This project aims to provide observability for the Oracle Database so that users can understand performance and diagnose issues easily across applications and database. Over time, this project will provide not just metrics, but also logging and tracing support, and integration into popular frameworks like Spring Boot. The project aims to deliver functionality to support both cloud and on-premises databases, including those running in Kubernetes and containers.
From the first production release, v1.0, onwards, this project provides a Prometheus exporter for Oracle Database that is based in part on a Prometheus exporter created by Seth Miller with changes to comply with various Oracle standards and policies.
Contributions are welcome - please see contributing.
- Release Notes
- Roadmap
- Standard metrics
- Database permissions required
- Installation
- Custom metrics
- Controlling memory usage
- Grafana dashboards
- Monitoring Transactional Event Queues
- Developer notes
This release includes the following changes:
- Introduced a new feature to periodically restart the process if requested.
- Introduced a new feature to periodically attempt to free OS memory if requested.
- Updated some third-party dependencies.
This release just updates some third-party dependencies.
This release includes the following changes:
- The query for the standard metric
wait_classhas been updated so that it will work in both container databases and pluggable databases, including in Oracle Autonomous Database instances. Note that this query will not return any data unless the database instance is under load. - Support for reading the database password from OCI Vault has been added (see details)
- Log messages have been improved
- Some dependencies have been updated
The first production release, v1.0, includes the following features:
- A number of standard metrics are exposed,
- Users can define custom metrics,
- Oracle regularly reviews third-party licenses and scans the code and images, including transitive/recursive dependencies for issues,
- Connection to Oracle can be a basic connection or use an Oracle Wallet and TLS - connection to Oracle Autonomous Database is supported,
- Metrics for Oracle Transactional Event Queues are also supported,
- A Grafana dashboard is provided for Transacational Event Queues, and
- A pre-built container image is provided, based on Oracle Linux, and optimized for size and security.
Note that this exporter uses a different Oracle Database driver which in turn uses code directly written by Oracle to access the database. This driver does require an Oracle client. In this initial release, the client is bundled into the container image, however we intend to make that optional in order to minimize the image size.
The interfaces for this version have been kept as close as possible to those of earlier alpha releases in this repository to assist with migration. However, it should be expected that there may be breaking changes in future releases.
We always welcome input on features you would like to see supported. Please open an issue in this repository with your suggestions.
Currently, we plan to address the following key features:
- Implement multiple database support - allow the exporter to publish metrics for multiple database instances,
- Implement connection storm protection - prevent the exporter from repeatedly connecting when the credentials fail, to prevent a storm of connections causing accounts to be locked across a large number of databases,
- Provide the option to have the Oracle client outside of the container image, e.g., on a shared volume,
- Implement the ability to update the configuration dynamically, i.e., without a restart,
- Implement support for exporting logs, including audit logs for example, from the database,
- Implement support for tracing within the database, e.g., using an execution context ID provide by an external caller,
- Provide additional pre-built Grafana dashboards,
- Integration with Spring Observability, e.g., Micrometer,
- Provide additional documentation and samples, and
- Integrate with the Oracle Database Operator for Kubernetes.
The following metrics are exposed currently.
- oracledb_exporter_last_scrape_duration_seconds
- oracledb_exporter_last_scrape_error
- oracledb_exporter_scrapes_total
- oracledb_up
- oracledb_activity_execute_count
- oracledb_activity_parse_count_total
- oracledb_activity_user_commits
- oracledb_activity_user_rollbacks
- oracledb_sessions_activity
- oracledb_wait_time_application
- oracledb_wait_time_commit
- oracledb_wait_time_concurrency
- oracledb_wait_time_configuration
- oracledb_wait_time_network
- oracledb_wait_time_other
- oracledb_wait_time_scheduler
- oracledb_wait_time_system_io
- oracledb_wait_time_user_io
- oracledb_tablespace_bytes
- oracledb_tablespace_max_bytes
- oracledb_tablespace_free
- oracledb_tablespace_used_percent
- oracledb_process_count
- oracledb_resource_current_utilization
- oracledb_resource_limit_value
For the built-in default metrics, the database user that the exporter uses to connect to the Oracle Database instance must have the SELECT_CATALOG_ROLE privilege and/or SELECT permission on the following tables.
