghost.default.((deployment)).bosh
director: ((director_name))
transport: udp
release: syslog
name: syslog_forwarder
releases:
- name: syslog
sha1: 658fe5d6f049ec50383c09c0b227261251bfd4eb
url: https://artifactory/cloudfoundry/syslog/syslog-11.6.1-ubuntu-xenial-621.tgz
version: 11.6.1Upload to bosh director: bosh update-runtime-config --name syslog-forward runtime-syslog-forward.yml
Add the following ops-files to your prometheus deployment:
manifests/operations/prometheus/loghost-enable.ymlmanifests/operations/prometheus/loghost-enable-security.yml
It will:
- define scrape config based on
bosh_exporterdiscovery - define new alerts
- add dashboards to Grafana
| name | description |
|---|---|
| loghost-concentrator-enable.yml | add instance with loghost_concentrator job listening on udp |
| loghost-concentrator-enable-tcp.yml | configure loghost_concentrator to listen on tcp addition to udp |
| loghost-dns-enable.yml | add loshost_dns job with empty aliases list |
| loghost-exporter-enable.yml | add loghost_exporter job which spawns grok_exporter with a default set of metrics |
| loghost-exporter-enable-security.yml | add security metrics to loghost_exporter job, grok rules for uaa and audispd |
| prometheus/loghost-enable.yml | add discovery scraping of grok_exporter, default alerts and dashboards |
| prometheus/loghost-enable-security.yml | add security alerts and dashboards |
In addition to grok_exporter grok-builtin-metrics, the release defines:
| name | dimensions | type | description |
|---|---|---|---|
| loghost_total | director, deployment, group | (Counter) | log processed |
| loghost_error_total | director, deployment, group | (Counter) | log detected as level error |
| loghost_auth_failures | director, deployment, group, source, ip | (Counter) | system authentication failures |
| loghost_auth_failures_last_5m | director, deployment, group, source, ip | (Gauge) | system authentication failures in the last 5 minutes (*) |
| loghost_auth_success | director, deployment, group, source, ip, username | (Counter) | system authentication success |
| loghost_auth_success_last_5m | director, deployment, group, source, ip, username | (Gauge) | system authentication success in the last 5 minutes (*) |
| loghost_uaa_client_login_success | director, deployment, group, ip, clientid | (Counter) | UAA client authentication success |
| loghost_uaa_client_login_success_last_5m | director, deployment, group, ip, clientid | (Gauge) | UAA client authentication success in the last 5 minutes (*) |
| loghost_uaa_client_login_failure | director, deployment, group, ip, clientid | (Counter) | UAA client authentication failures |
| loghost_uaa_client_login_failure_last_5m | director, deployment, group, ip, clientid | (Gauge) | UAA client authentication failures in the last 5 minutes (*) |
| loghost_uaa_user_login_success | director, deployment, group, ip, username | (Counter) | UAA user authentication success |
| loghost_uaa_user_login_success_last_5m | director, deployment, group, ip, username | (Gauge) | UAA user authentication success in the last 5 minutes (*) |
| loghost_uaa_user_login_failure | director, deployment, group, ip, username | (Counter) | UAA user authentication failures |
| loghost_uaa_user_login_failure_last_5m | director, deployment, group, ip, username | (Gauge) | UAA user failures in the last 5 minutes (*) |
With dimension values:
director,deployment,group: BOSH director name, deployment name and instance group name from where the log was originally emittedsource: theexefield of type=USER.*message ofaudispdip: the remote address from which the authentication was attemptedclientid: theclientidused to authenticate a client onUAAusername: theusernameused to authenticate a user onUAA
(*) Tech note: Because metrics dimensions values are created over time depending on encountered logs, we cannot rely on
rateorincreaseprometheus function to compute the number of failures on a period of time. As a bypass, we manually compute this metric with a hackish record rule defined as:sum(<metric> or <metric>{} * 0) by (<dimensions...>) - sum(<metric> offset 5m or <metric>{} * 0) by (<dimensions...>)