rosrun ORB_SLAM2 Mono Vocabulary/ORBvoc.txt Examples/RGB-D/TUM1realsense.yaml true export ROS_PACKAGE_PATH=$ROS_PACKAGE_PATH:/home/seba/Documents/VISION_SLAM/Examples/ROS/ORB_SLAM2
ORB SLAM Modified to save and load map as well as added comments to the header files.
Summery of algorithm
-
- read execution command line parameters
-
- creates the SLAM object, the only instance of the System class
-
- load the BoW vocabulary
-
- load the configuration file and parse it
-
- creates threads for the four main and parallel processes:
-
- LoopClosing
-
- LocalMapping
-
- Viewer
-
- Tracking (running on the main thread).
-
- creates threads for the four main and parallel processes:
-
- execute the entire process for each frame of the camera
The sequence of invocations is:
-
1 - System :: TrackMonocular, passing the color image of the camera
-
2- Tracking :: GrabImageMonocular, passing the Mat image in grayscale, creates the currentFrame from the image
-
3- Tracking :: Track, finite state machine that dispatches methods according to the state.
-
4- Tracking :: TrackWithMotionModel, invoked in the OK state
-
\ Section clas Classification of classes
-
ORB-SLAM2 has a .h file and another .cc file for each class, all declared in the ORB-SLAM2 namespace.
-
Adopts the following suffixes to name class member properties, specifying their type:
-
- m: member. All properties begin with m.
-
- p: pointer
-
- v: vector
-
- b: boolean
-
- n: integer
-
- f: float
-
There are exceptions, probably by mistake.
-
Examples:
-
- mvpMapPoints is a pointer vector member.
-
- mnId is an integer member Id.
-
There are several types of class:
-
- Classes that are repeatedly instantiated:
-
- Frame
-
- KeyFrame
-
- MapPoint
-
- Initializer
-
- ORBextractor
-
- ORBmatcher
-
- Classes that are instantiated only once and are associated with a thread:
-
- Tracking
-
- LocalMapping
-
- Viewer
-
- LoopClosing
-
- Classes that are instantiated only once and last:
-
- System
-
- Map
-
- KeyFrameDatabase
-
- MapDrawer
-
- FrameDrawer
-
- Classes that are not instantiated, have no properties, are repositories of class methods:
-
- Converter
-
- Optimizer
-
Exceptions:
-
ORBVocabulary.h is an exception to this rule, it does not define a class but a simple typedef.
-
ORBExtractor.h defines two classes, including ExtractorNode.
-
The Thirparty folder contains pruned versions of DBoW2 and g2o with their own styles.
-
Section ORB-SLAM concepts and their classes
-
Frame:
-
An ephemeral Frame object is created from each camera image.
-
Usually the current frame and the previous frame only remain, with only two instances of this class being simultaneously in the system.
-
The Frame object has the singular points detected, its anti-distorted version, its descriptors and the associated map points.
-
The class provides the methods for its construction from the image.
-
KeyFrame:
-
KeyFrame is created from a Frame when the system understands that it provides information to the map.
-
While a Frame is ephemeral, a KeyFrame is long-lived, it is the way a Frame becomes part of the map.
-
When a KeyFrame is created, it copies the main information from the current Frame, and computes more data, such as the BoWs of each descriptor.
-
The KeyFrame documentation explains the notation of arrays used in this and other classes.
-
MapPoint:
-
3D point of the world map. It not only has the coordinates of the point, but also the list of KeyFrames that observe it,
-
The list of descriptors associated with the point (a descriptor for each KeyFrame that observes it), among others.
-
Map:
-
World map. It has a list of MapPoitns, a list of KeyFrames, and methods for map management.
-
\ Section threads Description of threads
-
ORB-SLAM has four parallel threads, each with its own loop.
