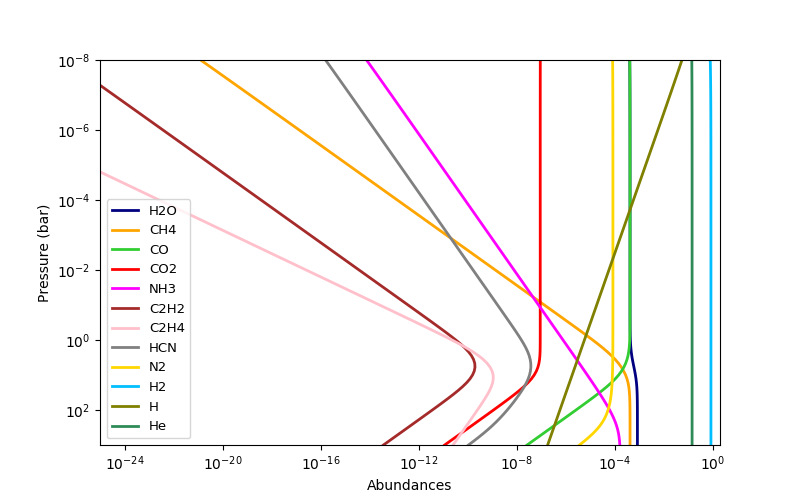
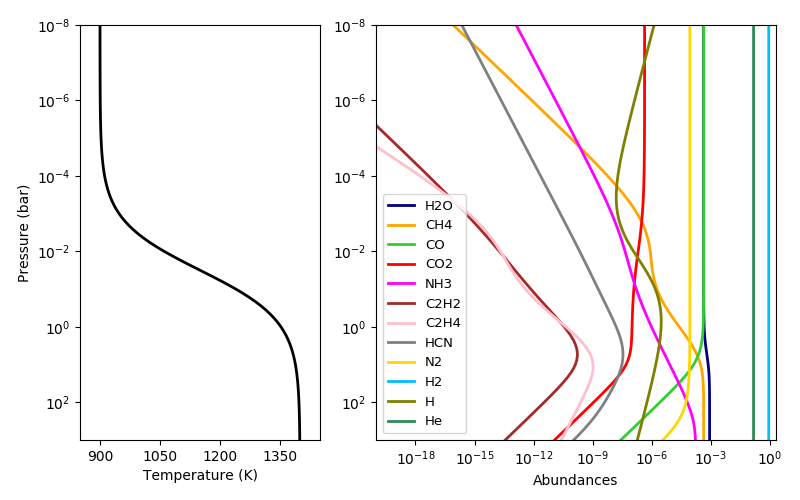
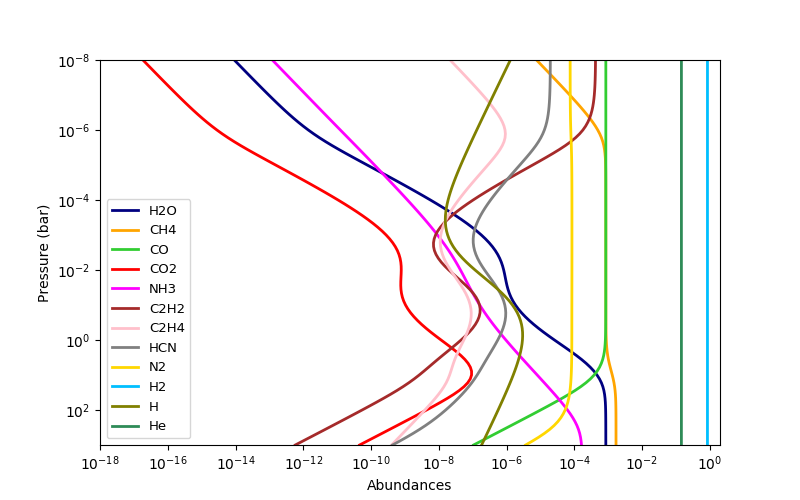
This code computes thermochemical-equilibrium abundances for a H-C-N-O system with known pressure, temperature, and elemental abundances. The output abundances are H2O, CH4, CO, CO2, NH3, C2H2, C2H4, HCN, and N2, H2, H, and He.
