NGINX Controller offers a simplified Life Cycle Management of your NGINX instances across all of your environment:
- Auto Scaling
- during Scale In / Scale Out, the instance register / unregister to NGINX Controller
- Up to date OS, software and Security signatures
- use the native feature
reimageorrolling upgradeof your Cloud Service Provider
- Source Of Truth
- a NGINX instance is bootstrapped from a standard Linux VM image, all of configurations are pushed from NGINX Controller
- Cloud agnostic
- same principles and onboarding scripts are reusable on any Cloud (Private, Public)
- Native Scaling Policy
- InfraOps are free to use the scaling policy offered by their Cloud Service Provider (CSP).
This repo provides a demo of a scaling group implementation using NGINX App Protect instances managed by NGINX Controller.
Last chapter warns you to take in consideration resiliency and DNS LB in order to enhance User Experience.
Contents
Demo done on Azure using a VM Scale Set.



When an new VM instance is bootstraped, this instance is up to date:
- OS packages
- Software: NGINX Plus, NGINX App Protect and NGINX Controller agent
- Security signatures
Then this instance retrieve his configuration from NGINX Controller. Therefore NGINX Controller is the Source of Truth for all of your managed NGINX instances.
In order to upgrade your cluster, the immutable approach is recommended: destroy & recreate your VM instances. As done on Kubernetes, the immutable approach is more simpler and safer than the mutable approach that will apply changes.
How to do that on Azure VM Scale Set?
If you select reimage,
it will remove the VMSS instance and replace it with a brand new one.
This can be used if you are having issues or need to upgrade per instance, that will delete it and redeploy it up to date.
Upgrading will apply any changes that were applied to the scaleset as a whole. So for example, if you apply a custom script extension to VMSS1 you need to update the VMSS instances in order for that custom script to actually be applied.
During a Scale In or reimage operation, an impact on User Experience exists if:
- persistency is set on the downstream Load Balancer
- no Global Load Balancing exists across regions or multi-cloud.
A user or a consumer have no access to the service during few seconds with no notification
A Web Browser opens up to 15 TCP sessions to a remote Domain service
and keeps it them alive in order to re-use then to send further HTTP transactions.
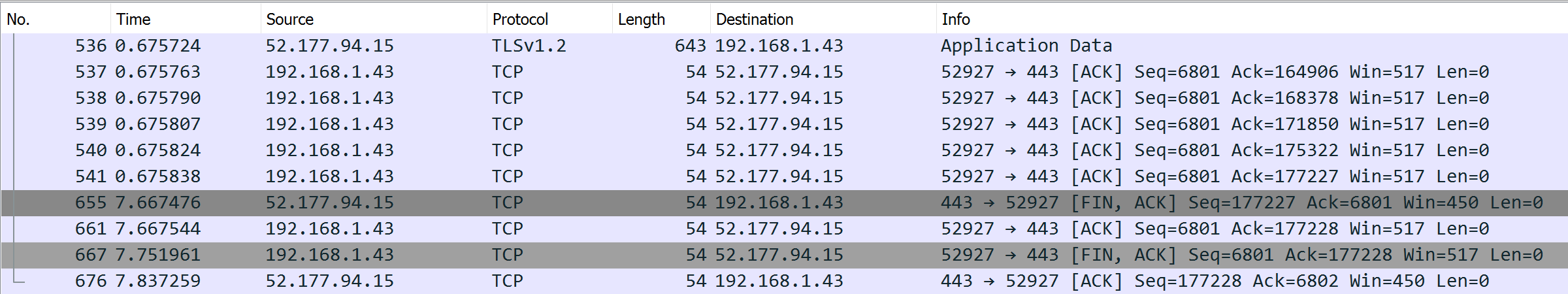
When a Scale In or reimage operation occurs, NGINX process received a SIG_TERM signal and all of NGINX workers are shutdown gracefully: current HTTP transactions are drained and then TCP sessions are closed.
The picture below shows a reimage operation that occurs at second #7.
However, the External Azure Load Balancer is configured with:
- a Persistency
- a health probe interval of 5s
- a unhealthy threshold of 2
In that case, further TCP sessions initiated from the browser will be stuck up to 15s to the same VM instance... that is unavailable.
After 15s, External Azure Load Balancer chose another pool member. Then the service is up again for this user.