- dba_tablespace_usage_metrics
- dba_tablespaces
- v$system_wait_class
- v$asm_diskgroup_stat
- v$datafile
- v$sysstat
- v$process
- v$waitclassmetric
- v$session
- v$resource_limit
There are a number of ways to run the exporter. In this section you will find information on running the exporter:
- In a container runtime like Docker, Podman, etc
- In a test/demo environment using Docker Compose
- In Kubernetes
- As a standalone binary
You can run the exporter in a local container using a conatiner image from Oracle Container Registry. The container image is available in the "observability-exporter" repository in the "Database" category. No authentication or license presentment/acceptance are required to pull this image from the registry.
If you need an Oracle Database to test the exporter, you can use this command to start up an instance of Oracle Database 23c Free which also requires no authentication or license presentment/acceptance to pull the image.
docker run --name free23c \
-d \
-p 1521:1521 \
-e ORACLE_PWD=Welcome12345 \
container-registry.oracle.com/database/free:latestThis will pull the image and start up the database with a listener on port 1521. It will also create a pluggable database (a database container) called "FREEPDB1" and will set the admin passwords to the password you specified on this command.
You can tail the logs to see when the database is ready to use:
docker logs -f free23c
(look for this message...)
#########################
DATABASE IS READY TO USE!
#########################To obtain the IP address of the container, which you will need to connect to the database, use this command. Note: depending on your platform and container runtime, you may be able to access the database at "localhost":
docker inspect free23c | grep IPA
"SecondaryIPAddresses": null,
"IPAddress": "172.17.0.2",
"IPAMConfig": null,
"IPAddress": "172.17.0.2",You need to give the exporter the connection details for the Oracle Database that you want it to run against. You can use a simple connection, or a wallet.
For a simple connection, you will provide the details using these variables:
DB_USERNAMEis the database username, e.g.,pdbadminDB_PASSWORDis the password for that user, e.g.,Welcome12345DB_CONNECT_STRINGis the connection string, e.g.,free23c:1521/freepdb
To run the exporter in a container and expose the port, use a command like this, with the appropriate values for the environment variables:
docker run -it --rm \
-e DB_USERNAME=pdbadmin \
-e DB_PASSWORD=Welcome12345 \
-e DB_CONNECT_STRING=free23c:1521/freepdb \
-p 9161:9161 \
container-registry.oracle.com/database/observability-exporter:1.2.0For a wallet connection, you must first set up the wallet. If you are using Oracle Autonomous Database, for example, you can download the wallet from the Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI) console.
- Unzip the wallet into a new directory, e.g., called
wallet. - Edit the
sqlnet.orafile and set theDIRECTORYto/wallet. This is the path inside the exporter container where you will provide the wallet. - Take a note of the TNS name from the
tnsnames.orathat will be used to connect to the database, e.g.,devdb_tp.
Now, you provide the connection details using these variables:
DB_USERNAMEis the database username, e.g.,pdbadminDB_PASSWORDis the password for that user, e.g.,Welcome12345DB_CONNECT_STRINGis the connection string, e.g.,devdb_tp?TNS_ADMIN=/walletORACLE_HOMEis the location of the Oracle Instant Client, i.e.,/lib/oracle/21/client64/lib. If you built your own container image, the path may be different.
To run the exporter in a container and expose the port, use a command like this, with the appropriate values for the environment variables, and mounting your wallet directory as /wallet in the container to provide access to the wallet:
docker run -it --rm \
-e DB_USERNAME=pdbadmin \
-e DB_PASSWORD=Welcome12345 \
-e DB_CONNECT_STRING=devdb_tp \
-v ./wallet:/wallet \
-p 9161:9161 \
container-registry.oracle.com/database/observability-exporter:1.2.0If you would like to set up a test environment with the exporter, you can use the provided "Docker Compose" file in this repository which will start an Oracle Database instance, the exporter, Prometheus and Grafana.
cd docker-compose
docker-compose up -dThe containers will take a short time to start. The first time, the Oracle container might take a few minutes to start while it creates the database instance, but this is a one-time operation, and subequent restarts will be much faster (a few seconds).
Once the containers are all running, you can access the services using these URLs:
- Exporter
- Prometheus - try a query for "oracle".
- Grafana - username is "admin" and password is "grafana". An Oracle Database dashboard is provisioned and configured to use data from the exporter.
