TOG 2021 [Paper] [Project Page]
by Gal Metzer, Rana Hanocka, Raja Giryes, and Daniel Cohen-Or
- Clone this repo:
- Relies on PyTorch version 1.7.1
- Pytorch Geometric
- Everything can be installed via conda environment
conda env create -f env.yml(creates an environment called self-sample)
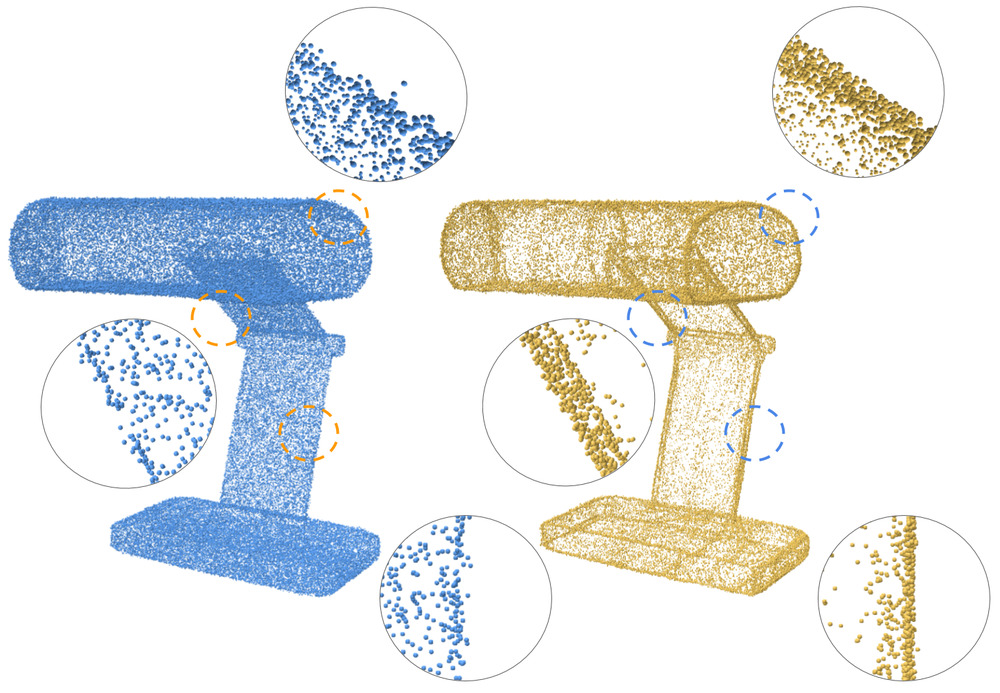
The demos folder contains examples from the paper.
For each shape the demo runs the optimization and inference parts.
For instance, to run the lamp demo simply execute from the root project folder:
demos/lamp.sh
The results would be found at demos-results/lamp/lamp_result.xyz,
and respectively for the other shapes as well.
- alien, anchor, lamp - sharp point consolidation
- candle, scanned Leg, tiki - sparse point consolidation
- camera_noised - denoising
If you find this code useful, please consider citing our paper
@article{metzer2020self,
author = {Metzer, Gal and Hanocka, Rana and Giryes, Raja and Cohen-Or, Daniel},
title = {Self-Sampling for Neural Point Cloud Consolidation},
year = {2021},
issue_date = {October 2021},
publisher = {Association for Computing Machinery},
address = {New York, NY, USA},
volume = {40},
number = {5},
issn = {0730-0301},
url = {https://doi.org/10.1145/3470645},
doi = {10.1145/3470645},
}
If you have questions or issues running this code, please open an issue.
Note: the original implementation used this implementation
of PointNet++, which is not guaranteed to supported newer versions of pytorch.
This implementation uses Pytorch Geometric instead,
which can not hold large subsets at train time.
Therefore, demos are designed for subset sizes lower than used in the paper. Increasing the subset size to 12K-14K on an appropriate GPU, improves the accuracy of the results.