| page_type | languages | products | name | description | urlFragment | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
sample |
|
|
Deploy an Azure Kubernetes Service cluster with Crossplane using Terraform |
This sample shows how to deploy an Azure Kubernetes Service cluster with Crossplane using Terraform |
aks-crossplane-terraform |
In this sample, I shows how to automate the deployment via Terraform of an Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS) cluster with Crossplane and the Upbound Azure Providers.
Crossplane is an open source Kubernetes extension that transforms your Kubernetes cluster into a universal control plane. Crossplane lets you manage anything, anywhere, all through standard Kubernetes APIs. Crossplane can even let you order a pizza directly from Kubernetes. If it has an API, Crossplane can connect to it. With Crossplane, platform teams can create new abstractions and custom APIs with the full power of Kubernetes policies, namespaces, role based access controls and more. Crossplane brings all your non-Kubernetes resources under one roof. Custom APIs, created by platform teams, allow security and compliance enforcement across resources or clouds, without exposing any complexity to the developers. A single API call can create multiple resources, in multiple clouds and use Kubernetes as the control plane for everything.
For more information, see:
NOTE
You can find thearchitecture.vsdxfile used for the diagram under thevisiofolder.
- An active Azure subscription. If you don't have one, create a free Azure account before you begin.
- Visual Studio Code installed on one of the supported platforms along with the HashiCorp Terraform.
- Azure CLI version 2.49.0 or later installed. To install or upgrade, see Install Azure CLI.
aks-previewAzure CLI extension of version 0.5.140 or later installed- Terraform v1.5.2 or later.
- The deployment must be started by a user who has sufficient permissions to assign roles, such as a
User Access AdministratororOwner. - Your Azure account also needs
Microsoft.Resources/deployments/writepermissions at the subscription level.
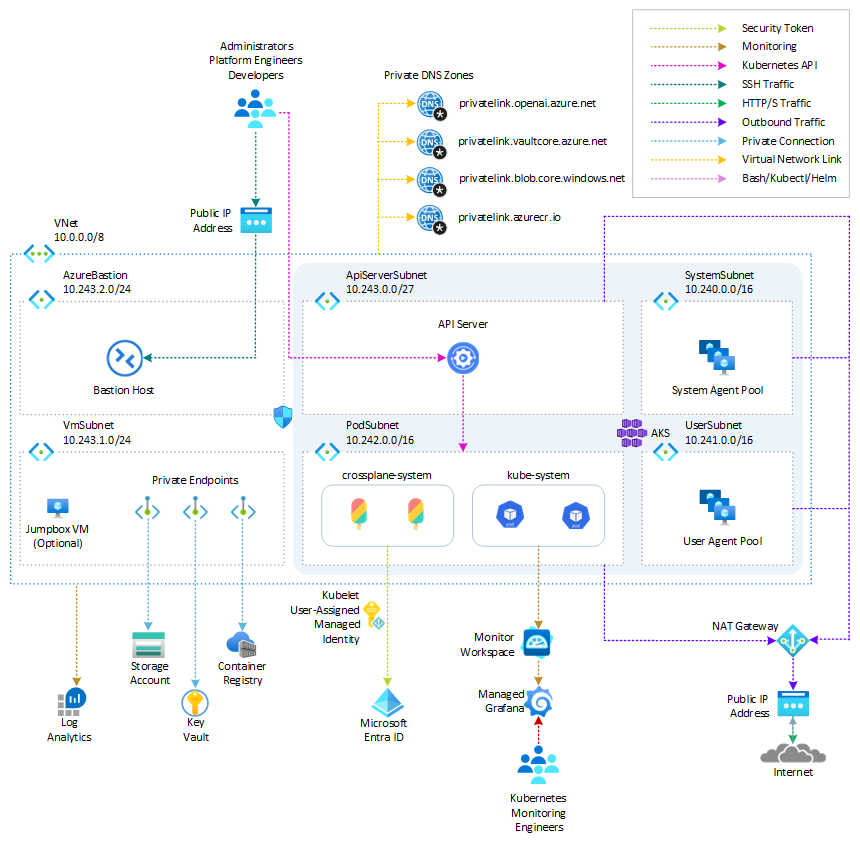
The following diagram shows the architecture and network topology deployed by the sample:
This project provides a set of Terraform modules to deploy thw following resources:
- Azure Kubernetes Service: A public or private Azure Kubernetes Service(AKS) cluster composed of a:
- A
systemnode pool in a dedicated subnet. The default node pool hosts only critical system pods and services. The worker nodes have node taint which prevents application pods from beings scheduled on this node pool. - A
usernode pool hosting user workloads and artifacts in a dedicated subnet.