To run the exporter in Kubernetes, you need to complete the following steps. All steps must be completed in the same Kunernetes namespace. The examples below assume you want to use a namespace called exporter, you must change the commands if you wish to use a different namespace.
Create a secret with the Oracle database user and password that the exporter should use to connect to the database using this command. You must specify the correct user and password for your environment. This example uses pdbadmin as the user and Welcome12345 as the password:
kubectl create secret generic db-secret \
--from-literal=username=pdbadmin \
--from-literal=password=Welcome12345 \
-n exporterCreate a config map with the wallet (if you are using one) using this command. Run this command in the wallet directory you created earlier.
kubectl create cm db-metrics-tns-admin \
--from-file=cwallet.sso \
--from-file=ewallet.p12 \
--from-file=ewallet.pem \
--from-file=keystore.jks \
--from-file=ojdbc.properties \
--from-file=sqlnet.ora \
--from-file=tnsnames.ora \
--from-file=truststore.jks \
-n exporterIf you have defined any custom metrics, you must create a config map for the metrics definition file. For example, if you created a configuration file called txeventq-metrics.toml, then create the config map with this command:
kubectl create cm db-metrics-txeventq-exporter-config \
--from-file=txeventq-metrics.toml \
-n exporterA sample Kubernetes manifest is provided here. You must edit this file to set the namespace you wish to use, the database connect string to use, and if you have any custom metrics, you will need to uncomment and customize some sections in this file.
Once you have made the necessary updates, apply the file to your cluster using this command:
kubectl apply -f metrics-exporter-deployment.yamlYou can check the deployment was successful and monitor the exporter startup with this command:
kubectl get pods -n exporter -wYou can view the exporter's logs with this command:
kubectl logs -f svc/metrics-exporter -n exporterCreate a Kubernetes service to allow access to the exporter pod(s). A sample Kubernetes manifest is provided here. You may need to customize this file to update the namespace.
Once you have made any necessary udpates, apply the file to your cluster using this command:
kubectl aspply -f metrics-exporter-service.yamlCreate a Kubernetes service monitor to tell Prometheus (for example) to collect metrics from the exporter. A sample Kubernetes manifest is provided here. You may need to customize this file to update the namespace.
Once you have made any necessary udpates, apply the file to your cluster using this command:
kubectl aspply -f metrics-service-monitor.yamlYou may need to update your Prometheus configuration to add a target. If so, you can use this example job definition as a guide:
- job_name: 'oracle-exporter'
metrics_path: '/metrics'
scrape_interval: 15s
scrape_timeout: 10s
static_configs:
- targets:
- metrics-exporter.exporter.svc.cluster.local:9161See Grafana dashboards below.
Pre-compiled versions for Linux 64 bit can be found under releases.
In order to run, you'll need the Oracle Instant Client Basic for your operating system. Only the basic version is required for execution.
The following command line arguments (flags) can be passed to the exporter:
Usage of oracledb_exporter:
--log.format value
If set use a syslog logger or JSON logging. Example: logger:syslog?appname=bob&local=7 or logger:stdout?json=true. Defaults to stderr.
--log.level value
Only log messages with the given severity or above. Valid levels: [debug, info, warn, error, fatal].
--custom.metrics string
File that may contain various custom metrics in a TOML file.
--default.metrics string
Default TOML file metrics.
--web.systemd-socket
Use systemd socket activation listeners instead of port listeners (Linux only).
--web.listen-address string
Address to listen on for web interface and telemetry. (default ":9161")
--web.telemetry-path string
Path under which to expose metrics. (default "/metrics")
--database.maxIdleConns string
Number of maximum idle connections in the connection pool. (default "0")
--database.maxOpenConns string
Number of maximum open connections in the connection pool. (default "10")
--web.config.file
Path to configuration file that can enable TLS or authentication.The exporter will read the password from a secret stored in OCI Vault if you set these two environment variables:
VAULT_IDshould be set to the OCID of the OCI vault that you wish to useVAULT_SECRET_NAMEshould be set to the name of the secret in the OCI vault which contains the database password
The exporter allows definition of arbitrary custom metrics in a TOML file. To specify this file to the exporter, you can:
- Use
--custom.metricsflag followed by the name of the TOML file, or - Export
CUSTOM_METRICSvariable environment (export CUSTOM_METRICS=my-custom-metrics.toml)
This file must contain the following elements:
- One or several metric sections (
[[metric]]) - For each section: a context, a request and a map between the field(s) in the request and comment(s).
