The OpenGL implementation of the paper: Real-Time Geometric Glint Anti-Aliasing with Normal Map Filtering.
Xavier Chermain (ICUBE), Simon LUCAS (ICUBE), Basile Sauvage (ICUBE), Jean-Michel Dishler (ICUBE) and Carsten Dachsbacher (KIT).
Accepted for i3D 2021.
- Compile and build the project (look at the corresponding Section).
cd ./<build_dir>/geometric_glint_aa./geometric_glint_aa <scene>
Arctic: Figure 1Sponza: Figure 10Sphere: Figure 8 and Figure 9Tubes: Figure 7Ogre: Extra
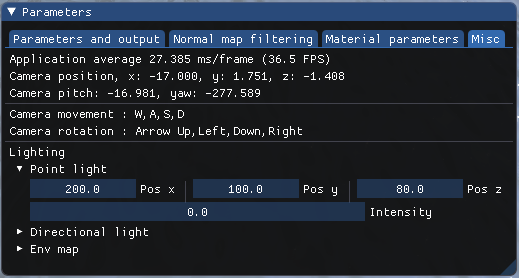
The W, A, S, D and Arrow Up, Left, Down, Right keys control the position and the orientation of the camera.
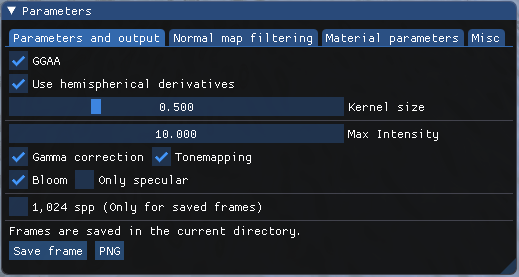
- The GGAA filter can be activated or deactivated and the kernel size can be modified.
- All post-processing effects can be removed independently (bloom, tone mapping, gamma correction).
- Specular from the glinty BRDF can be rendered independently.
- Frames can be saved in
.pngor.exrfile format. - Reference images can be computed if the button
1,024 sppis on. Warning: the supersampling is only done when frames are saved into png or exr files. Generated references can't be seen directly in the application.
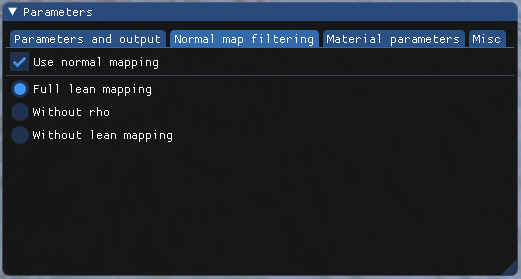
- Normal mapping can be activated or deactivated.
- You can choose to use LEAN mapping or not, as well as using the slope
correlation factor
rhoor not.
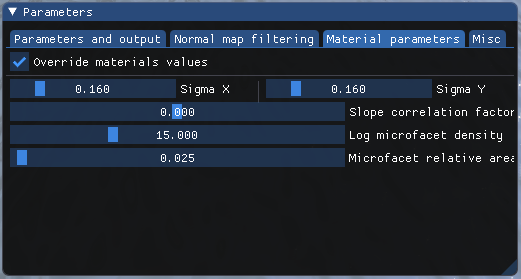
- When the checkbox
Override materials valuesis on, you can override the predefined materials parameters.
- Display frame rate.
- You can modify the lighting here.
- Contribution 1: Geometric Glint Anti-Aliasing (GGAA),
geometric_glint_aa/shader/improved_glint_envmap.frag.glsl - Contribution 2: Slope Correlation Factor,
geometric_glint_aa/shader/improved_glint_envmap.frag.glsl
The files are organized as follows:
geometric_glint_aa: the folder containing the paper code (CPU and GPU side),geometric_glint_aa/shader: folder of the compute, vertex, and fragment shaders (GPU),geometric_glint_aa/scene_obj.*: the API / CPU part, with the loading of the dictionary in an array texture.
media: the data.media/dictionary: the dictionary used by Chermain et al. 2020,media/snow: the custom scene of an Arctic landscape (with a snowman behind the camera),media/sponza: Sponza,media/sphere: the mesh and material of a sphere,media/silver-snowflake-ornament: Silver Snowflake Ornament,media/ogre: Jerry the Ogre.
opengl: The files of the OpenGL framework.