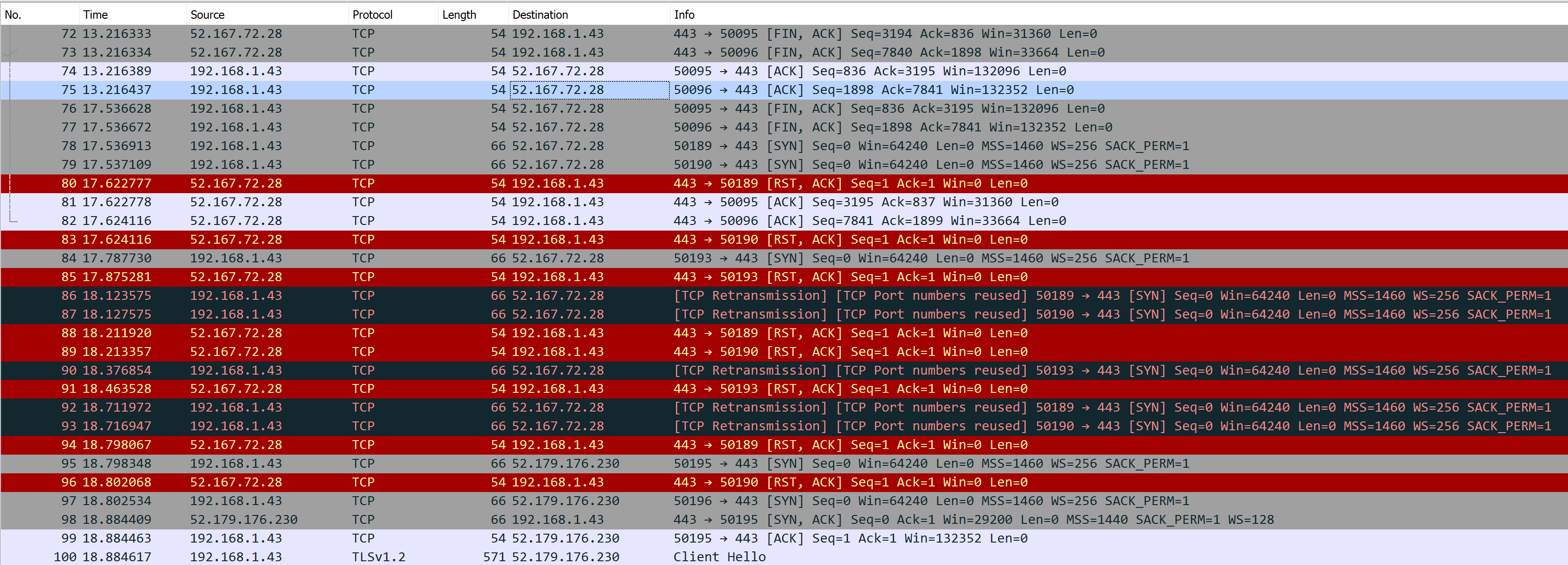
Source: full PCAP capture with no DNS LB here
Do not persist? No, it's not a solution, persistence is useful for :
- Web Application Firewall security features that track user sessions (CSRF, DeviceID, JS injection, cookie...)
