A tool to find and manage duplicate files.
Spice will recursively traverse the directory that the user provides and will calculate an MD5 hash for each file that it encounters. It will store the hash in a special tree structure, where each character of a hash is a child node, with the absolute file paths as leaves. If a node has multiple children that are leaves, a duplicate file was found.
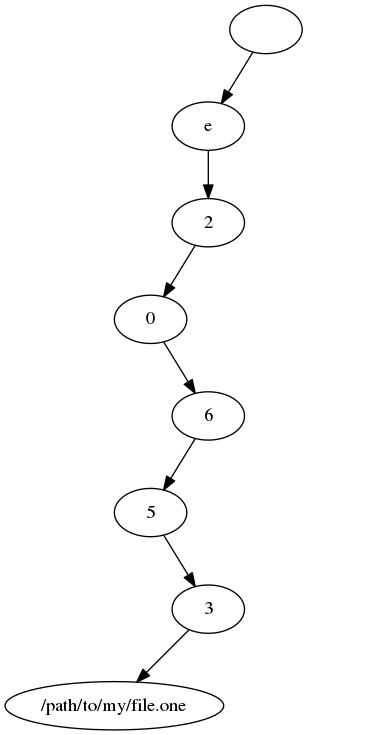
Consider the following example: the first file found is "/path/to/my/file.one" with the corresponding hash value
e20653
(This hash value was chosen as an arbitrary example and is obviously not a proper MD5 hash, as it is way to short.)
The tree that is constructed from this first file/hash pair would look like this:
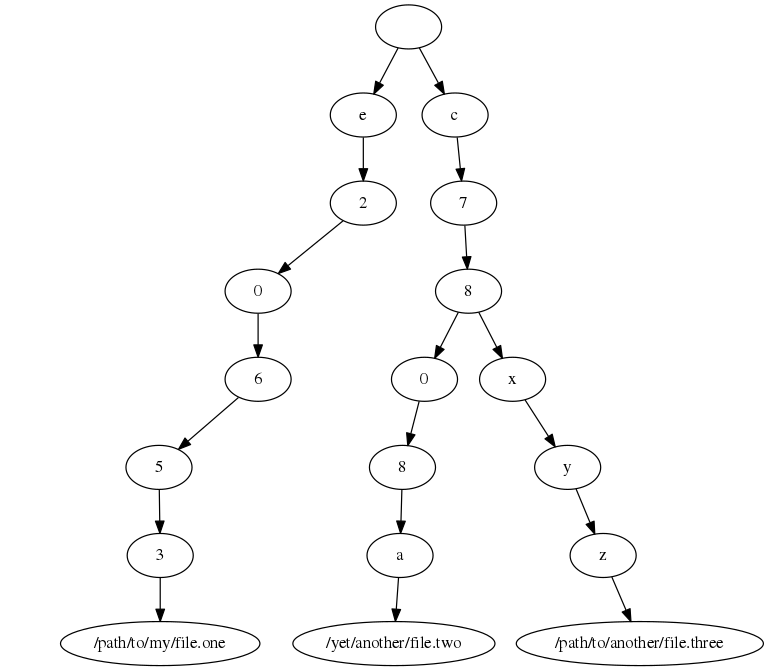
Now a second file, "/yet/another/file.two", with the corresponding hash value
c7808a
and a third file, "/path/to/another/file.three", with the hash value
c78xyz
are found and added. The tree then will look like this:
At this point, no duplicates have been found yet.
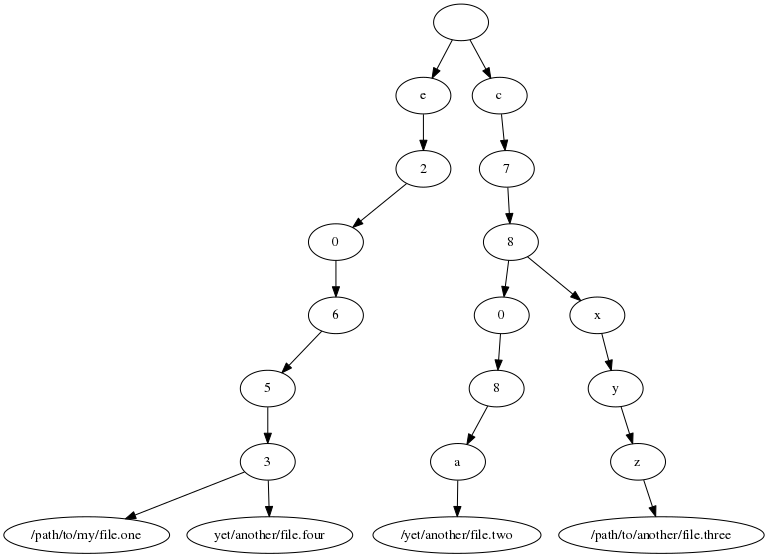
Now the next file Spice encounters, "yet/another/file.four", is a duplicate of the first file we had found before, it also has the hash value
e20653
After inserting it, the tree will now contain a node that has two leaves as children:
Traversing the directory structure and building the tree is done in O(n log n). When Spice has finished its traversal, it will simply identify all those nodes with more than one leaf as child, which is also done in O(n log n).
Install OPAM, the OCaml compiler, and GNU m4. Then initialise OPAM. On Debian run:
# apt-get install opam ocaml m4
$ opam init
$ eval $(opam config env)Then install Jane Street's Dune, Core, and expectation-test libraries via OPAM by running:
$ opam install dune core ppx_expectClone or download this repository, and build by running
$ bash build.sh