Here's a simple example:
[[metric]]
context = "test"
request = "SELECT 1 as value_1, 2 as value_2 FROM DUAL"
metricsdesc = { value_1 = "Simple example returning always 1.", value_2 = "Same but returning always 2." }
NOTE: Do not add a semicolon (
;) at the end of the SQL queries.
This file produce the following entries in the exporter:
# HELP oracledb_test_value_1 Simple example returning always 1.
# TYPE oracledb_test_value_1 gauge
oracledb_test_value_1 1
# HELP oracledb_test_value_2 Same but returning always 2.
# TYPE oracledb_test_value_2 gauge
oracledb_test_value_2 2
You can also provide labels using labels field. Here's an example providing two metrics, with and without labels:
[[metric]]
context = "context_no_label"
request = "SELECT 1 as value_1, 2 as value_2 FROM DUAL"
metricsdesc = { value_1 = "Simple example returning always 1.", value_2 = "Same but returning always 2." }
[[metric]]
context = "context_with_labels"
labels = [ "label_1", "label_2" ]
request = "SELECT 1 as value_1, 2 as value_2, 'First label' as label_1, 'Second label' as label_2 FROM DUAL"
metricsdesc = { value_1 = "Simple example returning always 1.", value_2 = "Same but returning always 2." }
This TOML file produces the following result:
# HELP oracledb_context_no_label_value_1 Simple example returning always 1.
# TYPE oracledb_context_no_label_value_1 gauge
oracledb_context_no_label_value_1 1
# HELP oracledb_context_no_label_value_2 Same but returning always 2.
# TYPE oracledb_context_no_label_value_2 gauge
oracledb_context_no_label_value_2 2
# HELP oracledb_context_with_labels_value_1 Simple example returning always 1.
# TYPE oracledb_context_with_labels_value_1 gauge
oracledb_context_with_labels_value_1{label_1="First label",label_2="Second label"} 1
# HELP oracledb_context_with_labels_value_2 Same but returning always 2.
# TYPE oracledb_context_with_labels_value_2 gauge
oracledb_context_with_labels_value_2{label_1="First label",label_2="Second label"} 2
Last, you can set metric type using metricstype field.
[[metric]]
context = "context_with_labels"
labels = [ "label_1", "label_2" ]
request = "SELECT 1 as value_1, 2 as value_2, 'First label' as label_1, 'Second label' as label_2 FROM DUAL"
metricsdesc = { value_1 = "Simple example returning always 1 as counter.", value_2 = "Same but returning always 2 as gauge." }
# Can be counter or gauge (default)
metricstype = { value_1 = "counter" }
This TOML file will produce the following result:
# HELP oracledb_test_value_1 Simple test example returning always 1 as counter.
# TYPE oracledb_test_value_1 counter
oracledb_test_value_1 1
# HELP oracledb_test_value_2 Same test but returning always 2 as gauge.
# TYPE oracledb_test_value_2 gauge
oracledb_test_value_2 2
You can find working examples of custom metrics for slow queries, big queries and top 100 tables. An exmaple of custom metrics for Transacational Event Queues is also provided.
If you run the exporter as a container image and want to include your custom metrics in the image itself, you can use the following example Dockerfile to create a new image:
FROM container-registry.oracle.com/database/observability-exporter:1.2.0
COPY custom-metrics.toml /
ENTRYPOINT ["/oracledb_exporter", "--custom.metrics", "/custom-metrics.toml"]If you are running in an environment with limited memory, or you are running a large number of exporters, you may want to control the exporter's usage of memory.
