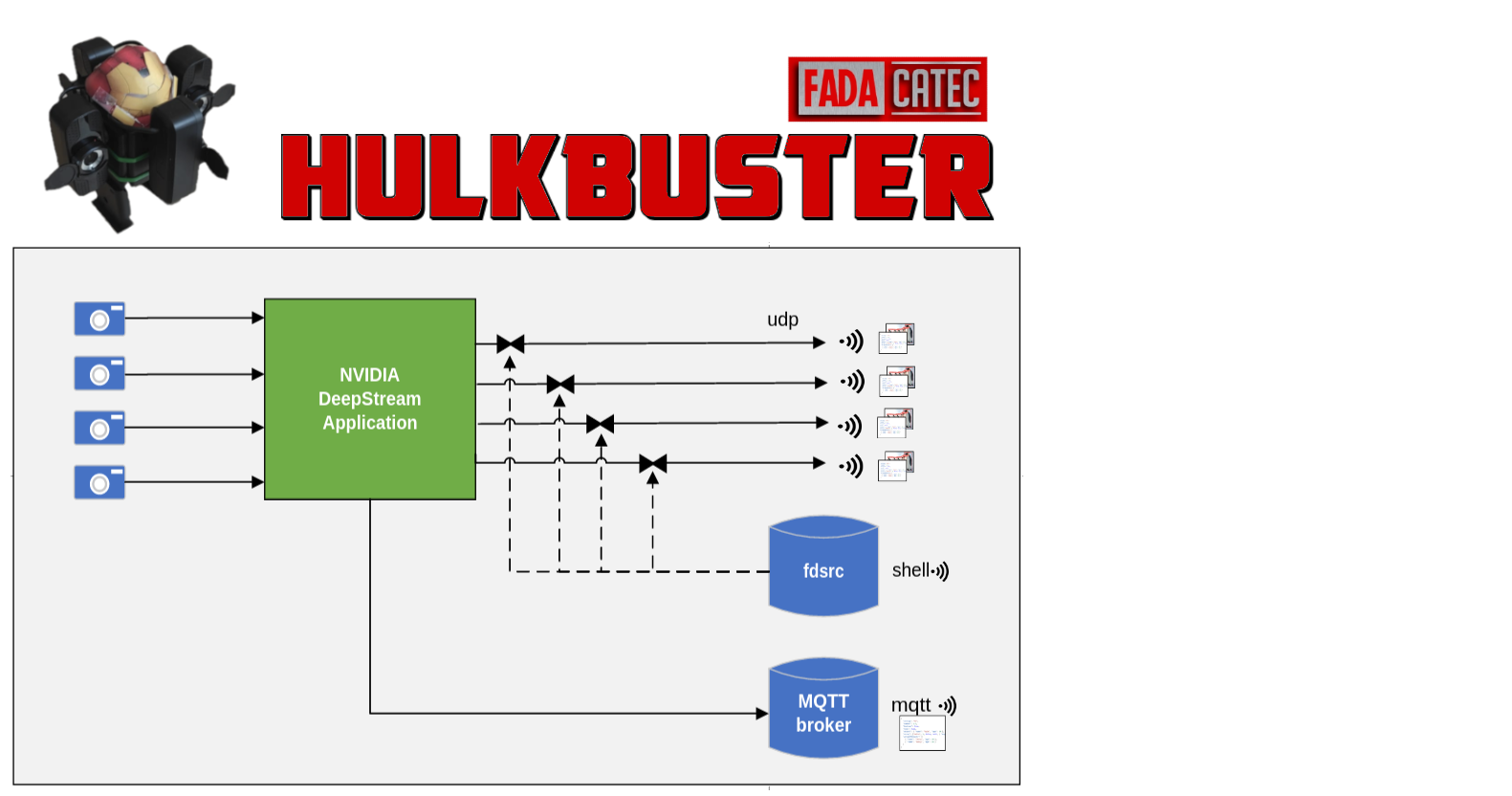
The Hulkbuster is a feature-rich Nvidia Deepstream sample application for object detection.
