In this lesson, you'll learn about the supervised learning algorithm K-Nearest Neighbors, and how you can use it to make predictions for classification and regression tasks!
You will be able to:
- Implement a basic KNN Algorithm from scratch
K-Nearest Neighbors (or KNN, for short) is a supervised learning algorithm that can be used for both Classification and Regression tasks. KNN is a distance-based classifier, meaning that it implicitly assumes that the smaller the distance between 2 points, the more similar they are. In KNN, each column acts as a dimension. In a dataset with two columns, we can easily visualize this by treating values for one column as X coordinates and and the other as Y coordinates. Since this is a Supervised Learning Algorithm, you must also have the labels for each point in our dataset, or else you wouldn't know what to predict!
KNN is unique compared to other classifiers in that it does almost nothing during the "fit" step, and all the work during the "predict" step. During the 'fit' step, KNN just stores all the training data and corresponding labels. No distances are calculated at this point.
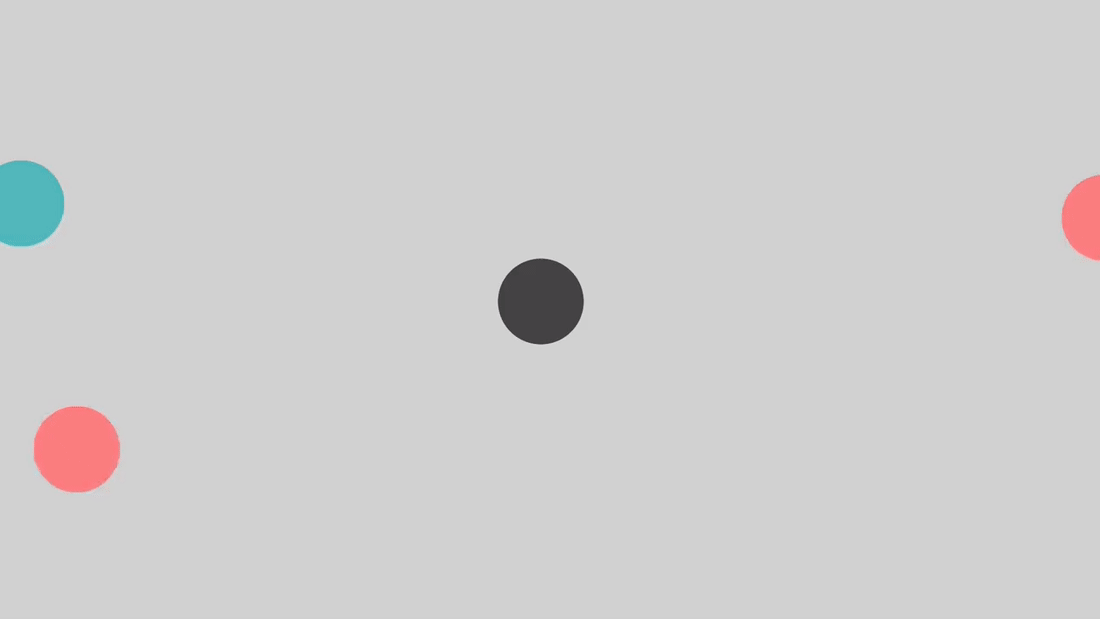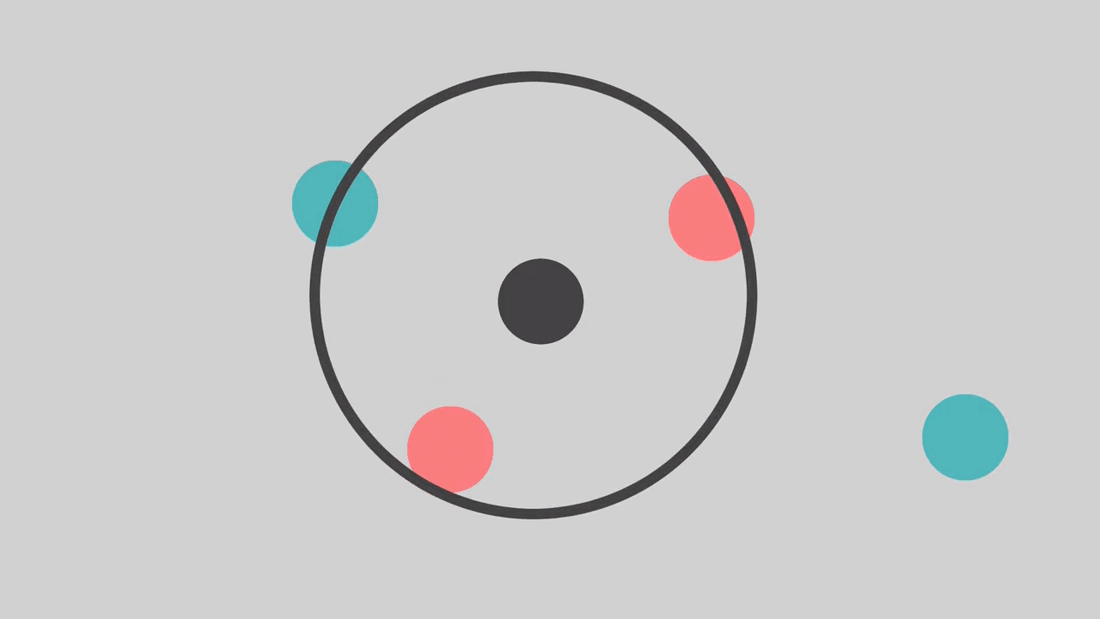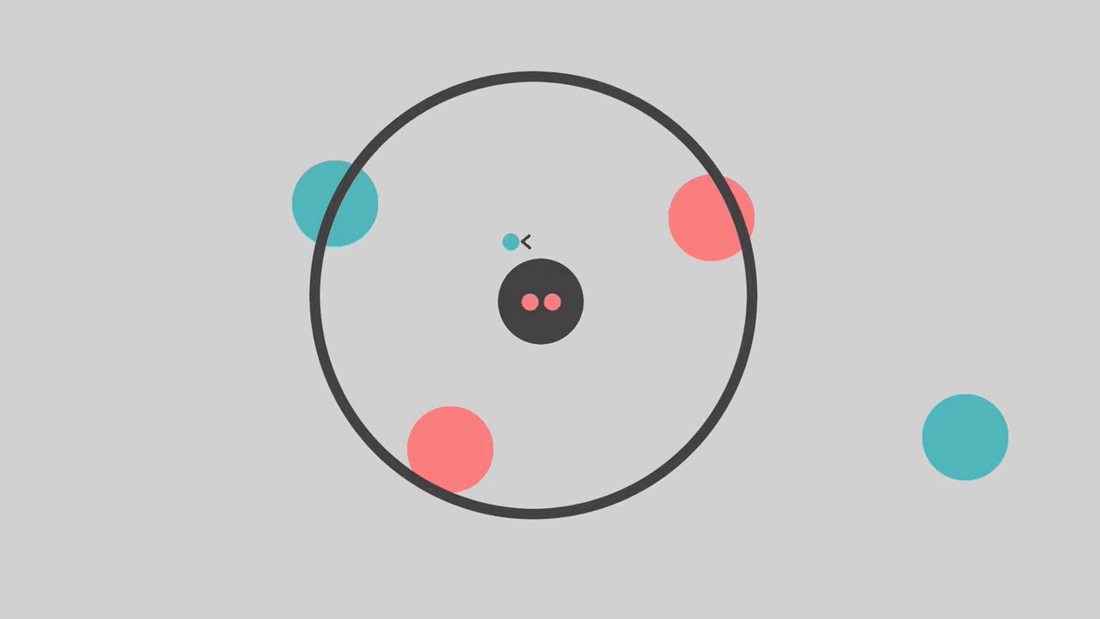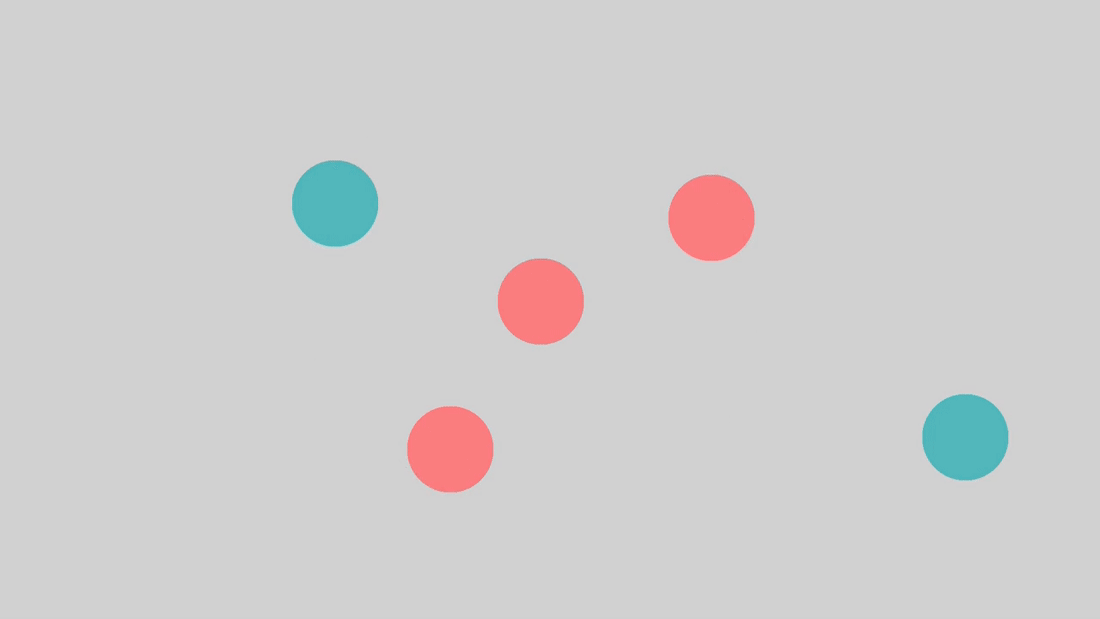
All the magic happens during the 'predict' step. During this step, KNN takes a point that you want a class prediction for, and calculates the distances between that point and every single point in the training set. It then finds the K closest points, or Neighbors, and examines the labels of each. You can think of each of the K-closest points getting a 'vote' about the predicted class. Naturally, they all vote for the same class that they are. The majority wins out, and the algorithm predicts the point in question as whichever class has the highest count among all of the k-nearest neighbors.
In the following animation, K=3.
When using KNN, you can use Manhattan, Euclidean, Minkowski Distance, or any other distance metric. Choosing an appropriate distance metric is essential and will depend on the context of the problem at hand.
How to evaluate the model performance depends on whether you're using the model for a classification or regression task. KNN can be used for regression (by averaging the target scores from each of the K-nearest neighbors), as well as for both binary and multicategorical classification tasks.
Evaluating classification performance for KNN works the same as evaluating performance for any other classification algorithm--you just need a set of predictions, and the corresponding ground-truth labels for each of the points you made a prediction on. You can then compute evaluation metrics such as Precision, Recall, Accuracy, and F1-Score.
Great! In the next lab, you'll implement KNN using Python!