Under normal circumstances, the exporter process will retain OS memory that was used by the Go garbage collector but is no longer needed, in case it may be needed again in the future, unless the host OS is under memory pressure. The result of this behavior (which is the normal behavior of the Go runtime) is that the resident set size will not decrease until the host OS memory is almost all used. Under most circumstances, this will not cause any issues, but if you are in an environment where you need to conserve memory, the following options are provided:
- You may set the
FREE_INTERVALenvironment variable to a Go duration string, e.g.,60sand run the exporter in debug mode by setting theGODEBUGenvironment variable to a value includingmadvdontneed=1, e.g.,GODEBUG=gctrace=1,madvdontneed=1. The exporter will call the FreeOSMemory() at the specified interval. This tells the Go runtime to attempt to release memory which is no longer needed. Please note that this does not guarantee that the memory will be released to the OS, but over time you should see the RSS shrink sooner than without these settings. - You may set the
RESTART_INTERVALenvironment variable to a Go duration string, e.g.,10m. The exporter will restart its own process at the specified iterval (by calling the OSexecsyscall). As no new process is created, the process identifier (PID) does not change, but the machine code, data, heap, and stack of the process are replaced by those of the new program (source: Wikipedia). This has the side effect of freeing the resident set, so that it will return to its original size. - In addition to these, you may also set
GOMAXPROCS,GOGC, andGOMEMLIMIT(see documentation) to further limit the amount of resources that the Go runtime may use.
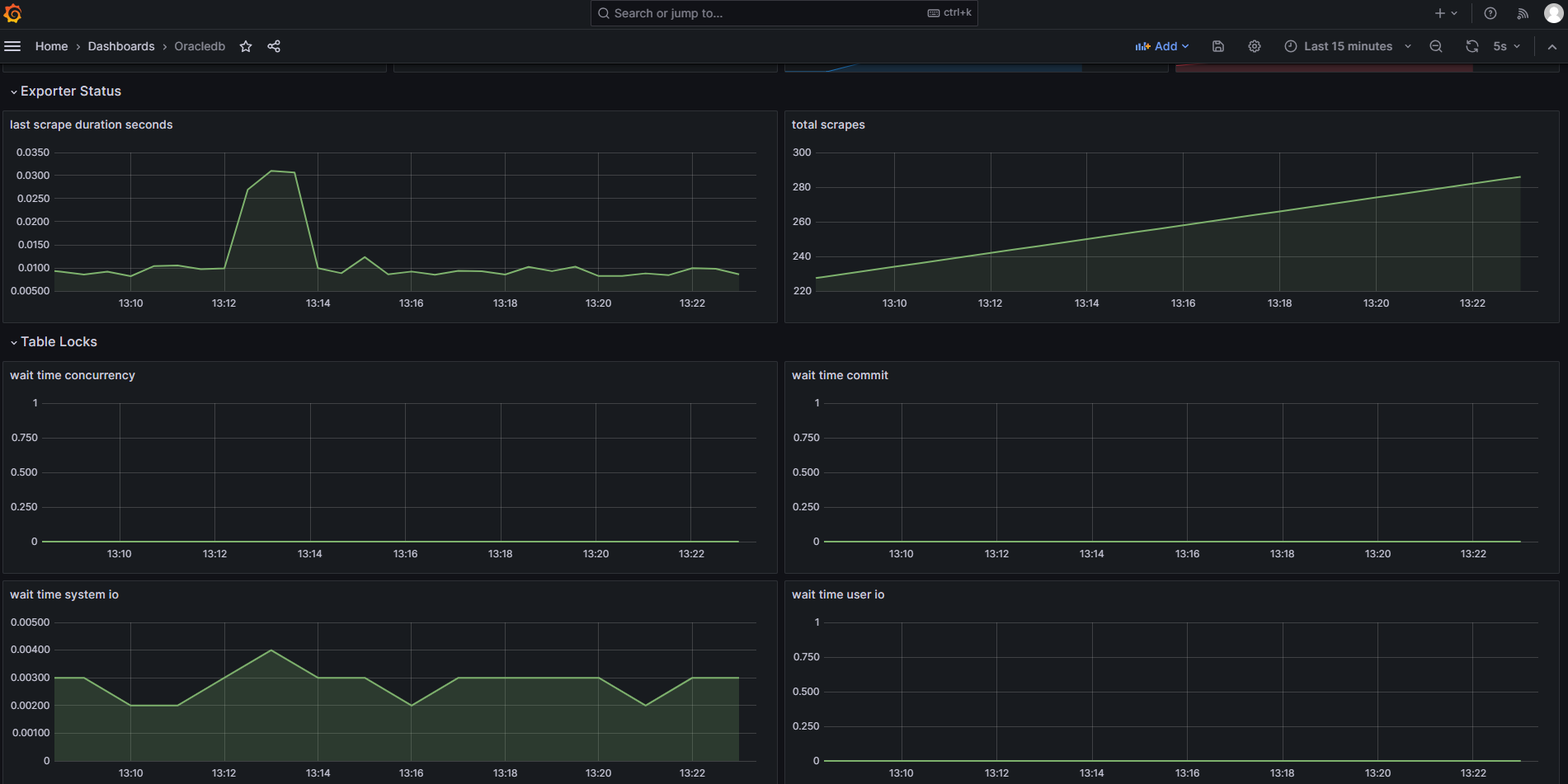
A sample Grafana dashboard definition is provided in this directory. You can import this into your Grafana instance, and set it to use the Prometheus datasource that you have defined for the Prometheus instance that is collecting metrics from the exporter.