-
- Tracking is the preponderant object of the main thread, which is responsible for processing each incoming image, Detecting singular points, calculating descriptors, matches with the previous frame,
-
trying to identify known points on the map. Decide when to add a new Keyframe and when not to add new points to the map.
-
- LocalMapping tries to add points to the map each time a KeyFrame is added. Add points by triangulation with neighboring KeyFrames.
-
Also optimizes the map by removing redundant keyframes.
-
- LoopClosing tries to compare the current observation with the map thus detecting loops.
-
-Viewer handles the two views: the map and the processed image.
Authors: Raul Mur-Artal, Juan D. Tardos, J. M. M. Montiel and Dorian Galvez-Lopez (DBoW2)
Note: This is a modified version of original ORB_SLAM2 and features implemented by Mathew Denny and fixed by Hangqiu; binary vocabulary loading from Poine. Other good features from other contributors will be merged soon.
13 Jan 2017: OpenCV 3 and Eigen 3.3 are now supported.
22 Dec 2016: Added AR demo (see section 7).
ORB-SLAM2 is a real-time SLAM library for Monocular, Stereo and RGB-D cameras that computes the camera trajectory and a sparse 3D reconstruction (in the stereo and RGB-D case with true scale). It is able to detect loops and relocalize the camera in real time. We provide examples to run the SLAM system in the KITTI dataset as stereo or monocular, in the TUM dataset as RGB-D or monocular, and in the EuRoC dataset as stereo or monocular. We also provide a ROS node to process live monocular, stereo or RGB-D streams. The library can be compiled without ROS. ORB-SLAM2 provides a GUI to change between a SLAM Mode and Localization Mode, see section 9 of this document.
###Related Publications:
[Monocular] Raúl Mur-Artal, J. M. M. Montiel and Juan D. Tardós. ORB-SLAM: A Versatile and Accurate Monocular SLAM System. IEEE Transactions on Robotics, vol. 31, no. 5, pp. 1147-1163, 2015. (2015 IEEE Transactions on Robotics Best Paper Award). PDF.
[Stereo and RGB-D] Raúl Mur-Artal and Juan D. Tardós. ORB-SLAM2: an Open-Source SLAM System for Monocular, Stereo and RGB-D Cameras. ArXiv preprint arXiv:1610.06475 PDF.
[DBoW2 Place Recognizer] Dorian Gálvez-López and Juan D. Tardós. Bags of Binary Words for Fast Place Recognition in Image Sequences. IEEE Transactions on Robotics, vol. 28, no. 5, pp. 1188-1197, 2012. PDF
#1. License
ORB-SLAM2 is released under a GPLv3 license. For a list of all code/library dependencies (and associated licenses), please see Dependencies.md.
For a closed-source version of ORB-SLAM2 for commercial purposes, please contact the authors: orbslam (at) unizar (dot) es.
If you use ORB-SLAM2 (Monocular) in an academic work, please cite:
@article{murTRO2015,
title={{ORB-SLAM}: a Versatile and Accurate Monocular {SLAM} System},
author={Mur-Artal, Ra\'ul, Montiel, J. M. M. and Tard\'os, Juan D.},
journal={IEEE Transactions on Robotics},
volume={31},
number={5},
pages={1147--1163},
doi = {10.1109/TRO.2015.2463671},
year={2015}
}
if you use ORB-SLAM2 (Stereo or RGB-D) in an academic work, please cite:
@article{murORB2,
title={{ORB-SLAM2}: an Open-Source {SLAM} System for Monocular, Stereo and {RGB-D} Cameras},
author={Mur-Artal, Ra\'ul and Tard\'os, Juan D.},
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:1610.06475},
year={2016}
}
#2. Prerequisites We have tested the library in Ubuntu 12.04, 14.04 and 16.04, but it should be easy to compile in other platforms. A powerful computer (e.g. i7) will ensure real-time performance and provide more stable and accurate results.
We use the new thread and chrono functionalities of C++11.