- A
- User-defined Managed Identity: a user-defined managed identity used by the AKS cluster to create additional resources like load balancers and managed disks in Azure.
- Azure Virtual Machine: Terraform modules can optionally create a jump-box virtual machine to manage the private AKS cluster.
- Azure Bastion Host: a separate Azure Bastion is deployed in the AKS cluster virtual network to provide SSH connectivity to both agent nodes and virtual machines.
- Azure NAT Gateway: a bring-your-own (BYO) Azure NAT Gateway to manage outbound connections initiated by AKS-hosted workloads. The NAT Gateway is associated to the
SystemSubnet,UserSubnet, andPodSubnetsubnets. The outboundType property of the cluster is set touserAssignedNatGatewayto specify that a BYO NAT Gateway is used for outbound connections. NOTE: you can update theoutboundTypeafter cluster creation and this will deploy or remove resources as required to put the cluster into the new egress configuration. For more information, see Updating outboundType after cluster creation. - Azure Storage Account: this storage account is used to store the boot diagnostics logs of both the service provider and service consumer virtual machines. Boot Diagnostics is a debugging feature that allows you to view console output and screenshots to diagnose virtual machine status.
- Azure Container Registry: an Azure Container Registry (ACR) to build, store, and manage container images and artifacts in a private registry for all container deployments.
- Azure Key Vault: an Azure Key Vault used to store secrets, certificates, and keys that can be mounted as files by pods using Azure Key Vault Provider for Secrets Store CSI Driver. For more information, see Use the Azure Key Vault Provider for Secrets Store CSI Driver in an AKS cluster and Provide an identity to access the Azure Key Vault Provider for Secrets Store CSI Driver.
- Azure Private Endpoints: an Azure Private Endpoint is created for each of the following resources:
- Azure Container Registry
- Azure Key Vault
- Azure Storage Account
- API Server when deploying a private AKS cluster.
- Azure Private DNDS Zones: an Azure Private DNS Zone is created for each of the following resources:
- Azure Container Registry
- Azure Key Vault
- Azure Storage Account
- API Server when deploying a private AKS cluster.
- Azure Network Security Group: subnets hosting virtual machines and Azure Bastion Hosts are protected by Azure Network Security Groups that are used to filter inbound and outbound traffic.
- Azure Log Analytics Workspace: a centralized Azure Log Analytics workspace is used to collect the diagnostics logs and metrics from all the Azure resources:
- Azure Kubernetes Service cluster
- Azure Key Vault
- Azure Network Security Group
- Azure Container Registry
- Azure Storage Account
- Azure jump-box virtual machine
- Azure Monitor workspace: An Azure Monitor workspace is a unique environment for data collected by Azure Monitor. Each workspace has its own data repository, configuration, and permissions. Log Analytics workspaces contain logs and metrics data from multiple Azure resources, whereas Azure Monitor workspaces currently contain only metrics related to Prometheus. Azure Monitor managed service for Prometheus allows you to collect and analyze metrics at scale using a Prometheus-compatible monitoring solution, based on the Prometheus. This fully managed service allows you to use the Prometheus query language (PromQL) to analyze and alert on the performance of monitored infrastructure and workloads without having to operate the underlying infrastructure. The primary method for visualizing Prometheus metrics is Azure Managed Grafana. You can connect your Azure Monitor workspace to an Azure Managed Grafana to visualize Prometheus metrics using a set of built-in and custom Grafana dashboards.