The dashboard shows some basic information, as shown below:
Oracle Transactional Event Queues ("TxEventQ") is a fault-tolerant, scalable, real-time messaging backbone offered by converged Oracle Database that allows you to build an enterprise-class event-driven architectures.
Access to the real-time broker, producer, and consumer metrics in a single dashboard and receiving alerts for issues allows teams to understand the state of their system.
The exporter includes a set of metrics for monitoring TxEventQ and a pre-built Grafana dashboard.
Note: The metrics are written for Oracle Database 21c or later.
If you need to create a topic to monitor, you can use these statements to create and start a topic, and create a subscriber:
declare
subscriber sys.aq$_agent;
begin
-- create the topic
dbms_aqadm.create_transactional_event_queue(
queue_name => 'my_topic',
multiple_consumers => true -- true makes a pub/sub topic
);
-- start the topic
dbms_aqadm.start_queue(
queue_name => 'my_topic'
);
-- create a subscriber
dbms_aqadm.add_subscriber(
queue_name => 'my_teq',
subscriber => sys.aq$_agent(
'my_subscriber', -- the subscriber name
null, -- address, only used for notifications
0 -- protocol
),
rule => 'correlation = ''my_subscriber'''
);
end;You can produce a message with these commands:
declare
enqueue_options dbms_aq.enqueue_options_t;
message_properties dbms_aq.message_properties_t;
message_handle raw(16);
message SYS.AQ$_JMS_TEXT_MESSAGE;
begin
-- create the message payload
message := SYS.AQ$_JMS_TEXT_MESSAGE.construct;
message.set_text('{"orderid": 12345, "username": "Jessica Smith"}');
-- set the consumer name
message_properties.correlation := 'my_subscriber';
-- enqueue the message
dbms_aq.enqueue(
queue_name => 'my_topic',
enqueue_options => enqueue_options,
message_properties => message_properties,
payload => message,
msgid => message_handle);
-- commit the transaction
commit;
end;The metrics definitions are provided in this file. You need to provide this file to the exporter, e.g., by adding it to your container image, or creating a Kubernetes config map containing the file and mounting that config map as a volume in your deployment. You also need to set the CUSTOM_METRICS environment variable to the location of this file.