We use Pangolin for visualization and user interface. Dowload and install instructions can be found at: https://github.com/stevenlovegrove/Pangolin.
We use OpenCV to manipulate images and features. Dowload and install instructions can be found at: http://opencv.org. Required at leat 2.4.3. Tested with OpenCV 2.4.11 and OpenCV 3.2.
Required by g2o (see below). Download and install instructions can be found at: http://eigen.tuxfamily.org. Required at least 3.1.0.
We use modified versions of the DBoW2 library to perform place recognition and g2o library to perform non-linear optimizations. Both modified libraries (which are BSD) are included in the Thirdparty folder.
We provide some examples to process the live input of a monocular, stereo or RGB-D camera using ROS. Building these examples is optional. In case you want to use ROS, a version Hydro or newer is needed.
#3. Building ORB-SLAM2 library and TUM/KITTI examples
Clone the repository:
git clone https://github.com/raulmur/ORB_SLAM2.git ORB_SLAM2
We provide a script build.sh to build the Thirdparty libraries and ORB-SLAM2. Please make sure you have installed all required dependencies (see section 2). Execute:
cd ORB_SLAM2
chmod +x build.sh
./build.sh
This will create libORB_SLAM2.so at lib folder and the executables mono_tum, mono_kitti, rgbd_tum, stereo_kitti, mono_euroc and stereo_euroc in Examples folder.
#4. Monocular Examples
-
Download a sequence from http://vision.in.tum.de/data/datasets/rgbd-dataset/download and uncompress it.
-
Execute the following command. Change
TUMX.yamlto TUM1.yaml,TUM2.yaml or TUM3.yaml for freiburg1, freiburg2 and freiburg3 sequences respectively. ChangePATH_TO_SEQUENCE_FOLDERto the uncompressed sequence folder.
./Examples/Monocular/mono_tum Vocabulary/ORBvoc.txt Examples/Monocular/TUMX.yaml PATH_TO_SEQUENCE_FOLDER
-
Download the dataset (grayscale images) from http://www.cvlibs.net/datasets/kitti/eval_odometry.php
-
Execute the following command. Change
KITTIX.yamlby KITTI00-02.yaml, KITTI03.yaml or KITTI04-12.yaml for sequence 0 to 2, 3, and 4 to 12 respectively. ChangePATH_TO_DATASET_FOLDERto the uncompressed dataset folder. ChangeSEQUENCE_NUMBERto 00, 01, 02,.., 11.
./Examples/Monocular/mono_kitti Vocabulary/ORBvoc.txt Examples/Monocular/KITTIX.yaml PATH_TO_DATASET_FOLDER/dataset/sequences/SEQUENCE_NUMBER
-
Download a sequence (ASL format) from http://projects.asl.ethz.ch/datasets/doku.php?id=kmavvisualinertialdatasets
-
Execute the following first command for V1 and V2 sequences, or the second command for MH sequences. Change PATH_TO_SEQUENCE_FOLDER and SEQUENCE according to the sequence you want to run.
./Examples/Monocular/mono_euroc Vocabulary/ORBvoc.txt Examples/Monocular/EuRoC.yaml PATH_TO_SEQUENCE_FOLDER/mav0/cam0/data Examples/Monocular/EuRoC_TimeStamps/SEQUENCE.txt
./Examples/Monocular/mono_euroc Vocabulary/ORBvoc.txt Examples/Monocular/EuRoC.yaml PATH_TO_SEQUENCE/cam0/data Examples/Monocular/EuRoC_TimeStamps/SEQUENCE.txt
#5. Stereo Examples
-
Download the dataset (grayscale images) from http://www.cvlibs.net/datasets/kitti/eval_odometry.php
-
Execute the following command. Change
KITTIX.yamlto KITTI00-02.yaml, KITTI03.yaml or KITTI04-12.yaml for sequence 0 to 2, 3, and 4 to 12 respectively. ChangePATH_TO_DATASET_FOLDERto the uncompressed dataset folder. ChangeSEQUENCE_NUMBERto 00, 01, 02,.., 11.
