Jenetics is an Genetic Algorithm, Evolutionary Algorithm and Genetic Programming library, respectively, written in Java. It is designed with a clear separation of the several concepts of the algorithm, e.g. Gene, Chromosome, Genotype, Phenotype, Population and fitness Function. Jenetics allows you to minimize and maximize the given fitness function without tweaking it. In contrast to other GA implementations, the library uses the concept of an evolution stream (EvolutionStream) for executing the evolution steps. Since the EvolutionStream implements the Java Stream interface, it works smoothly with the rest of the Java Stream API.
Other languages
- Jenetics.Net: Experimental .NET Core port in C# of the base library.
The library is fully documented (javadoc) and comes with an user manual (pdf).
- JRE 8: Java runtime version 8 is needed for using the library, respectively for running the examples.
- JDK 8: The Java JDK 8 must be installed.
- Gradle 4.x: Gradle is used for building the library. (Gradle is download automatically, if you are using the Gradle Wrapper script
./gradlew, located in the base directory, for building the library.)
- TestNG 6.x: Jenetics uses TestNG framework for unit tests.
- Apache Commons Math 3.6: Library is used for testing statistical collectors.
For building the Jenetics library from source, download the most recent, stable package version from Github (or Sourceforge) and extract it to some build directory.
$ unzip jenetics-<version>.zip -d <builddir>
<version> denotes the actual Jenetics version and <builddir> the actual build directory. Alternatively you can check out the master branch from Github.
$ git clone https://github.com/jenetics/jenetics.git <builddir>
Jenetics uses Gradle as build system and organizes the source into sub-projects (modules). Each sub-project is located in it’s own sub-directory:
Published projects
The following projects/modules are also published to Maven.
- jenetics
: This project contains the source code and tests for the Jenetics core-module.
- jenetics.ext
: This module contains additional non-standard GA operations and data types. It also contains classes for solving multi-objective problems (MOEA).
- jenetics.prog
: The modules contains classes which allows to do genetic programming (GP). It seamlessly works with the existing
EvolutionStreamand evolutionEngine. - jenetics.xml
: XML marshalling module for the Jenetics base data structures.
Non-published projects
- jenetics.example: This project contains example code for the core-module.
- jenetics.doc: Contains the code of the web-site and the manual.
- jenetics.tool: This module contains classes used for doing integration testing and algorithmic performance testing. It is also used for creating GA performance measures and creating diagrams from the performance measures.
For building the library change into the <builddir> directory (or one of the module directory) and call one of the available tasks:
- compileJava: Compiles the Jenetics sources and copies the class files to the
<builddir>/<module-dir>/build/classes/maindirectory. - jar: Compiles the sources and creates the JAR files. The artifacts are copied to the
<builddir>/<module-dir>/build/libsdirectory. - javadoc: Generates the API documentation. The Javadoc is stored in the
<builddir>/<module-dir>/build/docsdirectory - test: Compiles and executes the unit tests. The test results are printed onto the console and a test-report, created by TestNG, is written to
<builddir>/<module-dir>directory. - clean: Deletes the
<builddir>/build/*directories and removes all generated artifacts.
For building the library jar from the source call
$ cd <build-dir>
$ ./gradlew jar
The minimum evolution Engine setup needs a genotype factory, Factory<Genotype<?>>, and a fitness Function. The Genotype implements the Factory interface and can therefore be used as prototype for creating the initial Population and for creating new random Genotypes.
import io.jenetics.BitChromosome;
import io.jenetics.BitGene;
import io.jenetics.Genotype;
import io.jenetics.engine.Engine;
import io.jenetics.engine.EvolutionResult;
import io.jenetics.util.Factory;
public class HelloWorld {
// 2.) Definition of the fitness function.
private static Integer eval(Genotype<BitGene> gt) {
return gt.getChromosome()
.as(BitChromosome.class)
.bitCount();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 1.) Define the genotype (factory) suitable
// for the problem.
Factory<Genotype<BitGene>> gtf =
Genotype.of(BitChromosome.of(10, 0.5));
// 3.) Create the execution environment.
Engine<BitGene, Integer> engine = Engine
.builder(HelloWorld::eval, gtf)
.build();
// 4.) Start the execution (evolution) and
// collect the result.