These calculations are valid over:
- pressures from 10-8 to 103 bar,
- temperatures from 200 to ~2000 K,
- C-N-O elemental abundances from 10-3 to 102 times solar abundances in hydrogen-dominated systems.
- Patricio Cubillos (IWF) patricio.cubillos@oeaw.ac.at
- Jasmina Blecic (NYU Abu Dhabi)
- Ian Dobbs-Dixon (NYU Abu Dhabi)
rate is compatible with both Python2 and Python3, and runs (at least) in both Linux and OSX.
To obtain the rate code, clone this repository to your local machine with the following terminal commands:
# Clone the repository to your working directory:
git clone https://github.com/pcubillos/rate/The following Python script shows how to compute equilibrium abundances with rate:
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# Make sure to have/add the path to the rate package in your pythonpath:
import rate
# Initialize object with solar composition:
r = rate.Rate(C=2.5e-4, N=1.0e-4, O=5.0e-4, fHe=0.0851)
# Define atmospheric profile:
nlayers = 100
press = np.logspace(-8, 3, nlayers) # bars
temp1 = np.tile(1400.0, nlayers) # kelvin
# Compute abundances:
Q1 = r.solve(temp1, press)
# See results:
labels = r.species
cols = ["navy", "orange", "limegreen", "red", "magenta", "brown",
"pink", "0.5", "gold", "deepskyblue", "olive", "seagreen"]
plt.figure(-1, (8,5))
plt.clf()
for q, col, lab in zip(Q1, cols, labels):
plt.loglog(q, press, lw=2, color=col, label=lab)
plt.ylim(np.amax(press), np.amin(press))
plt.legend(loc="lower left", fontsize=9.5)
plt.xlim(1e-25, 2)
plt.xlabel("Abundances")
plt.ylabel("Pressure (bar)")
plt.xticks(np.logspace(-24, 0, 7))# A 'more interesting' temperature profile:
temp2 = 900+500/(1+np.exp(-(np.log10(press)+1.5)*1.5))
Q2 = r.solve(temp2, press)
plt.figure(-2, (8,5))
plt.clf()
ax = plt.axes([0.1, 0.12, 0.3, 0.83])
plt.semilogy(temp2, press, lw=2, color="k")
plt.ylim(np.amax(press), np.amin(press))
plt.xlim(850, 1450)
ax.set_xticks([900, 1050, 1200, 1350])
plt.ylabel("Pressure (bar)")
plt.xlabel("Temperature (K)")
ax = plt.axes([0.47, 0.12, 0.5, 0.83])
for q, col, lab in zip(Q2, cols, labels):
plt.loglog(q, press, lw=2, color=col, label=lab)
plt.ylim(np.amax(press), np.amin(press))
plt.xlim(1e-20, 2)
plt.xticks(np.logspace(-18, 0, 7))
plt.legend(loc="lower left", fontsize=9.5)
plt.xlabel("Abundances")# A carbon-dominated atmosphere, same temperature as before:
Q3 = r.solve(temp2, press, C=1e-3)
plt.figure(-3, (8,5))
plt.clf()
for q, col, lab in zip(Q3, cols, labels):
plt.loglog(q, press, lw=2, color=col, label=lab)
plt.ylim(np.amax(press), np.amin(press))
plt.legend(loc="lower left", fontsize=9.5)
plt.xlim(1e-18, 2)
plt.xlabel("Abundances")
plt.ylabel("Pressure (bar)")Please, be kind and acknowledge the effort of the authors by citing the article associated to this project:
Cubillos, Blecic, & Dobbs-Dixon (2019): Towards More Reliable Analytic Thermochemical-equilibrium Abundances, ApJ, 872, 111.
Copyright (c) 2018-2019 Patricio Cubillos and contributors.
rate is open-source software under the MIT license (see LICENSE).