./Examples/Stereo/stereo_kitti Vocabulary/ORBvoc.txt Examples/Stereo/KITTIX.yaml PATH_TO_DATASET_FOLDER/dataset/sequences/SEQUENCE_NUMBER
-
Download a sequence (ASL format) from http://projects.asl.ethz.ch/datasets/doku.php?id=kmavvisualinertialdatasets
-
Execute the following first command for V1 and V2 sequences, or the second command for MH sequences. Change PATH_TO_SEQUENCE_FOLDER and SEQUENCE according to the sequence you want to run.
./Examples/Stereo/stereo_euroc Vocabulary/ORBvoc.txt Examples/Stereo/EuRoC.yaml PATH_TO_SEQUENCE/mav0/cam0/data PATH_TO_SEQUENCE/mav0/cam1/data Examples/Stereo/EuRoC_TimeStamps/SEQUENCE.txt
./Examples/Stereo/stereo_euroc Vocabulary/ORBvoc.txt Examples/Stereo/EuRoC.yaml PATH_TO_SEQUENCE/cam0/data PATH_TO_SEQUENCE/cam1/data Examples/Stereo/EuRoC_TimeStamps/SEQUENCE.txt
#6. RGB-D Example
-
Download a sequence from http://vision.in.tum.de/data/datasets/rgbd-dataset/download and uncompress it.
-
Associate RGB images and depth images using the python script associate.py. We already provide associations for some of the sequences in Examples/RGB-D/associations/. You can generate your own associations file executing:
python associate.py PATH_TO_SEQUENCE/rgb.txt PATH_TO_SEQUENCE/depth.txt > associations.txt
- Execute the following command. Change
TUMX.yamlto TUM1.yaml,TUM2.yaml or TUM3.yaml for freiburg1, freiburg2 and freiburg3 sequences respectively. ChangePATH_TO_SEQUENCE_FOLDERto the uncompressed sequence folder. ChangeASSOCIATIONS_FILEto the path to the corresponding associations file.
./Examples/RGB-D/rgbd_tum Vocabulary/ORBvoc.txt Examples/RGB-D/TUMX.yaml PATH_TO_SEQUENCE_FOLDER ASSOCIATIONS_FILE
#7. ROS Examples
- Add the path including Examples/ROS/ORB_SLAM2 to the ROS_PACKAGE_PATH environment variable. Open .bashrc file and add at the end the following line. Replace PATH by the folder where you cloned ORB_SLAM2:
export ROS_PACKAGE_PATH=${ROS_PACKAGE_PATH}:PATH/ORB_SLAM2/Examples/ROS
- Execute
build_ros.shscript:
chmod +x build_ros.sh
./build_ros.sh
For a monocular input from topic /camera/image_raw run node ORB_SLAM2/Mono. You will need to provide the vocabulary file and a settings file. See the monocular examples above.
rosrun ORB_SLAM2 Mono PATH_TO_VOCABULARY PATH_TO_SETTINGS_FILE
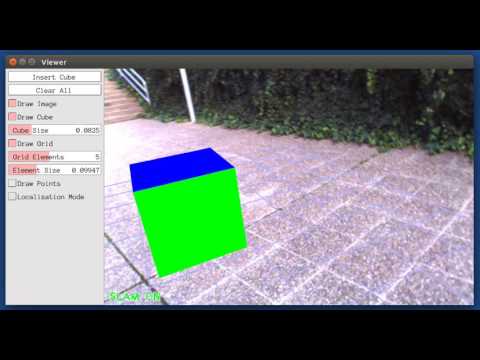
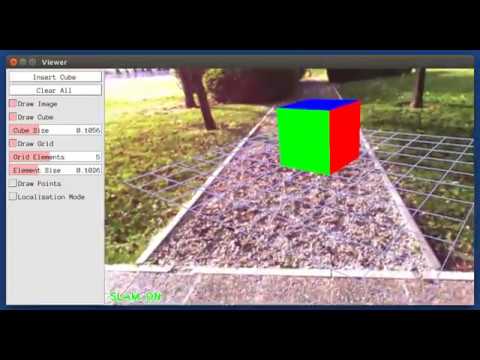
This is a demo of augmented reality where you can use an interface to insert virtual cubes in planar regions of the scene.
