This is a simple pytorch-lightning reimplementation of the 'Maximum Density Divergence for Domain Adaptation' paper, which can be read here, while the code has been adapted from here.
As stated in the paper abstract: "Unsupervised domain adaptation addresses the problem of transferring knowledge from a well-labeled source domain to an unlabeled target domain where the two domains have distinctive data distributions. Thus, the essence of domain adaptation is to mitigate the distribution divergence between the two domains. The state-of-the-art methods practice this very idea by either conducting adversarial training or minimizing a metric which defines the distribution gaps. In this paper, we propose a new domain adaptation method named Adversarial Tight Match (ATM) which enjoys the benefits of both adversarial training and metric learning. Specifically, at first, we propose a novel distance loss, named Maximum Density Divergence (MDD), to quantify the distribution divergence. MDD minimizes the inter-domain divergence and maximizes the intra-class density. Then, to address the equilibrium challenge issue in adversarial domain adaptation, we consider leveraging the proposed MDD into adversarial domain adaptation framework".
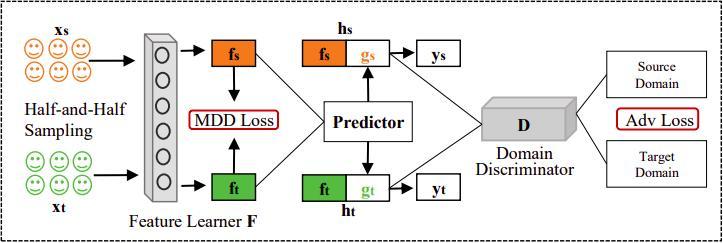
The general framework is depicted in the following figure:
Before training, one can automatically download Office-31, Image-clef and Office-Home datasets with the following commands:
python download_dataset.py --dataset image-clefpython download_dataset.py --dataset office-31python download_dataset.py --dataset office-home
Soon will be availble other datasets, such as MNIST, SVHN and so on.
This repo has been tested on a Linux machine (Ubuntu 18.04 LTS) with:
- python 3.8
- Albumentations
- PyTorch 1.7
- Pytorch-Lightning 1.1.3
To completely install the requirements run:
pip install -U -r requirements.txt
To train a model one have to execute the main.py script, that can be run with the following command line arguments:
usage: main.py [-h] [--feature_ext {resnet18,resnet34,resnet50,resnet101,resnet152}] [--use_bottleneck]
[--bottleneck_dim BOTTLENECK_DIM] [--new_classifier] [--random_proj] [--random_proj_dim RANDOM_PROJ_DIM] [--lr LR] [--momentum MOMENTUM] [--left_weight LEFT_WEIGHT] [--right_weight RIGHT_WEIGHT]
[--cls_weight CLS_WEIGHT] [--mdd_weight MDD_WEIGHT] [--entropic_weight ENTROPIC_WEIGHT] [--loss_trade_off LOSS_TRADE_OFF] [--scheduler_lr SCHEDULER_LR] [--scheduler_weight-decay SCHEDULER_WEIGHT_DECAY]
[--scheduler_gamma SCHEDULER_GAMMA] [--scheduler_power SCHEDULER_POWER] [--dset {office-31,image-clef,office-home}] [--source_domain SOURCE_DOMAIN] [--target_domain TARGET_DOMAIN] [--num_workers NUM_WORKERS]
[--train_batch_size TRAIN_BATCH_SIZE] [--test_batch_size TEST_BATCH_SIZE] [--test_10crop]
model arguments:
--feature_ext {resnet18,resnet34,resnet50,resnet101,resnet152}
feature extractor type
--use_bottleneck whether to use bottleneck in the classifier
--bottleneck_dim BOTTLENECK_DIM
whether to use bottleneck in the classifier
--new_classifier whether to train a new classifier
--random_proj whether use random projection
--random_proj_dim RANDOM_PROJ_DIM
random projection dimension
--lr LR learning rate
--momentum MOMENTUM momentum for the optimizer
--left_weight LEFT_WEIGHT
--right_weight RIGHT_WEIGHT
--cls_weight CLS_WEIGHT
--mdd_weight MDD_WEIGHT
--entropic_weight ENTROPIC_WEIGHT
--loss_trade_off LOSS_TRADE_OFF
--scheduler_lr SCHEDULER_LR
learning rate for pretrained layers
--scheduler_weight-decay SCHEDULER_WEIGHT_DECAY
weight decay for pretrained layers
--scheduler_gamma SCHEDULER_GAMMA
gamma parameter for the inverse learning rate scheduler
--scheduler_power SCHEDULER_POWER
power parameter for the inverse learning rate scheduler
data arguments:
--dset {office-31,image-clef,office-home}
The dataset or source dataset type
--source_domain SOURCE_DOMAIN
The source domain
--target_domain TARGET_DOMAIN
The target domain
--num_workers NUM_WORKERS
Pytorch DataLoader num workers
--train_batch_size TRAIN_BATCH_SIZE
Training batch size
--test_batch_size TEST_BATCH_SIZE
Testing batch size
--test_10crop Testing with random 10 crop
Further optional arguments are the ones of the Trainer class of pytorch-lightning. Run python main.py --help to completely view the command line arguments .