"Back off! You're steaming up my a̶r̶m̶o̶r̶ Jetson!" - Hulkbuster
The main Deepstream application. Beefy Nvds pipeline with the following features:
- Fully C-written implementation
- Multiple
v4l2srcinput sources - Yolo inference engine through
DeepStream-Yolotool - Custom CLI for live pipeline control through custom CLI
(◐ . ◐ ) - Object detection results
- Sent to MQTT via
gst-nvmsgbroker - Attached to video frames as udp-ready metadata via rtp headers
\(◐ O ◐\)
- Sent to MQTT via
- Ubuntu: Runs out of the box in a NVDS-Lite environment. Host must have
mosquitto. - Jetson: UNTESTED
- Pre-launch setup:
- Arrange your camera v4l2
/dev/videoXids inhulkbuster/src/main.c - In a side terminal, launch mosquitto at the right port (see
hulkbuster/src/main.c, default 1234). - Log into NVDS container OR match dependencies (former is assumed):
user@host:nvds-hulbuster$ nvds-lite root@nvds:/# cd /host/ root@nvds:/host/# - Arrange your camera v4l2
- Build application:
# make(cleanup withmake clean) - Run application:
# ./hulkbuster.o - Live pipeline interaction:
- Sending any input through STDIN to the hulkbuster app reveals a controller CLI
- Write in
helpto see available pipeline-altering commands
If the NVDS-Lite container messes your permissions on exit, restore them with $ chown -R "$USER" *.
"I'm Iron Man! Let's get this s̶h̶o̶w̶ meta on the road." - Tony GStark
Complementary app. Elementary Gstreamer pipeline that will take incoming UDP streams from the hulkbuster and drop their meta to its stdout.
- Gstreamer-1.0 install w/ rtp plugins
- Mosquitto
- Make sure the UDP port matches the Hulkbuster's
- Build with
$ makealong with hulkbuster OR$ pushd receiver && make && popd - Run with
$ ./receiver.oOR$ ./receiver/bin/receiver.o - Cleanup with
make clean
cams.sh: Prompts v4l2-ctl for your available cameras and prints their/dev/videoXready to copypaste into your C / bash script.
This section briefly discusses novel tools used to achieve the target features the Hulkbuster application aims for.
A #defined compound artificial element worth mentioning. It concatenates the nvstreammux & nvstreamdemux elements and places valves in between. These valves allow stopping a UDP stream, yet keep inference and MQTT detections going on. While small, it does have a noticeable impact on performance. Should be used sparingly.
// in hulkbuster/src/main.c
#define REMUX \
" nvstreamdemux name=demux " \
" demux.src_0 ! valve name=remux_v0 drop=false ! remux.sink_0 " \
" demux.src_1 ! valve name=remux_v1 drop=false ! remux.sink_1 " \
" demux.src_2 ! valve name=remux_v2 drop=false ! remux.sink_2 " \
" demux.src_3 ! valve name=remux_v3 drop=false ! remux.sink_3 " \
" nvstreammux name=remux nvbuf-memory-type=0 " \
" batch-size="BATCH" width=640 height=640 " \
" sync-inputs=1 batched-push-timeout=500000 """
A CLI alternative to GstDaemon, used to set / get properties of pipeline elements. Most useful to switch valve elements to control parallel video streams. The handling of streams and (mostly) meta required writing an app with Pad Probes, which are not supported by GstDaemon pipeline declaration. Usage instructions below:
-
No install, just
#includethe fileshulkbuster/src/gstfdcontrol.chulkbuster/include/gstfdcontrol.h
-
In your application, add this sub-pipeline:
fdsrc fd=0 name=control ! fakesink dump=false async=falsefdsrc: file descriptor sourcefd=0: setsstdinas sourcename=control: alias for easier handling
fakesink: to discard processed buffersdump=false: set to true only for debugging. Will dump allfdsrcreceived data to stdout.async=false: drops the need for a pipeline preroll, which pauses the pipeline until first buffer (i.e. whole application would block until something comes through stdin)source
-
In your application, attach a
control_handlerprobe pad tofdsrc:place_probe(pipeline, "control", control_handler, pipeline);- All text processing happens at
control_handler - Pass a pointer to the pipeline as user data
- See
place_probeimplementation in./hulkbuster/src/main.c - See
control_handlerimplementation in./hulkbuster/src/gstfdcontrol.c
- All text processing happens at
Find an example usage snippet below. The following simulates the hulkbuster's output, {} denotes fake hints introduced to the reader.
{ DEEPSTREAM PIPELINE BOOT OUTPUT UP UNTIL HERE }
Running...
Adjusting muxer's batch push timeout based on FPS of fastest source to 33333
Adjusting muxer's batch push timeout based on FPS of fastest source to 33333
{ Press Enter }
>>> help
Gstreamer Control Handler.