The node reads images from topic /camera/image_raw.
rosrun ORB_SLAM2 MonoAR PATH_TO_VOCABULARY PATH_TO_SETTINGS_FILE
For a stereo input from topic /camera/left/image_raw and /camera/right/image_raw run node ORB_SLAM2/Stereo. You will need to provide the vocabulary file and a settings file. If you provide rectification matrices (see Examples/Stereo/EuRoC.yaml example), the node will recitify the images online, otherwise images must be pre-rectified.
rosrun ORB_SLAM2 Stereo PATH_TO_VOCABULARY PATH_TO_SETTINGS_FILE ONLINE_RECTIFICATION
Example: Download a rosbag (e.g. V1_01_easy.bag) from the EuRoC dataset (http://projects.asl.ethz.ch/datasets/doku.php?id=kmavvisualinertialdatasets). Open 3 tabs on the terminal and run the following command at each tab:
roscore
rosrun ORB_SLAM2 Stereo Vocabulary/ORBvoc.txt Examples/Stereo/EuRoC.yaml true
rosbag play --pause V1_01_easy.bag /cam0/image_raw:=/camera/left/image_raw /cam1/image_raw:=/camera/right/image_raw
Once ORB-SLAM2 has loaded the vocabulary, press space in the rosbag tab. Enjoy!. Note: a powerful computer is required to run the most exigent sequences of this dataset.
For an RGB-D input from topics /camera/rgb/image_raw and /camera/depth_registered/image_raw, run node ORB_SLAM2/RGBD. You will need to provide the vocabulary file and a settings file. See the RGB-D example above.
rosrun ORB_SLAM2 RGBD PATH_TO_VOCABULARY PATH_TO_SETTINGS_FILE
#8. Processing your own sequences You will need to create a settings file with the calibration of your camera. See the settings file provided for the TUM and KITTI datasets for monocular, stereo and RGB-D cameras. We use the calibration model of OpenCV. See the examples to learn how to create a program that makes use of the ORB-SLAM2 library and how to pass images to the SLAM system. Stereo input must be synchronized and rectified. RGB-D input must be synchronized and depth registered.
#9. SLAM and Localization Modes You can change between the SLAM and Localization mode using the GUI of the map viewer.
This is the default mode. The system runs in parallal three threads: Tracking, Local Mapping and Loop Closing. The system localizes the camera, builds new map and tries to close loops.
This mode can be used when you have a good map of your working area. In this mode the Local Mapping and Loop Closing are deactivated. The system localizes the camera in the map (which is no longer updated), using relocalization if needed.
#10. Docker image
A Dockerfile is provided under the /docker directory and the image is available in docker hub. You can, of course, modify the Dockerfile and build your own image.
There are two Dockerfile provided. The "Dockerfile.ubuntu" is used to build the Ubuntu and third-party libs.
docker build -t orb_slam2:build -f Dockerfile.ubuntu ./docker
docker build -t orb_slam2:dev -f Dockerfile ./docker
The ORB-SLAM2 lib and the examples are built under /opt/ORB_SLAM2
docker pull youyu/orb_slam2:latest
You have to run the Docker image under the GUI (X) environment.
docker run -it --rm -e DISPLAY=$DISPLAY -v /tmp/.X11-unix:/tmp/.X11-unix youyu/orb-slam2:latest
You have to use "-v" to mount your local data directory into the container. Check Docker doc for more detailed information.