The database user that the exporter uses to connect to the database will also need additional permissions, which can be granted with these statements. This example assumes the exporter connects with the username "exporter":
grant execute on dbms_aq to exporter;
grant execute on dbms_aqadm to exporter;
grant execute on dbms_aqin to exporter;
grant execute on dbms_aqjms_internal to exporter;
grant execute on dbms_teqk to exporter;
grant execute on DBMS_RESOURCE_MANAGER to exporter;
grant select_catalog_role to exporter;
grant select on sys.aq$_queue_shards to exporter;
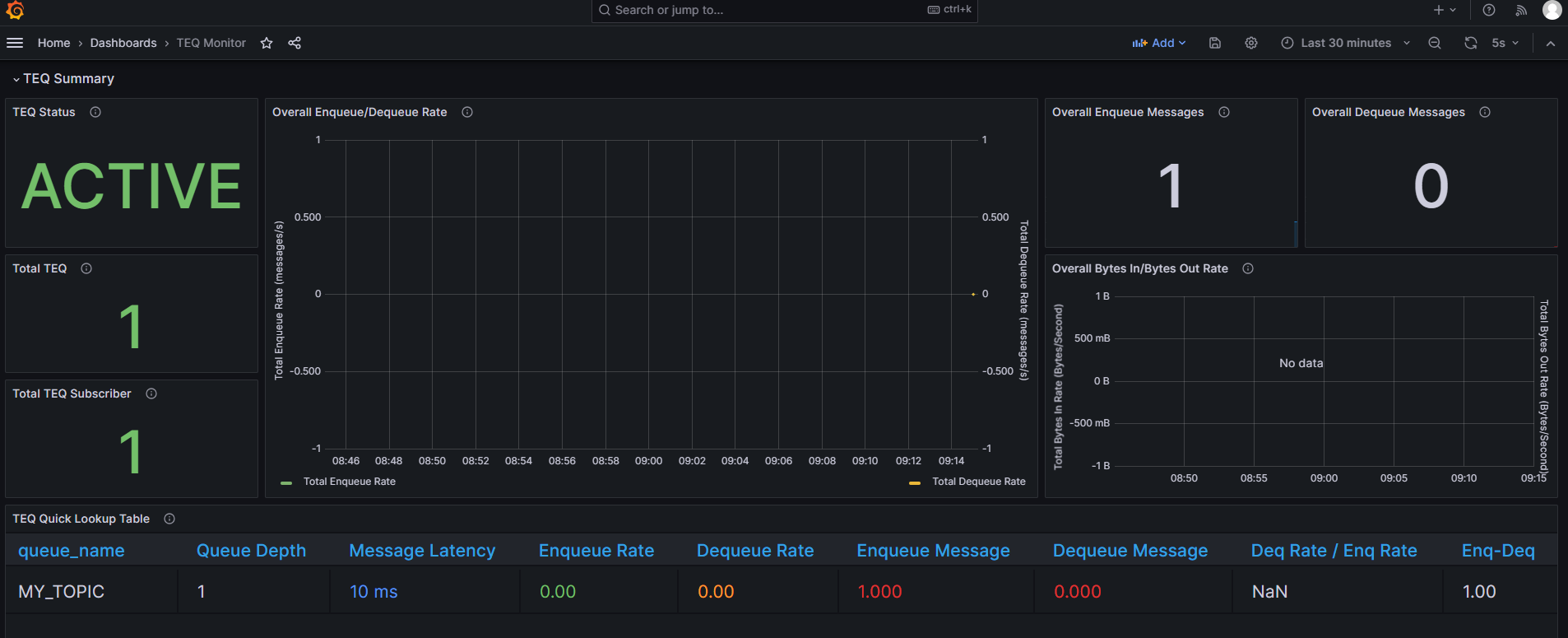
grant select on user_queue_partition_assignment_table to exporter;A Grafana dashboard for Transactional Event Queues is provided in this file. This can be imported into your Grafana environment. Choose the Prometheus datasource that is collecting metrics from the exporter.
Note: You may not see any activity on the dashboard unless there are clients producing and consuming messages from topics.
The dashboard will look like this:
The exporter itself is fairly simple. The initialization is done as follows:
- Parse flags options
- Load the default toml file (
default-metrics.toml) and store each metric in aMetricstruct - Load the custom toml file (if a custom toml file is given)
- Create an
Exporterobject - Register exporter in prometheus library
- Launching a web server to handle incoming requests
These operations are mainly done in the main function.
After this initialization phase, the exporter will wait for the arrival of a request.
Each time, it will iterate over the content of the metricsToScrape structure (in the function scrape func (e * Export) scrape (ch chan <- prometheus.Metric)).
For each element (of Metric type), a call to the ScrapeMetric function will be made which will itself make a call to the ScrapeGenericValues function.
The ScrapeGenericValues function will read the information from the Metric structure and, depending on the parameters, will generate the metrics to return. In particular, it will use the GeneratePrometheusMetrics function which will make SQL calls to the database.
To build a container image, run the following command:
make dockerRun build:
make go-buildThis will create binaries and archives inside the dist folder for the building operating system.
This project welcomes contributions from the community. Before submitting a pull request, please review our contribution guide
Please consult the security guide for our responsible security vulnerability disclosure process
Copyright (c) 2016, 2023, Oracle and/or its affiliates.
Released under the Universal Permissive License v1.0 as shown at https://oss.oracle.com/licenses/upl/ and the MIT License (MIT)