By now, only the office-31 and image-clef datasets are available, and one can train a model for example with:
python main.py --gpus "2,3" --feature_ext resnet50 --dset office-31 --source_domain amazon --target_domain webcam --max_steps 5000 --max_epochs 1 --default_root_dir ./chkpts --mdd_weight 0.01 --lr 0.001 --train_batch_size 32 --benchmark --new_classifier --use_bottleneck --val_check_interval 500 --accelerator ddppython main.py --gpus "2,3" --feature_ext resnet50 --dset image-clef --source_domain c --target_domain i --max_steps 5000 --max_epochs 1 --default_root_dir ./chkpts --mdd_weight 0.01 --lr 0.001 --train_batch_size 32 --benchmark --new_classifier --use_bottleneck --val_check_interval 500 --accelerator ddp
During training one can inspect the model behaviour with, for example, Tensorboard with the following command:
tensorboard --logdir ./chkpts/
We are trying to reproduce the reference paper performaces, we'll update here our best results.
| Model | A → W | A → D | D → W | D → A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Paper | 95.7% | 96.4% | 99.3% | 74.1% |
| This repo | 95.3%1 | 94.8%2 | 98.6%3 | 73.4%4 |
Achieved with:
python main.py --gpus "1,2" --feature_ext resnet50 --dset office-31 --source_domain amazon --target_domain webcam --max_steps 10000 --max_epochs 1 --default_root_dir ./chkpts --mdd_weight 0.01 --lr 0.01 --train_batch_size 32 --benchmark --accelerator ddp --test_10crop True --new_classifier --use_bottleneckpython main.py --gpus "1,2" --feature_ext resnet50 --dset office-31 --source_domain amazon --target_domain dslr --max_steps 15000 --max_epochs 1 --default_root_dir ./chkpts --mdd_weight 0.01 --lr 0.01 --train_batch_size 32 --benchmark --accelerator ddp --test_10crop True --new_classifier --use_bottleneckpython main.py --gpus "1,2" --feature_ext resnet50 --dset office-31 --source_domain dslr --target_domain webcam --max_steps 10000 --max_epochs 1 --default_root_dir ./chkpts --mdd_weight 0.01 --lr 0.01 --train_batch_size 32 --benchmark --accelerator ddp --test_10crop True --new_classifier --use_bottleneckpython main.py --gpus "1,2" --feature_ext resnet50 --dset office-31 --source_domain dslr --target_domain amazon --max_steps 10000 --max_epochs 1 --default_root_dir ./chkpts --mdd_weight 0.01 --lr 0.01 --train_batch_size 32 --benchmark --accelerator ddp --test_10crop True --new_classifier --use_bottleneck
| Model | C → I |
|---|---|
| Paper | 93.5% |
| This repo | 93.1%1 |
Achieved with:
python main.py --gpus "2,3" --feature_ext resnet50 --dset image-clef --source_domain c --target_domain i --max_steps 15000 --max_epochs 1 --default_root_dir ./chkpts --mdd_weight 0.01 --lr 0.01 --train_batch_size 32 --benchmark --accelerator ddp --test_10crop --new_classifier --use_bottleneck
Cite the paper as follows (copied-pasted it from arxiv for you):
@article{Li_2020,
title={Maximum Density Divergence for Domain Adaptation},
ISSN={1939-3539},
url={http://dx.doi.org/10.1109/TPAMI.2020.2991050},
DOI={10.1109/tpami.2020.2991050},
journal={IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence},
publisher={Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE)},
author={Li, Jingjing and Chen, Erpeng and Ding, Zhengming and Zhu, Lei and Lu, Ke and Shen, Heng Tao},
year={2020},
pages={1–1}
}
This project is licensed under the MIT License
Copyright (c) 2021 Federico Belotti, Orobix Srl (www.orobix.com).