URBO's API. This project is the backend application of URBO solution for smart cities.
| Master | Dev |
|---|---|
This is the code repository for URBO Core API, the backend application for the URBO project.
This repository provides the base code for the web API and needs to be complemented with pluggable verticals.
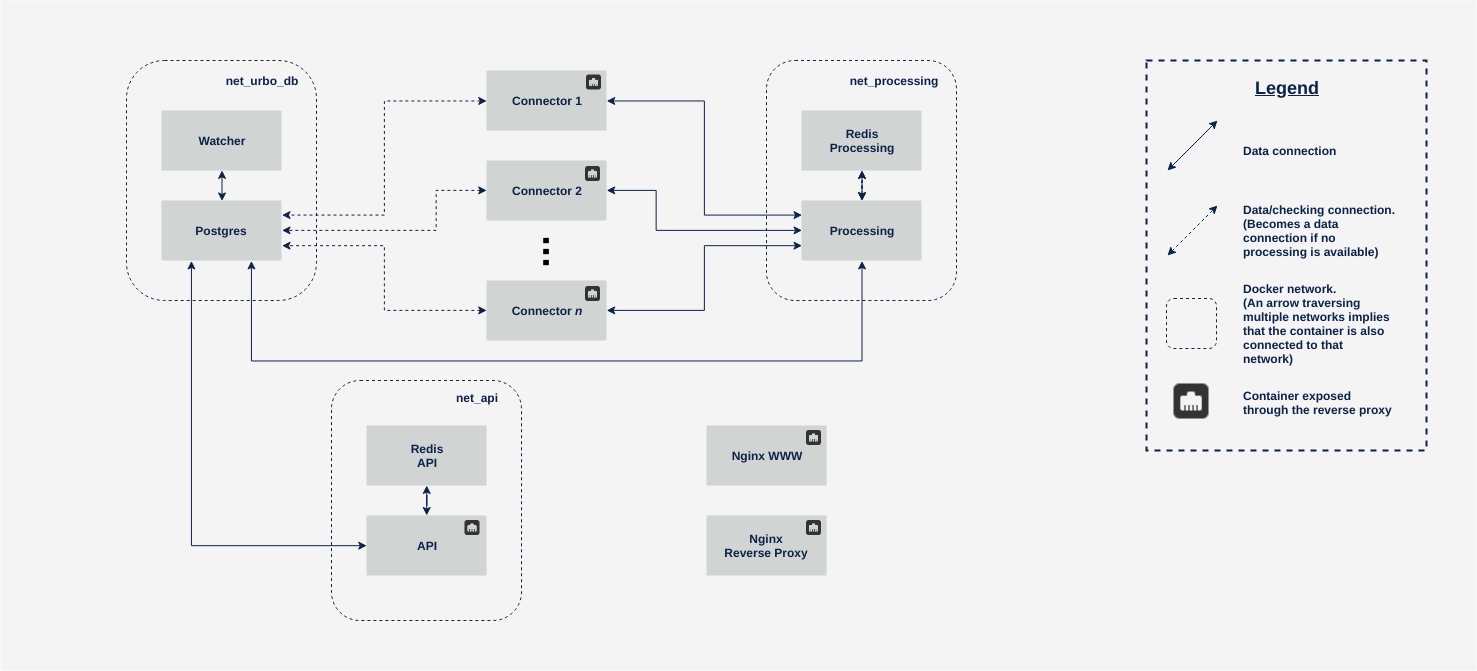
The following diagram represents the architecture of the project.
- NodeJS version 6.x or greater.
- Docker version 18.02 or greater.
- We recommend using GNU/Linux as server, but is not mandatory.
The development configurations for the different containers required by the API are defined in the docker-compose.override.yml file. By default, docker-compose will override/merge the configuration existing in the docker-compose.yml file with the contents of the .override.yml file. This means that when you execute docker-compose up you will start the development environment by default. You can find more information about how docker-compose allows you to extend configurations here.
