A python package which can read CINRAD radar data, perform calculations and visualize the data.
example folder contains detailed examples!
pip install cinrad
Python 3.5 +
Cartopy
Metpy
Shapefile
Pykdtree (optional)
You can also download from github page and build from source
python setup.py install
This submodule contains data structure used in this program.
Radial type data: cinrad.datastruct.Radial
Cross-section type data: cinrad.datastruct.Slice_
Grid type data: cinrad.datastruct.Grid
Decode CINRAD radar data.
from cinrad.io import CinradReader, StandardData
f = CinradReader(your_radar_file) #Old version data
f = StandardData(your_radar_file) #New standard data
f.get_data(tilt, drange, dtype) #Get data
f.get_raw(tilt, drange, dtype)The get_raw method returns radar records without other geographic information.
cinrad.io.PUP provides functions to decode PUP data. The extracted data can be further used to create PPI. (Only radial data are supported.)
cinrad.io.SWAN provides similar interface to decode SWAN data.
from cinrad.io import PUP
f = PUP(your_radar_file)
data = f.get_data()This submodule provides some useful algorithms in radar meteorology. All functions only accept numpy.ndarray as input data. This submodule extends the usage of this program, as these functions can accept customized data rather than only the data decoded by cinrad.io.
For direct computation of decoded data, cinrad.easycalc provides functions that simplify the process of calculation. For functions contained in this submodule, only a list of reflectivity data is required as the argument.
Code to generate the required list:
r_list = [f.get_data(i, 230, 'REF') for i in f.angleindex_r]
# or
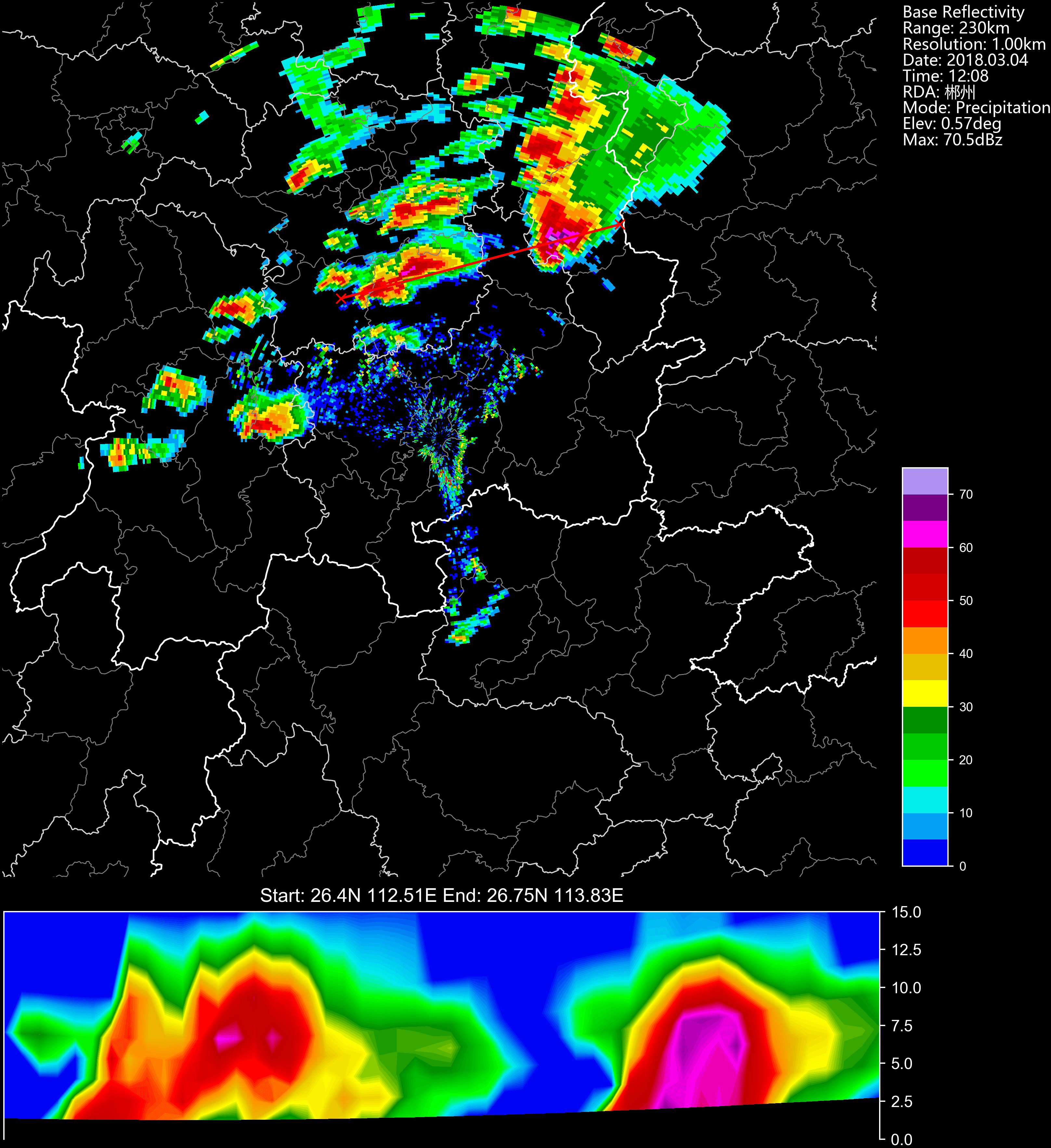
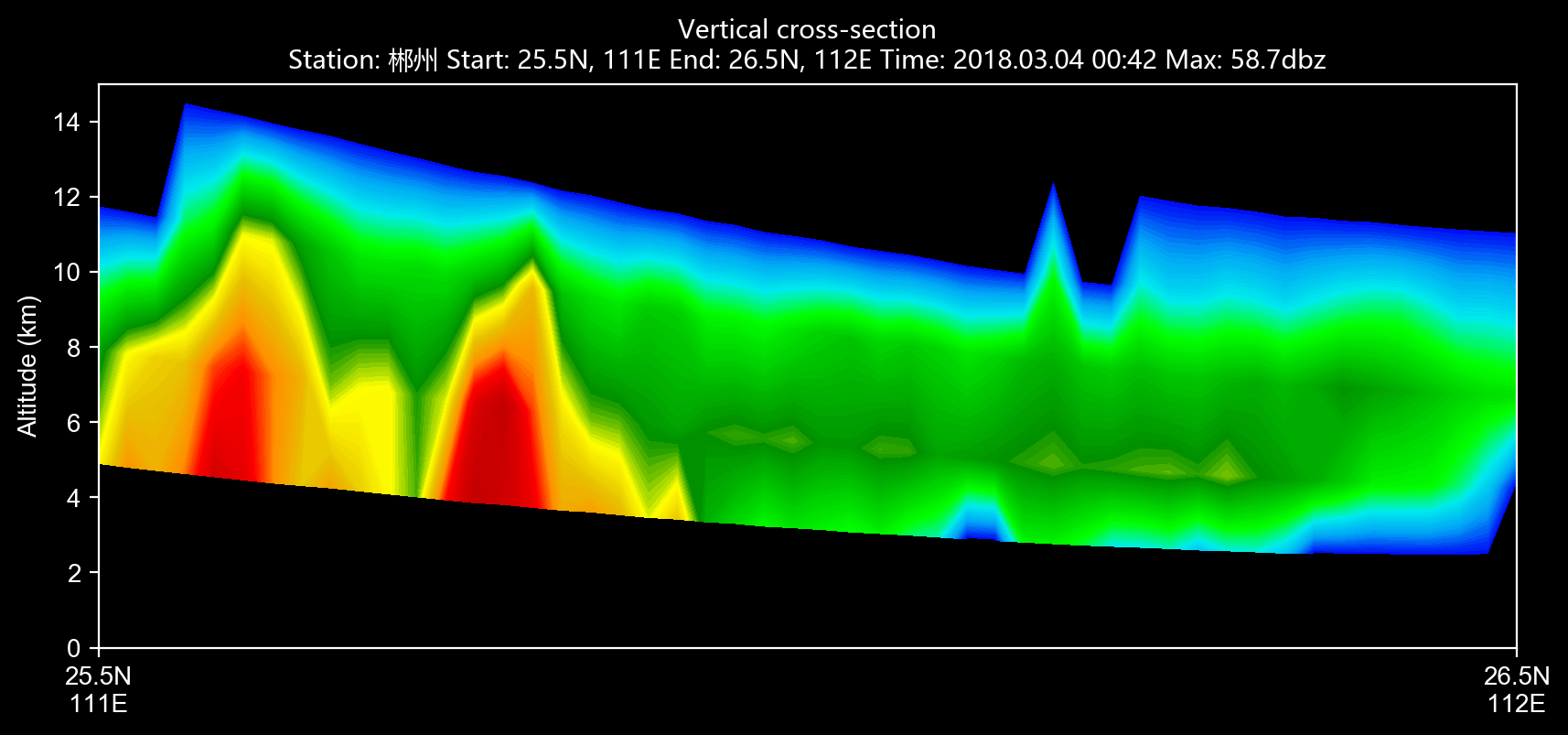
r_list = list(f.iter_tilt(230, 'REF'))cinrad.easycalc.VCS provides calculation of vertical cross-section for all variables.