- troubleshooting purpose
DNS Load Balancing
Use a DNS LB record to Load-Balance traffic across 2 regions or multi-cloud. 2 Public IPs are returned for your DNS domain. If a TCP session on one Public IP returns a RST, Web Browser will switch automatically to the other Public IP after 1s. Acceptable impact for a good User Experience, well done! :o)
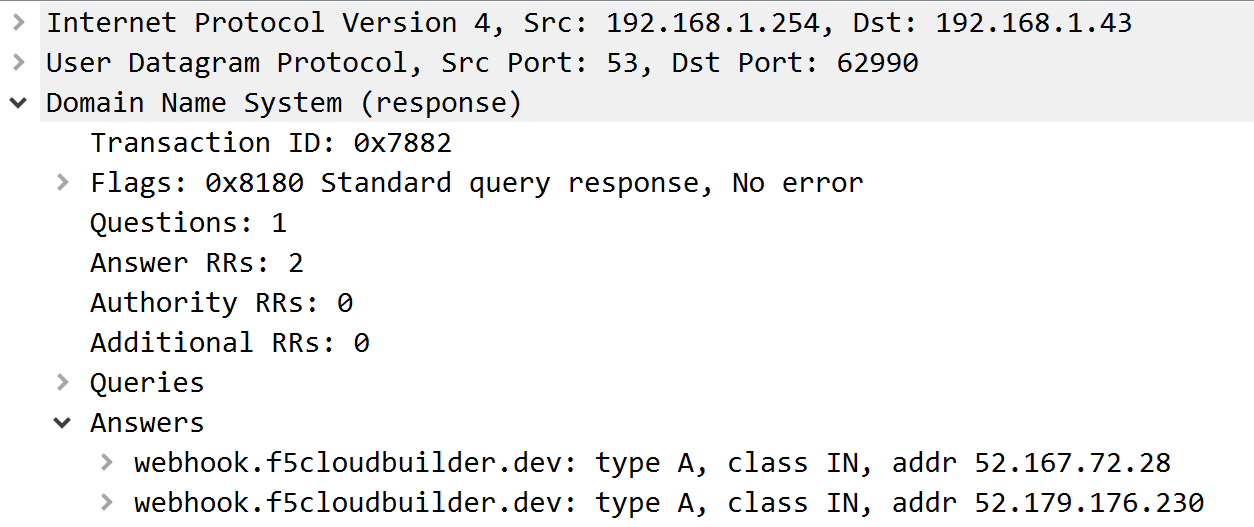
F5 Cloud Services DNS LB hosts
webhook.f5cloudbuilder.devA record that returns 2 Public IPs:52.167.72.28 ; 52.179.176.230
- Web Browser resolves
webhook.f5cloudbuilder.devand keeps it in DNS Cache - Because DNS Cache TTL in Chrome is 60s minimum (here), TTL of A record must be set at least to 60s
- Web Browser resolves
- Web Browser makes TCP connexions only to IP
52.167.72.28
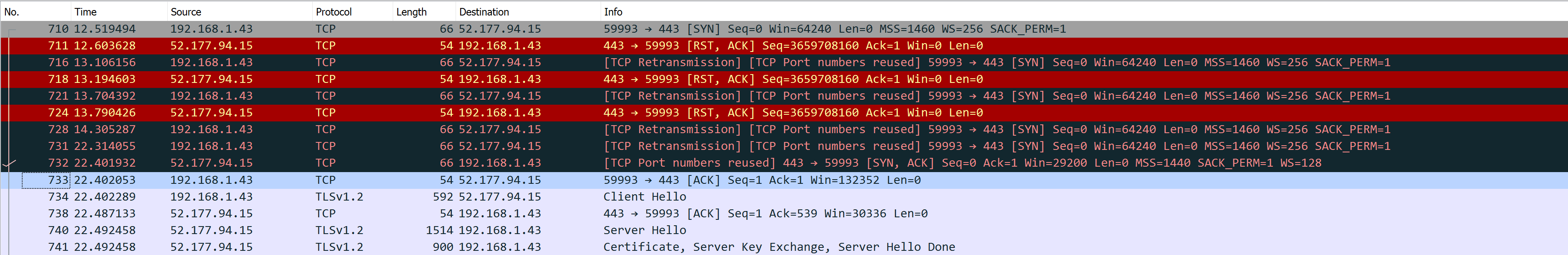
- At second #13 in the picture bellow, NGINX VM is shutdown and NGINX closes all TCP connexions gracefully
- At second #17 Web Browser opens new TCP connexions to the same Public IP
52.167.72.28and Azure Load Balancer responds with TCP RST due to persistence linked to a NGINX VM shutdown - At second #18 Web Browser opens new TCP connexions to the second Public IP
52.179.176.230
Source: full PCAP capture with DNS LB here
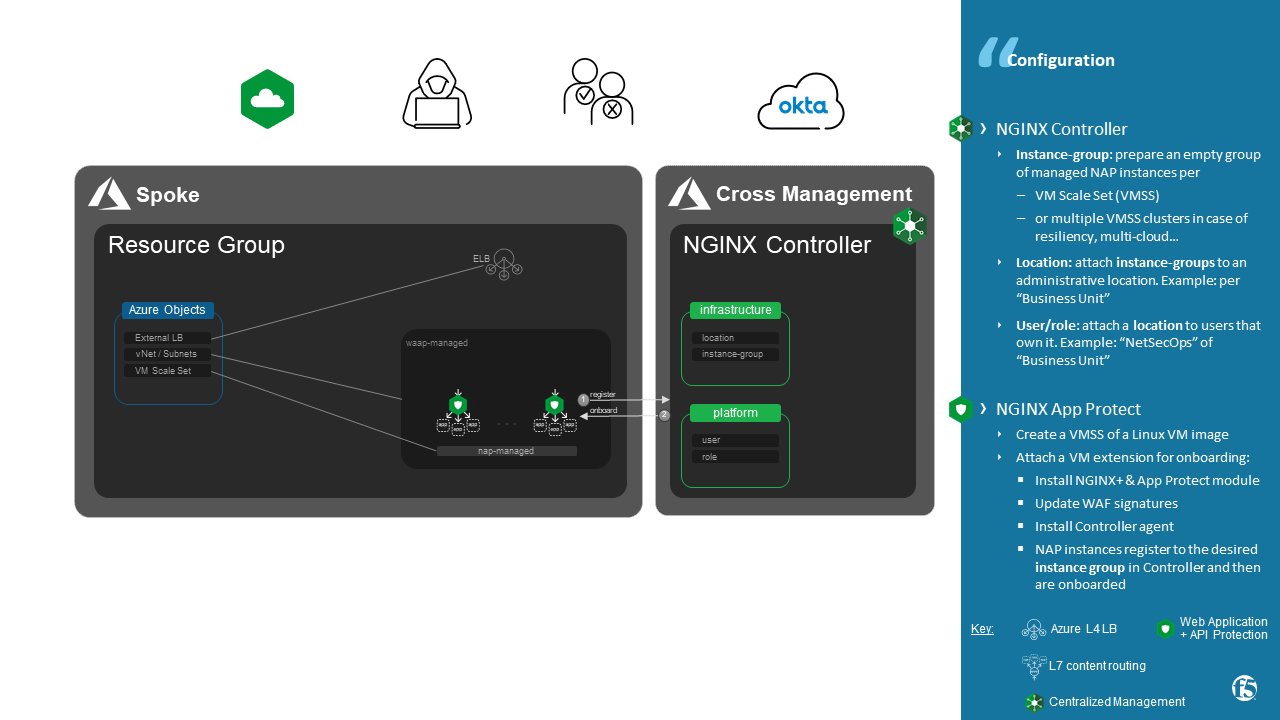
- Components:
- A NGINX Controller hosted in a "Cross Management" / "Shared service" / "Out of Band" zone
- A VM Scale Set of NGINX App Protect instances
- An External Azure Load Balancer to publish a Public IP