If you wish to change/update the configurations you can create a new docker-compose.*.yml file, that file will be ignored by default by git, so you can create as many configurations as you wish.
In order to use these configs you will have to append to your docker-compose commands two -f flags. For example:
docker-compose -f docker-compose.yml -f docker-compose.example.yml up -d
This leads to more difficult to read commands, our recommendation is to create an alias in your shell, let's call it dcp:
alias dcp="docker-compose -f docker-compose.yml -f docker-compose.example.yml"
With this alias you can issue commands faster, the previous example ends up like this:
dcp up -d
Remember that you can still use other docker-compose commands with this shortcut: dcp build, dcp down ...
In order to run this application you will need to install UrboCore API along with some pluggable verticals. Check API development mode if you wish to debug the API.
- Clone this repository
- Set up the database as is explained in the Setting up the database section.
- Create the config file on
config.ymltakingconfig.sample.ymlas template and fill it. - Install needed verticals as is explained in the Managing pluggable verticals section.
- Run server using docker-compose.
docker-compose up api
# Or
dcp up -d api # To use your custom configuration
The postgis service defined in the docker-compose files will mount by default a volume to the db directory in the repository. This directory contains the base functions and scripts necessary for Urbo to work properly. Follow these steps:
- Create a Docker volume named
urbo-db-data. This volume will store all data related to the Postgres container. You do not have to worry if your db container gets destroyed as long as this volume stays intact.
docker volume create urbo-db-data
-
(Optional) Create an alternative docker-compose.*.yml file with alternative values for the database environment variables. At startup a database and a new PostgreSQL user are created in order to be used by the API. The created user will be granted full access to the new database. The process will end with the creation of a superuser that can manage the application. You can change the following environment variables:
URBO_DB_OWNER: The urbo database's owner. This is the name of the Postgres user that will have full access to the database created.URBO_DB_PASSWD: The password to for the PostgreSQL user.URBO_DB_NAME: The name for the new database.URBO_ADMIN_EMAIL: The login email for the admin user.URBO_ADMIN_PASSWD: The password for the admin user.
-
Start the database:
docker-compose up -d postgis # Maps port 5435 on your host to the 5432 port in the container
The process of installing a vertical consists in copying the necessary resources (routes, models, etc.) into the verticals folder inside the container. Both production and development configurations can be modified in order to declare a docker volume and mount the resources. The install-vertical tool is handy if you wish to copy those resources from a directory containing different verticals. Take into account that you will need to install Node.js and the necessary dependencies in your host.
To install or update a vertical you just need to execute:
npm run-script install-vertical -- <vertical-source-path> <vertical-name>
Remember to restart the server in order to apply this changes.
The same way you can install a new vertical you can delete it too executing:
npm run-script delete-vertical -- <vertical-name>
Remember to restart the server in order to apply this changes.
You can think of other approaches, such as copying the resources manually (look for the api directory inside each vertical) into one directory and mounting that. Keep in mind that you need to preserve the index.js file existing in the verticals folders.
The docker-compose.override.yml file creates containers with an alternative configuration for the Postgres and the API:
- Postgres:
- Publishes to your host the default PostgreSQL port in 5435. Useful for local connections with psql or PgAdmin.
- API:
- Starts the Node server with the Inspector mode. This mode allows you to debug the API with your favourite IDE, text editor or Chromium-based web browser. The debug port (9229) will be bridged to your host, so you can debug as if you had an instance of the server running on your machine. The API will start with a breakpoint on the first line of code, you will need to connect to the debug process in order to continue with the execution.
- Publishes the Urbo API container listening port in your host's 3005 port. Send HTTP requests to the API in http://localhost:3005
To run the tests, just execute:
docker-compose run api npm run-script test
The API documentation is available at https://geographicags.github.io/Urbo-docs/.
To update and upload the API documentation:
- Install mkdocs:
pip install mkdocs
- Build and upload
rm -R site
mkdocs gh-deploy --clean
- In case you only want to build the documentation:
mkdocs build
UrboCore API is licensed under Affero General Public License (GPL) version 3.