import cinrad
from cinrad.visualize import Section
f = cinrad.io.CinradReader(your_radar_file)
rl = [f.get_data(i, 230, 'REF') for i in f.angleindex_r]
vcs = cinrad.easycalc.VCS(rl)
sec = vcs.get_section(start_cart=(111, 25.5), end_cart=(112, 26.7)) # pass geographic coordinates (longitude, latitude)
sec = vcs.get_section(start_polar=(115, 350), end_polar=(130, 30)) # pass polar coordinates (distance, azimuth)
fig = Section(sec)
fig('D:\\')cinrad.easycalc.GridMapper can merge different radar scans into a cartesian grid.
This submodule provides algorithms to correct raw radar fields.
This function can unwrap the folded velocity using algorithm originated from pyart. (needs C compiler)
import cinrad
#(some codes omitted)
v = f.get_data(1, 230, 'VEL')
v_corrected = cinrad.correct.dealias(v)Visualize the data stored in acceptable format (cinrad.datastruct). It also means that you can using customized data to construct a object belongs to one of the class in cinrad.datastruct and then perform visualization. For further information about this method, please see the examples contained in example folder.
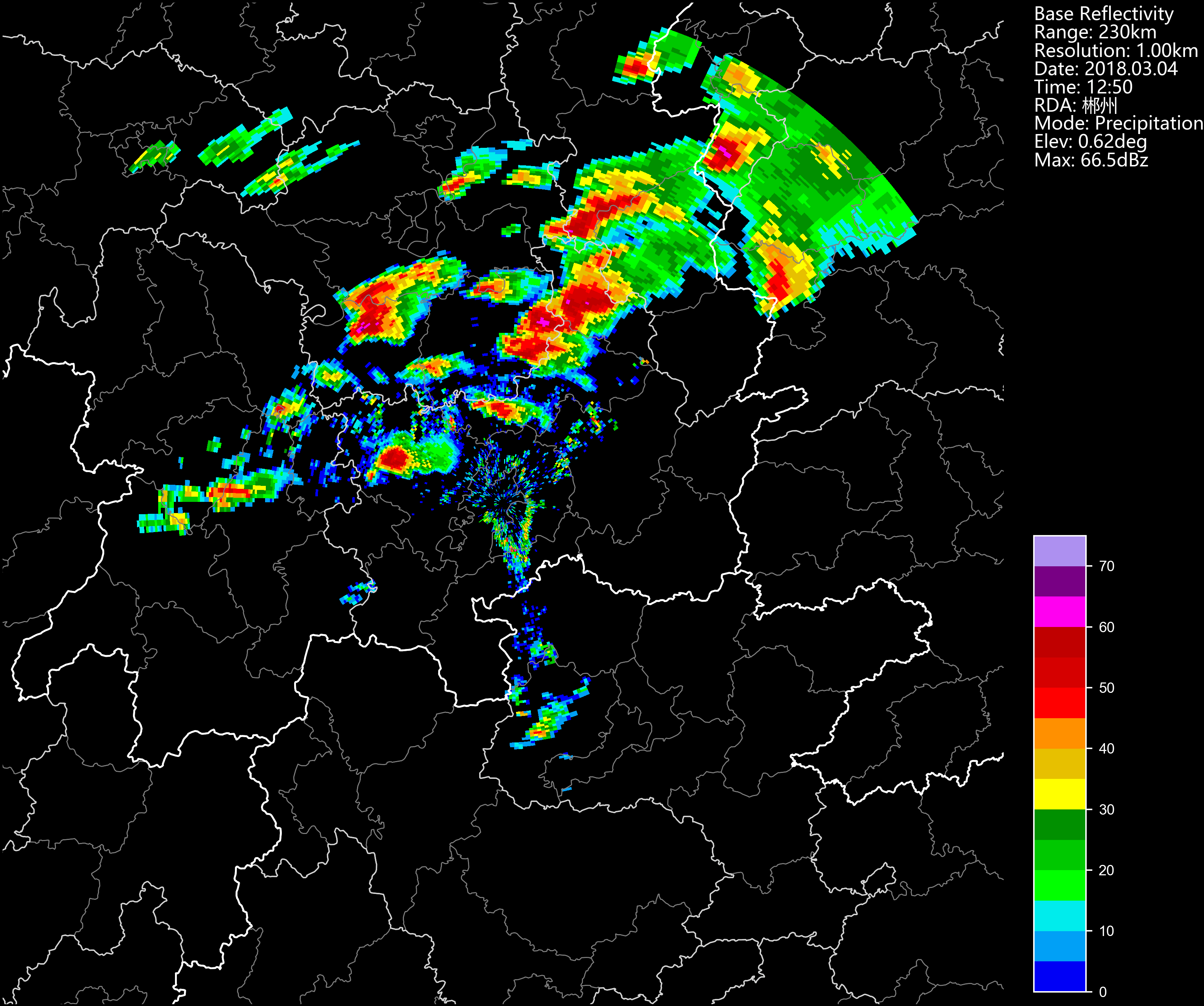
from cinrad.visualize import PPI
fig = PPI(R) #Plot PPI
fig('D:\\') #Pass the path to save the fig
from cinrad.visualize import Section
fig = Section(Slice_) #Plot VCS
fig('D:\\')
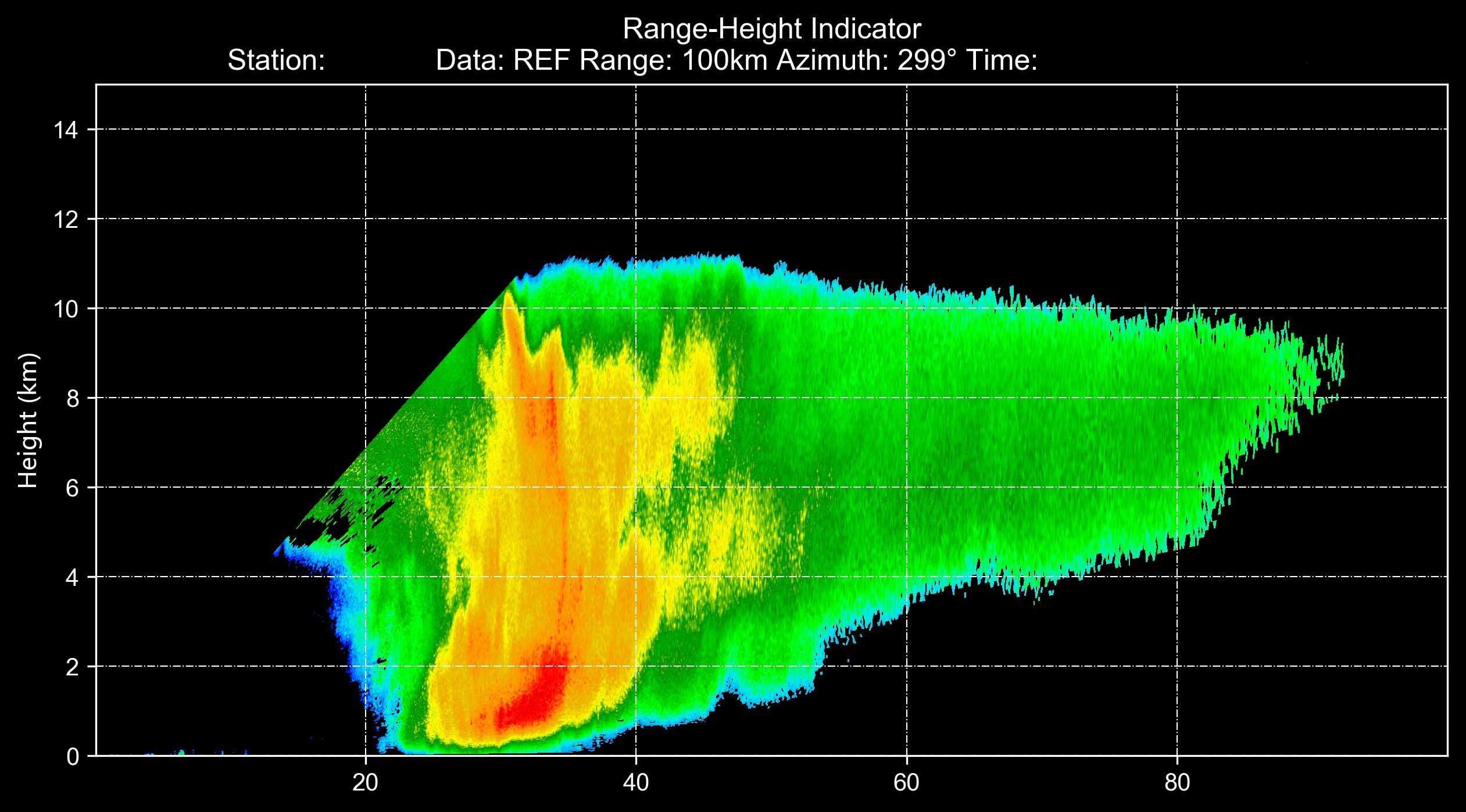
from cinrad.visualize import RHI
fig = RHI(rhi) #Plot data from RHI scan mode
fig('D:\\')The path passed into the class can either be the folder path or the file path. Also, if no path is passed, the figure will be saved at the folder named PyCINRAD in the home folder (e.g. C:\Users\tom).
The summary of args that can be passed into PPI are listed as follows.
| arg | function |
|---|---|
cmap |
colormaps used for plotting |
norm |
norm used for plotting |
nlabel |
number of labels on the colorbar |
label |
labels on the colorbar |
highlight |
highlight area of input name |
dpi |
dpi of figure |
extent |
area to plot e.g. extent=[90, 91, 29, 30] |
section |
cross-section data to ppi plot |
style |
control the background color black or white |
add_city_names |
annotate name of city on the plot |
Beside args, class PPI has some other auxiliary plotting functions.
Plot range rings on the PPI plot.
Plot VCS section under the PPI plot.
This function is very similar to vcs argument of class PPI, but the range of y-axis can be adjusted only by this function.
Plot PUP STI product on the current PPI map, including past positions, current position, and forecast positions.
If you are interested in this program, you can join the developers of this program. Any contribution is appreciated!
If you have questions or advise about this program, you can create a issue or email me at 274555447@qq.com.