Once a VM is started, VM is onboarded using an Extension: Shell or Cloud Init commands that must includes to run the 2 scripts below. Example of Extension here in Jinja2 format for Ansible
install_managed_nap.sh install and run:
- NGINX+: Application Load-Balancer
- App Protect module: Web Application and API Protection
- last WAF signature update
- NGINX Controller agent: register VM instance and pull configuration
Input variables:
| Variable | Description |
|---|---|
EXTRA_NGINX_CONTROLLER_IP |
NGINX Controller IP |
EXTRA_NGINX_CONTROLLER_USERNAME |
NGINX Controller user account |
EXTRA_NGINX_CONTROLLER_PASSWORD |
NGINX Controller user password |
EXTRA_NGINX_PLUS_VERSION |
NGINX+ version to install |
EXTRA_LOCATION |
Location name, same as created on NGINX Controller |
EXTRA_VMSS_NAME |
VM Scale Set name, same as the Instance Group created on NGINX Controller |
scale_in_monitor.sh monitors a Scale In or a reimage event. When a Scale In or a reimage event occurs, this script is responsible to unregister this instance from NGINX Controller
Input variables:
| Variable | Description |
|---|---|
ENV_CONTROLLER_API_URL |
NGINX Controller IP and port |
ENV_CONTROLLER_USERNAME |
NGINX Controller user account with less privilege on Instance Group |
ENV_CONTROLLER_PASSWORD |
NGINX Controller user password |
ENV_CONTROLLER_LOCATION |
Location name, same as created on NGINX Controller |
ENV_CONTROLLER_INSTANCE_NAME |
Hostname of the NGINX instance |