Genotype<BitGene> result = engine.stream()
.limit(100)
.collect(EvolutionResult.toBestGenotype());
System.out.println("Hello World:\n" + result);
}
}In contrast to other GA implementations, the library uses the concept of an evolution stream (EvolutionStream) for executing the evolution steps. Since the EvolutionStream implements the Java Stream interface, it works smoothly with the rest of the Java streaming API. Now let's have a closer look at listing above and discuss this simple program step by step:
-
The probably most challenging part, when setting up a new evolution
Engine, is to transform the problem domain into a appropriateGenotype(factory) representation. In our example we want to count the number of ones of aBitChromosome. Since we are counting only the ones of one chromosome, we are adding only oneBitChromosometo ourGenotype. In general, theGenotypecan be created with 1 to n chromosomes. -
Once this is done, the fitness function which should be maximized, can be defined. Utilizing the new language features introduced in Java 8, we simply write a private static method, which takes the genotype we defined and calculate it's fitness value. If we want to use the optimized bit-counting method,
bitCount(), we have to cast theChromosome<BitGene>class to the actual usedBitChromosomeclass. Since we know for sure that we created the Genotype with aBitChromosome, this can be done safely. A reference to the eval method is then used as fitness function and passed to theEngine.buildmethod. -
In the third step we are creating the evolution
Engine, which is responsible for changing, respectively evolving, a given population. TheEngineis highly configurable and takes parameters for controlling the evolutionary and the computational environment. For changing the evolutionary behavior, you can set different alterers and selectors. By changing the usedExecutorservice, you control the number of threads, the Engine is allowed to use. An newEngineinstance can only be created via its builder, which is created by calling theEngine.buildermethod. -
In the last step, we can create a new
EvolutionStreamfrom ourEngine. TheEvolutionStreamis the model or view of the evolutionary process. It serves as a »process handle« and also allows you, among other things, to control the termination of the evolution. In our example, we simply truncate the stream after 100 generations. If you don't limit the stream, theEvolutionStreamwill not terminate and run forever. Since theEvolutionStreamextends thejava.util.stream.Streaminterface, it integrates smoothly with the rest of the Java Stream API. The final result, the bestGenotypein our example, is then collected with one of the predefined collectors of theEvolutionResultclass.
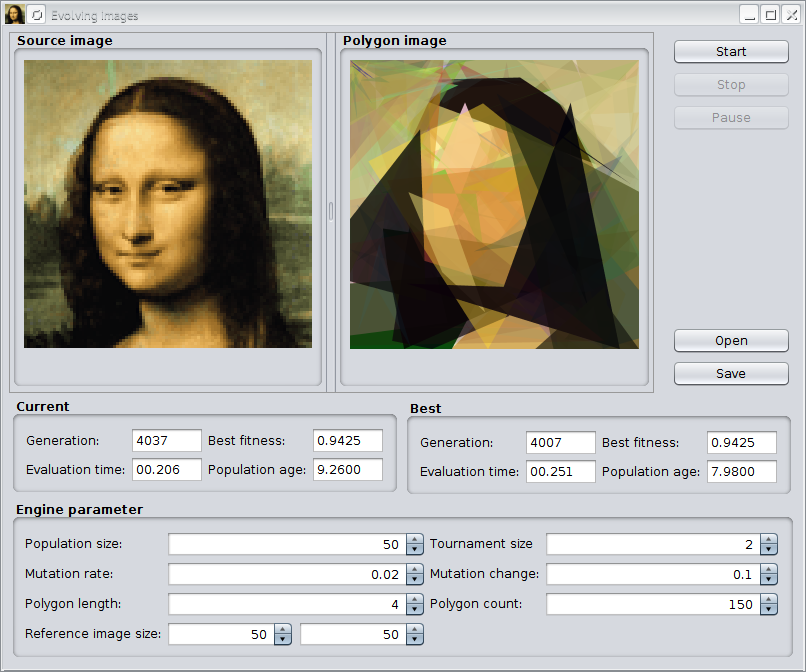
This example tries to approximate a given image by semitransparent polygons. It comes with an Swing UI, where you can immediately start your own experiments. After compiling the sources with
$ ./gradlew compileTestJava
you can start the example by calling
$ ./jrun io.jenetics.example.image.EvolvingImages
The previous image shows the GUI after evolving the default image for about 4,000 generations. With the »Open« button it is possible to load other images for polygonization. The »Save« button allows to store polygonized images in PNG format to disk. At the button of the UI, you can change some of the GA parameters of the example.
- Chartsy|One: Chartsy|One is a Netbeans based tool for stock market investors and traders.
- Chronetic: Chronetic is an open-source time pattern analysis library built to describe time-series data.
- APP4MC: Eclipse APP4MC is a platform for engineering embedded multi- and many-core software systems.
- Stephan Pirnbaum. Die Evolution im Algorithmus - Teil 2: Multikriterielle Optimierung und Architekturerkennung. JavaSPEKTRUM 03/2018, pp 66–69, May 2018.
- W. Geithner, Z. Andelkovic, S. Appel, O. Geithner, F. Herfurth, S. Reimann, G. Vorobjev, F. Wilhelmstötter. Genetic Algorithms for Machine Optimization in the Fair Control System Environment. The 9th International Particle Accelerator Conference (IPAC'18), May 2018.
- Stephan Pirnbaum. Die Evolution im Algorithmus - Teil 1: Grundlagen. JavaSPEKTRUM 01/2018, pp 64–68, Jan. 2018.
- Alexander Felfernig, Rouven Walter, José A. Galindo, David Benavides, Seda Polat Erdeniz, Müslüm Atas, Stefan Reiterer. Anytime diagnosis for reconfiguration. Journal of Intelligent Information Systems, pp 1–22, Jan. 2018.
- Bruce A. Johnson. From Raw Data to Protein Backbone Chemical Shifts Using NMRFx Processing and NMRViewJ Analysis. Protein NMR: Methods and Protocols, pp. 257--310, Springer New York, Nov. 2017.
- Cuadra P., Krawczyk L., Höttger R., Heisig P., Wolff C. Automated Scheduling for Tightly-Coupled Embedded Multi-core Systems Using Hybrid Genetic Algorithms. Information and Software Technologies: 23rd International Conference, ICIST 2017, Druskininkai, Lithuania. Communications in Computer and Information Science, vol 756. Springer, Cham, Sep. 2017.
- Michael Trotter, Guyue Liu, Timothy Wood. Into the Storm: Descrying Optimal Configurations Using Genetic Algorithms and Bayesian Optimization. Foundations and Applications of Self* Systems (FAS*W), 2017 IEEE 2nd International Workshops Sep. 2017.
- Emna Hachicha, Karn Yongsiriwit, Mohamed Sellami. Genetic-Based Configurable Cloud Resource Allocation in QoS-Aware Business Process Development. Information and Software Technologies: 23rd International Conference, ICIST 2017, Druskininkai, Lithuania. Web Services (ICWS), 2017 IEEE International Conference, Jun. 2017.
- Abraão G. Nazário, Fábio R. A. Silva, Raimundo Teive, Leonardo Villa, Antônio Flávio, João Zico, Eire Fragoso, Ederson F. Souza. Automação Domótica Simulada Utilizando Algoritmo Genético Especializado na Redução do Consumo de Energia. Computer on the Beach 2017 pp. 180-189, March 2017.
- Bandaru, S. and Deb, K. Metaheuristic Techniques. Decision Sciences. CRC Press, pp. 693-750, Nov. 2016.
- Lyazid Toumi, Abdelouahab Moussaoui, and Ahmet Ugur. EMeD-Part: An Efficient Methodology for Horizontal Partitioning in Data Warehouses. Proceedings of the International Conference on Intelligent Information Processing, Security and Advanced Communication. Djallel Eddine Boubiche, Faouzi Hidoussi, and Homero Toral Cruz (Eds.). ACM, New York, NY, USA, Article 43, 7 pages, 2015.
- Andreas Holzinger (Editor), Igo Jurisica (Editor). Interactive Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining in Biomedical Informatics. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, Vol. 8401. Springer, 2014.
- Lyazid Toumi, Abdelouahab Moussaoui, Ahmet Ugur. Particle swarm optimization for bitmap join indexes selection problem in data warehouses. The Journal of Supercomputing, Volume 68, Issue 2, pp 672-708, May 2014.
- TANG Yi (Guangzhou Power Supply Bureau Limited, Guangzhou 511400, China) Study on Object-Oriented Reactive Compensation Allocation Optimization Algorithm for Distribution Networks, Oct. 2012.
- John M. Linebarger, Richard J. Detry, Robert J. Glass, Walter E. Beyeler, Arlo L. Ames, Patrick D. Finley, S. Louise Maffitt. Complex Adaptive Systems of Systems Engineering Environment Version 1.0. SAND REPORT, Feb. 2012.
- Introduction to Jenetics Library, by baeldung, April 11. 2017
- How to Solve Tough Problems Using Genetic Algorithms, by Tzofia Shiftan, April 6. 2017
- Genetic algorithms with Java, by William Antônio, January 10. 2017
- Jenetics 설치 및 예제, by JDM, May 8. 2015
- 유전 알고리즘 (Genetic Algorithms), by JDM, April 2. 2015
The library is licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0.
Copyright 2007-2018 Franz Wilhelmstötter
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
You may obtain a copy of the License at
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
limitations under the License.
- #325: Allow customization of fitness evaluation execution for bundling calculations
- #327: Improve CPU utilization during fitness evaluation.
- #335: Seq view wrapper for List and T[] types.