- Azure Managed Grafana: an Azure Managed Grafana instance used to visualize the Prometheus metrics generated by the Azure Kubernetes Service(AKS) cluster deployed by the Bicep modules. Azure Managed Grafana is a fully managed service for analytics and monitoring solutions. It's supported by Grafana Enterprise, which provides extensible data visualizations. This managed service allows to quickly and easily deploy Grafana dashboards with built-in high availability and control access with Azure security.
- NGINX Ingress Controller: this sample compares the managed and unmanaged NGINX Ingress Controller. While the managed version is installed using the Application routing add-on, the unmanaged version is deployed using the Helm Terraform Provider. You can use the Helm provider to deploy software packages in Kubernetes. The provider needs to be configured with the proper credentials before it can be used.
- Argo CD: Argo CD follows the GitOps pattern of using Git repositories as the source of truth for defining the desired application state. The package is installed via
Helm. - Crossplane: Crossplane is installed via
Helmwith a configurable collection of Upbound Azure Providers. TheConfigProvideris created via aYAML manifestand configured to use thekubeletuser-assigned managed identity to connect to Azure. This identity is assigned theOwnerrole over the Azure subscription. For more information, see Authentication using User-Assigned Managed Identities. - Cert-Manager: the
cert-managerpackage and Let's Encrypt certificate authority are used to issue a TLS/SSL certificate to the chat applications. - Prometheus: the AKS cluster is configured to collect metrics to the Azure Monitor workspace and Azure Managed Grafana. Nonetheless, the kube-prometheus-stack Helm chart is used to install Prometheus and Grafana on the AKS cluster.
- Workload namespace and service account: the Kubectl Terraform Provider and Kubernetes Terraform Provider are used to create the namespace and service account used by the chat applications.
- Azure Monitor ConfigMaps for Azure Monitor managed service for Prometheus and
cert-managerCluster Issuer are deployed using the Kubectl Terraform Provider and Kubernetes Terraform Provider.`
The scripts folder contains the following files Bash scripts to test Crossplane when the deployment completed.
The following script creates a test CompositeResourceDefinition. Composite resource definitions (XRDs) define the schema for a custom API. The XRD spec contains all the information about the API including the group, version, kind and schema. The XRD’s name must be the combination of the plural and group. The schema uses the OpenAPIv3 specification to define the API spec. The API defines a location that must be oneOf either EU or US. Apply this XRD to create the custom API in your Kubernetes cluster.
#!/bin/bash
# Create the CompositeResourceDefinition for the VirtualMachine resource
cat <<EOF | kubectl apply -f -
apiVersion: apiextensions.crossplane.io/v1
kind: CompositeResourceDefinition
metadata:
name: virtualmachines.compute.example.com
spec:
group: compute.example.com
names:
kind: VirtualMachine
plural: virtualmachines
versions:
- name: v1alpha1
schema:
openAPIV3Schema:
type: object
properties:
spec:
type: object
properties:
location:
type: string
oneOf:
- pattern: '^EU$'
- pattern: '^US$'
required:
- location
served: true
referenceable: true
claimNames:
kind: VirtualMachineClaim
plural: virtualmachineclaims
EOFAdding the claimNames allows you to access this API either at the cluster level with the VirtualMachine endpoint or in a namespace with the VirtualMachineClaim endpoint. The namespace scoped API is a Crossplane Claim.
NOTE
For more details on the fields and options of Composite Resource Definitions read the XRD documentation.
You can display the installed XRD with the kubectl get xrd command.
1kubectl get xrd
2NAME ESTABLISHED OFFERED AGE
3virtualmachines.compute.example.com True True 43sYou can view the new custom API endpoints running the kubectl api-resources | grep VirtualMachine command.