The OpenGL framework is based on [OpenGL 4 Cookbook] (https://github.com/PacktPublishing/OpenGL-4-Shading-Language-Cookbook-Third-Edition) and learnopengl.com.
The libraries used in this project are:
If you modify the glsl code, don't forget to re-run cmake.
Requirements. Based on readme.md of OpenGL 4 Cookbook.
To compile this example, you'll need the following:
- The GLM Mathematics Library version 0.9.6 or later. Note that versions
prior to 0.9.6 may not work properly because of a switch from degrees to
radians. GLM 0.9.5 will work, but you'll need to add
#define GLM_FORCE_RADIANSprior to including the glm header files. - GLFW version 3.0 or later.
- ASSIMP version 5.0 or later.
The example code builds with CMake.
- Install GLFW by following the instructions on their web site.
- Install the latest version of GLM. Note that for CMake to find GLM
correctly, you need to run the install "build" (e.g.
make install) or install GLM from your favorite package manager. Otherwise, the CMake config files will not be created/available. - Install the latest version of ASSIMP.
- Download this example code, or clone using git.
- Run cmake. If cmake has difficulties finding the GLFW or GLM installations,
set the variable
CMAKE_PREFIX_PATHto help cmake find them.
It can be tricky to get CMake to find the GLM libraries, unfortunately. See below for tips. - Compile by running
make.
When searching for GLM, CMake looks for the files glmConfig.cmake and glmConfigVersion.cmake.
If you install GLM using a package manager such as Homebrew on macOS, or a Linux package manager the cmake files should already be included.
Otherwise, if you're using the GLM source distribution, you'll have to run GLM through CMake to get it to
generate the glmConfig.cmake and glmConfigVersion.cmake files.
- Download GLM and extract it to some location:
GLM_SRC cd $GLM_SRCmkdir buildcd buildcmake -D GLM_TEST_ENABLE=OFF -D CMAKE_INSTALL_PREFIX=MY_GLM_LOCATION ..cmake --build . --target install
Replace GLM_SRC above with the place where you extracted the GLM zip file, and replace MY_GLM_LOCATION
with the location where you want to install GLM. This should generate the needed cmake files and install
all of GLM to MY_GLM_LOCATION.
- Use the Visual Studio target in CMake:
-G "Visual Studio...", open the Visual Studio solution. - The example code requires a command line argument to choose a scene. When running in VS, be sure to set the 'Command Argument' under 'Properties' for the appropriate scene.
Best solution for Windows + Visual Studio User. From Allen.
Windows doesn't own a unified folder (/usr/local/lib) to search library. Microsoft provides vcpkg for package management to speed up the development process.
- Install vcpkg (Follow the vcpkg installation instructions vcpkg document) You can instance a new powershell console and type
git clone https://github.com/Microsoft/vcpkg.git
cd vcpkg
PS> .\bootstrap-vcpkg.bat
- Install GLM, GLFW and ASSIMP via vcpkg.
x64 version:
vcpkg.exe install glfw3:x64-windows
vcpkg.exe install glm:x64-windows
vcpkg.exe install assimp:x64-windows
x86 version:
vcpkg.exe install glfw3
vcpkg.exe install glm
vcpkg.exe install assimp
- Add VCPKG Toolchain
-DCMAKE_TOOLCHAIN_FILE=C:/vcpkg/scripts/buildsystems/vcpkg.cmake
Replace
C:/vcpkg/scripts/buildsystems/vcpkg.cmakewith your VCPKG root. After this, CMake could find GLM, GLFW3 and ASSIMP automatically.
Use HomeBrew for dependencies (and cmake).
Tested on MacBookPro 2020 with AMD Radeon Pro 5500M.
An OpenGL header file and a function loader for a 4.5 core profile are included with this project. They were generated using GLAD. This loader should also work on MacOS under a 4.1 core profile, but of course not all functions will load.
- Windows 10,
- Linux,
- Mac OS/X,