Helper CLI for interacting with live pipelines.
Your STDIN is being sent to Gstreamer.
Usage:
set <element_name> <property_name> <value>
get <element_name> <property_name>
echo [args]
help
dummy
Kill the pipeline with ^C to exit, as usual.
>>>
Here's an overview on how UDP metadata transmission is achieved.
- Private deepstream metadata is generated by the
nvinferplugin - The detections in this struct are parsed to a string and moved to the more flexible GstMeta API
- Such string is attached to every last RTP packet encoding a frame
This approach is described in the following sample pipeline schematic:
video video application video
┌─────────┐ ┌──────┐ x-raw ┌─────┐ x-264 ┌───────┐ x-rtp UDP ┌─────────┐ ┌──────┐ x-raw
│ v4l2src ├─►│ NVDS ├───────│xh265├──────►│rtp*pay├─────────────── * ─►│rtp*depay├──►│decode├──────►
└─────────┘ └──────┘ └─────┘ └───────┘ └─────────┘ └──────┘
│ ▲ │ ▲ │
▼ | ▼ | ▼
NvdsMeta->GstMeta GstMeta->rtp header rtp header->stdout
See more on metadata at NVDS-Meta.
Here are some resources found useful during the development of this repo. Meant for quick reference only.
- Do not use single quotes in
gst-parse-launchpipelines nvmultistreamtilerandnvosdcan only be used once, else detections are corrupted / missplaced- Setups with many USB cameras are not always stable:
- Reference many usb cameras issues: reference + fix
- Error information prompting these:
- After pipeline tries to boot:
Failed to allocate required memory-> insist running the same commands. - Instantaneous
Segmentation fault-> review your cameras/dev/videoXids
- After pipeline tries to boot:
- Lowering camera bandwidth usage reduces the frequency of these issues, however they do happen sometimes
- Funky scenarios & advice:
- You might be able to stream at 1080 one time, but not a second one. If you believe your pipeline should work but it fails to allocate memory, insist
- 4 cameras sometimes seen to repeteadly fail on 640x480, but work on 1280x720 right after
- If they fail at 1280x720, try at 800x600 then go back again to 1280x720
- Rerun docker image after replugging cameras
- RidgeRun's Gstreamer debugging guide: GStreamer Debugging
- RidgeRun's Gstreamer general advice and pointers: Why RidgeRun loves GStreamer
fdsrcblocks the pipeline on start. Set its fakesink'sasync=falseto avoid the need for prerolling. source
- Networking apps inside/outside of docker:
mosquitto: no known issuesrtsp-simple-server: will NOT properly connect endpoints if running in docker.
- A few pipelines to quickly test udp
- Send
gst-launch-1.0 videotestsrc \ ! videoconvert \ ! x264enc tune=zerolatency \ ! rtph264pay \ ! udpsink host=127.0.0.1 port=1234 ;- Receive
gst-launch-1.0 udpsrc port=1234 \ ! application/x-rtp ! rtph264depay \ ! queue leaky=1 max-size-buffers=100 max-size-time=0 max-size-bytes=0 \ ! h264parse config-interval=-1 ! avdec_h264 \ ! queue leaky=1 max-size-buffers=100 max-size-time=0 max-size-bytes=0 \ ! videoconvert ! queue leaky=2 ! autovideosink sync=false async=false ; - Wiresharking the UDP streams:
sudo wireshark- Loopback (lo)
- Apply filter
udp.port==1234 - Run both wireshark and your app
- See your custom RTP headers (if not encrypted)
- Monitor the packages, find the last RTP of each frame and see the first dozen byte rows.
- Diagnose pipeline bandwith usage:
- Top bar Statistics -> I/O graphs
- A new window with a graph will pop up
- In the lower panel, select
All packets | * | Bytes | None
- Great C reference manual: Notes on Data Structures and Programming Techniques (CPSC 223, Spring 2022)
- Learn X in Y minutes C cheatsheet Where X=C
- Compilation process issues:
- Linker undefined:
/usr/bin/ld: /tmp/main.o: undefined reference to symbol 'WHATEVER'-> missing libraries atpkg-config --libs --cflags ** - What should I put in
pkg-config?- If facing linker error:
pkg-config --list-all | grep YOUR_HUNCH - See this thread: How are you supposed to know what library names are
- If facing linker error:
- Linker undefined: