Google Earth Engine codes to correct the radiometric effects (caused by different Local Incidence Angle) in Sentinel-1 SAR data.
This code repository is an attachment for the article in Remote Sensing: Paluba et al. (2021): "Land Cover-Specific Local Incidence Angle Correction: A Method for Time-Series Analysis of Forest Ecosystems" (doi: 10.3390/rs13091743). The repository contains a folder "javascript_codes" where you can find:
- A JavaScript Google Earth Engine (GEE) function "LC-SLIAC.js" to create a SAR image collection where bands have been corrected for effects of terrain
- A JavaScript GEE example usage of the function "LC-SLIAC_example.js", where three-month time series chart before and after the application of LC-SLIAC and the corrected image collection are added to the GEE Console
After requests from the GEE community, a new version of the code was added, which can be used globally, not only for countries in the European Union. See the details here. In the "javascript_codes" folder you can find two more scripts:
- A globally usable JavaScript Google Earth Engine (GEE) function "LC-SLIAC_global.js" to create a SAR image collection where bands have been corrected for effects of terrain
- A globally usable JavaScript GEE example usage of the function "LC-SLIAC_global_example.js", where three-month time series chart before and after the application of LC-SLIAC and the corrected image (test site in Vietnam)
The land cover-specific local incidence angle correction (LC-SLIAC) is based on the linear relationship between the backscatter values and the local incidence angle (LIA) for a given land cover type in the monitored area. Using the combination of CORINE Land Cover and Hansen Global Forest databases, a wide range of different LIAs for a specific forest type can be generated for each individual scene. The algorithm was developed and tested in the cloud-based platform Google Earth Engine (GEE) using Sentinel-1 open access data, Shuttle Radar Topography Mission (SRTM) digital elevation model, as well as CORINE Land Cover and Hansen Global Forest databases. The developed method was created primarily for time-series analysis of forests over mountainous areas. LC-SLIAC was tested in 16 study areas over several protected areas in Central Europe.
This methodology is mainly focused on the use in the analysis of forest time series. In general, this method is useful over mountainous areas with moderate to steep sloping terrain, where the variation in LIA values for forests is high. The results after correction by LC-SLIAC showed a statistically significant reduction in variance (of more than 40%) in areas with LIA range > 50° and LIA interquartile range (IQR) > 12°, while in areas with low LIA range (< 30°) and LIA IQR (< 6°), the decrease in variance was very low and statistically not significant. Time series after the correction showed a reduced fluctuation of backscatter values caused by different LIAs in each acquisition path, while this reduction was statistically significant (with up to 95% reduction of variance) in areas with a difference in LIA greater than or equal to 27°.
Methodology: The most important step in the methodology of the LC-SLIAC method was to calculate the LIA for every image pixel, where other parameters from the SRTM DEM (slope and aspect) and SAR image (viewing azimuth) needed to be calculated. For SAR images, the active shadow and layover areas were masked out, followed by the generation of forest mask, which was used to select an appropriate number of forest areas to explain the relationship between LIA and backscatter in the linear regression analysis. Figure 1 shows the steps used to generate the corrected image collection.
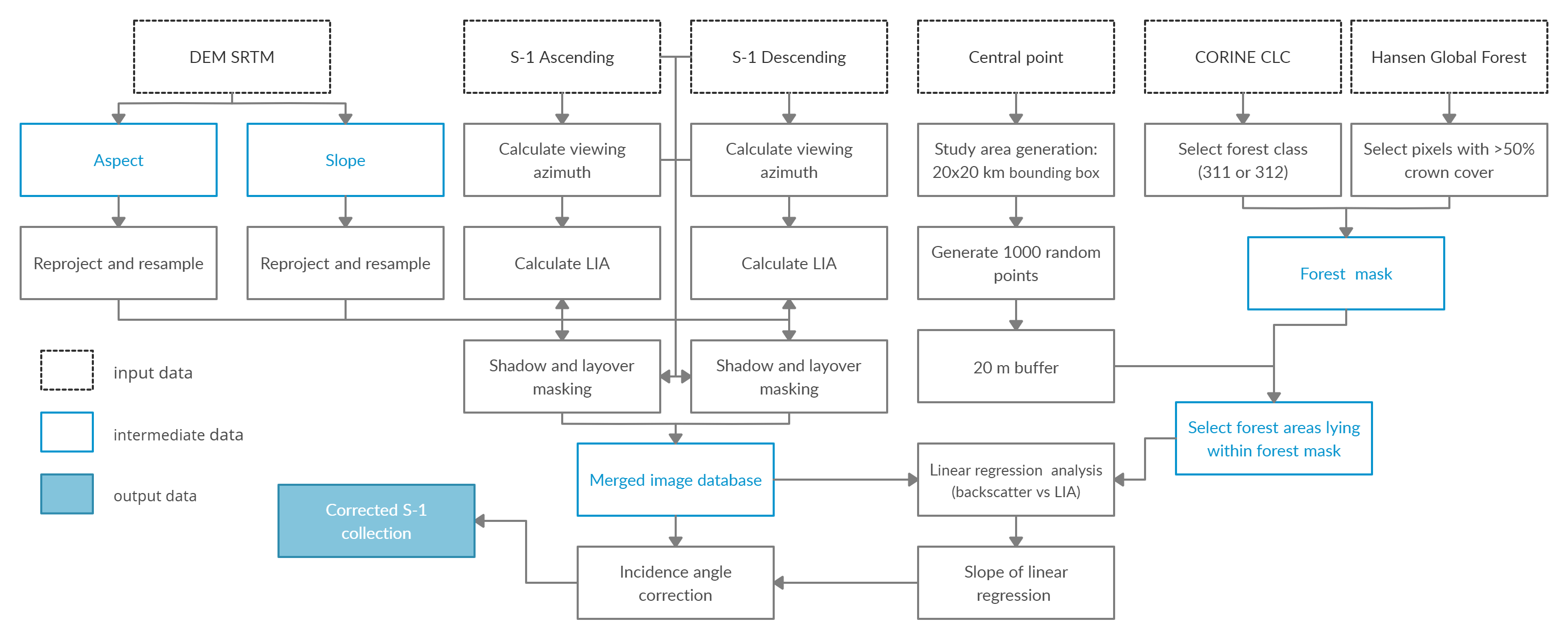 Figure 1. Methodology workflow used in this work
Figure 1. Methodology workflow used in this work
After requests from the GEE community, a new version of the code was added, which can be used globally, not only for countries in the European Union. For the "global" version of the LC-SLIAC, the Copernicus Global Land Cover Layers (CGLC) was used. The newest version (v 1.8) of the Hansen Global Forest Change database was used in this update, where data for 2020 are also available.
In the definition of forest type, there are 4 categories in the CGLC:
- 111 - Closed forest, evergreen needle leaf. Tree canopy >70 %, almost all needle leaf trees remain green all year. Canopy is never without green foliage.
- 112 - Closed forest, evergreen broad leaf. Tree canopy >70 %, almost all broadleaf trees remain green year round. Canopy is never without green foliage.
- 113 - Closed forest, deciduous needle leaf. Tree canopy >70 %, consists of seasonal needle leaf tree communities with an annual cycle of leaf-on and leaf-off periods.
- 114 - Closed forest, deciduous broad leaf. Tree canopy >70 %, consists of seasonal broadleaf tree communities with an annual cycle of leaf-on and leaf-off periods.
You can use this function after the reqirement call require('users/danielp/LC-SLIAC:LC-SLIAC'), i.e.:
require('users/danielp/LC-SLIAC:LC-SLIAC') or by copying the code in the "LC-SLIA.js" to your code editor and call it with defined parameters.
You can use this function after the reqirement call require('users/danielp/LC-SLIAC:LC-SLIAC_global'), i.e.:
require('users/danielp/LC-SLIAC:LC-SLIAC_global') or by copying the code in the "LC-SLIA_global.js" to your code editor and call it with defined parameters.
- ROI (type Geometry)
- Define the ROI for what you want to create a time series analysis
- startDate (type Date)
- Start date of the time series
- endDate (type Date)
- End date of the time series
- year (type Integer) - available only for the LC-SLIAC_global version
- Year for which the CGLC will be used. Available years: 2015-2019. Hopefully, the 2020 database will be available soon.
- landCoverType (type Integer)
- Define the land cover type. Currently tested for coniferous forest (312) and broadleaf forest (311).
- For the LC-SLIAC_global function, see the legend here
- S1Collection (type ImageCollection, optional, default: Sentinel-1 Image Collection with VV and VH bands)
- Define the S1 image collection for which you want to apply the LIA correction. Tested and designed for Sentinel-1 data
- boudningBoxSize (type Integer, optional, default: 10000)
- The bounding box size around the selected area to calculate the backscatter-LIA dependence. This area is also used to clip the resulted image collection after the correction.
- referenceAngle (type Integer, optional, deafault: 9999 = mean angle from found LIAs)
- Reference angle to which the backscatter values will be corrected. For time series analyses, it is recommended to use the default value - the mean value from the minimum and maximum value of observed LIA (from the available paths).
- acquistionMode (type String, optional, default: 'IW')
- Acqusition mode for Sentinel-1 data in GEE can be 'IW' (Interferometric Wide Swath), 'EW' (Extra Wide Swath) or 'SM' (Strip Map)
The main output of the LC-SLIAC function is the input Sentinel-1 image collection clipped to the predefined study area size by boudningBoxSize, extended by:
-
Image bands:
- LIA - the calculated local incidence angle image
- corrected_VH - VH band after LC-SLIAC where active shadow and layover areas are masked out
- corrected_VV - VV band after LC-SLIAC where active shadow and layover areas are masked out
-
Statistical parameters in the properties:
- VVscale, VH scale - the scale coefficient calculated from the regression analysis for VV and VH polarization, respectively
- VVoffset, VHoffset - the offset coefficient calculated from the regression analysis for VV and VH polarization, respectively
- VVnumberOfForestPoints, VHnumberOfForestPoints - the number of forest areas included in the regression analysis for VV and VH polarization, respectively
- VHR2, VVR2 - the resulted coefficient of determination (R2) of the regression analysis for VV and VH polarization, respectively
- VHpValue, VVpValue - the p-value for the regression analysis for VV and VH polarization, respectively
- MeanElevationOfForestPoints - mean elevation of selected forest areas for VV and VH polarization, respectively
- VV_LIAIQR, VH_LIAIQR - LIA interquartile range (IQR) for forest areas for VV and VH polarization, respectively
- LIA_range_VV, LIA_range_VH - LIA range for forest areas for VV and VH polarization, respectively
- lookAngleAzimuth - the calculated sensor's look angle
For long-term time series analysis, e.g. for the whole Sentinel-1 archive, it is recommended to zoom in to the selected study area, as it is done in the example script (LC-SLIAC_example.js).