1kubectl api-resources | grep VirtualMachine
2virtualmachineclaims compute.example.com/v1alpha1 true VirtualMachineClaim
3virtualmachines compute.example.com/v1alpha1 false VirtualMachineWhen you access the custom API Crossplane takes their inputs and combines them with a template describing what infrastructure to deploy. Crossplane calls this template a Composition. A Composition defines all the cloud resources to deploy. Each entry in the template is a full resource definitions, defining all the resource settings and metadata like labels and annotations. This template creates an Azure LinuxVirtualMachine NetworkInterface, Subnet VirtualNetwork and ResourceGroup. Crossplane uses patches to apply your input to the resource template. This Composition takes your location input and uses it as the location used in the individual resource. Apply this Composition to your cluster.
#!/bin/bash
# Create the Composition for the VirtualMachine resource
cat <<EOF | kubectl apply -f -
apiVersion: apiextensions.crossplane.io/v1
kind: Composition
metadata:
name: crossplane-quickstart-vm-with-network
spec:
resources:
- name: quickstart-vm
base:
apiVersion: compute.azure.upbound.io/v1beta1
kind: LinuxVirtualMachine
spec:
forProvider:
adminUsername: adminuser
adminSshKey:
- publicKey: ssh-rsa
AAAAB3NzaC1yc2EAAAADAQABAAABAQC+wWK73dCr+jgQOAxNsHAnNNNMEMWOHYEccp6wJm2gotpr9katuF/ZAdou5AaW1C61slRkHRkpRRX9FA9CYBiitZgvCCz+3nWNN7l/Up54Zps/pHWGZLHNJZRYyAB6j5yVLMVHIHriY49d/GZTZVNB8GoJv9Gakwc/fuEZYYl4YDFiGMBP///TzlI4jhiJzjKnEvqPFki5p2ZRJqcbCiF4pJrxUQR/RXqVFQdbRLZgYfJ8xGB878RENq3yQ39d8dVOkq4edbkzwcUmwwwkYVPIoDGsYLaRHnG+To7FvMeyO7xDVQkMKzopTQV8AuKpyvpqu0a9pWOMaiCyDytO7GGN
example@docs.crossplane.io
username: adminuser
location: "Central US"
osDisk:
- caching: ReadWrite
storageAccountType: Standard_LRS
resourceGroupNameSelector:
matchControllerRef: true
size: Standard_B1ms
sourceImageReference:
- offer: debian-11
publisher: Debian
sku: 11-backports-gen2
version: latest
networkInterfaceIdsSelector:
matchControllerRef: true
patches:
- type: FromCompositeFieldPath
fromFieldPath: "spec.location"
toFieldPath: "spec.forProvider.location"
transforms:
- type: map
map:
EU: "Sweden Central"
US: "Central US"
- name: quickstart-nic
base:
apiVersion: network.azure.upbound.io/v1beta1
kind: NetworkInterface
spec:
forProvider:
ipConfiguration:
- name: crossplane-quickstart-configuration
privateIpAddressAllocation: Dynamic
subnetIdSelector:
matchControllerRef: true
location: "Central US"
resourceGroupNameSelector:
matchControllerRef: true
patches:
- type: FromCompositeFieldPath
fromFieldPath: "spec.location"
toFieldPath: "spec.forProvider.location"
transforms:
- type: map
map:
EU: "Sweden Central"
US: "Central US"
- name: quickstart-subnet
base:
apiVersion: network.azure.upbound.io/v1beta1
kind: Subnet
spec:
forProvider:
addressPrefixes:
- 10.0.1.0/24
virtualNetworkNameSelector:
matchControllerRef: true
resourceGroupNameSelector:
matchControllerRef: true
- name: quickstart-network
base:
apiVersion: network.azure.upbound.io/v1beta1
kind: VirtualNetwork
spec:
forProvider:
addressSpace:
- 10.0.0.0/16
location: "Central US"
resourceGroupNameSelector:
matchControllerRef: true
patches:
- type: FromCompositeFieldPath
fromFieldPath: "spec.location"
toFieldPath: "spec.forProvider.location"
transforms:
- type: map
map:
EU: "Sweden Central"
US: "Central US"
- name: crossplane-resourcegroup
base:
apiVersion: azure.upbound.io/v1beta1
kind: ResourceGroup
spec:
forProvider:
location: Central US
patches:
- type: FromCompositeFieldPath
fromFieldPath: "spec.location"
toFieldPath: "spec.forProvider.location"
transforms:
- type: map
map:
EU: "Sweden Central"
US: "Central US"
compositeTypeRef:
apiVersion: compute.example.com/v1alpha1
kind: VirtualMachine
EOFThe compositeTypeRef defines which custom APIs can use this template to create resources.
NOTE
Read the Composition documentation for more information on configuring Compositions and all the available options.
Read the Patch and Transform documentation for more information on how Crossplane uses patches to map your inputs to Composition resource templates. You can view the Composition by running the kubectl get composition command:
1kubectl get composition
2NAME XR-KIND XR-APIVERSION AGE
3crossplane-quickstart-vm-with-network XVirtualMachine custom-api.example.org/v1alpha1 77sWith the custom API (XRD) installed and associated to a resource template (Composition), you can access the API to create resources. Create a VirtualMachine object to create the cloud resources.
#!/bin/bash
# Variables
name="bingo"
location="EU"
# With the custom API (XRD) installed and associated to a resource template (Composition) users can access the API to create resources.
# Create a VirtualMachine object to create the cloud resources.
cat <<EOF | kubectl apply -f -
apiVersion: compute.example.com/v1alpha1
kind: VirtualMachine
metadata:
name: $name
spec:
location: $location
EOFYou can the resource with the kubectl get VirtualMachine command.
NOTE
It may take up to five minutes for the resources to provision.
kubectl get VirtualMachine
NAME SYNCED READY COMPOSITION AGE
bingo True True crossplane-quickstart-vm-with-network 3m3sThis object is a Crossplane Composite Resource (XR). It’s a single object representing the collection of resources created from the Composition template. You can view the individual resources by running the kubectl get managed command.
kubectl get managed
NAME READY SYNCED EXTERNAL-NAME AGE
resourcegroup.azure.upbound.io/bingo-7jb4n True True bingo-7jb4n 3m43s
NAME READY SYNCED EXTERNAL-NAME AGE
linuxvirtualmachine.compute.azure.upbound.io/bingo-5h7p4 True True bingo-5h7p4 3m43s
NAME READY SYNCED EXTERNAL-NAME AGE
networkinterface.network.azure.upbound.io/bingo-j7fpx True True bingo-j7fpx 3m43s
NAME READY SYNCED EXTERNAL-NAME AGE
subnet.network.azure.upbound.io/bingo-b2dqt True True bingo-b2dqt 3m43s
NAME READY SYNCED EXTERNAL-NAME AGE
virtualnetwork.network.azure.upbound.io/bingo-pd2sw True True bingo-pd2sw 3m43sAccessing the API created all five resources defined in the template and linked them together. Look at a specific resource to see it’s created in the location used in the API.
kubectl describe linuxvirtualmachine | grep Location
Location: Sweden Central
Location: swedencentralYou can delete the resources with the kubectl delete VirtualMachine command.
kubectl delete VirtualMachine bingo
virtualmachine.compute.example.com "bingo" deletedVerify Crossplane deleted the resources with kubectl get managed after a few minutes.
Copyright (c) 2024 Paolo Salvatori
Permission is hereby granted, free of charge, to any person obtaining a copy of this software and associated documentation files (the "Software"), to deal in the Software without restriction, including without limitation the rights to use, copy, modify, merge, publish, distribute, sublicense, and/or sell copies of the Software, and to permit persons to whom the Software is furnished to do so, subject to the following conditions: The above copyright notice and this permission notice shall be included in all copies or substantial portions of the Software.
THE SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED "AS IS", WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO THE WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY, FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE AUTHORS OR COPYRIGHT HOLDERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY CLAIM, DAMAGES OR OTHER LIABILITY, WHETHER IN AN ACTION OF CONTRACT, TORT OR OTHERWISE, ARISING FROM, OUT OF OR IN CONNECTION WITH THE SOFTWARE OR THE USE OR OTHER DEALINGS IN THE SOFTWARE.