[paper] [slides] [video] [website]
We propose sparse attention (SpAtten) with KV token pruning, local V pruning, head pruning, and KV progressive quantization to improve LLM efficiency.
- [2023/10] SpAtten-LLM and SpAtten hardware released.
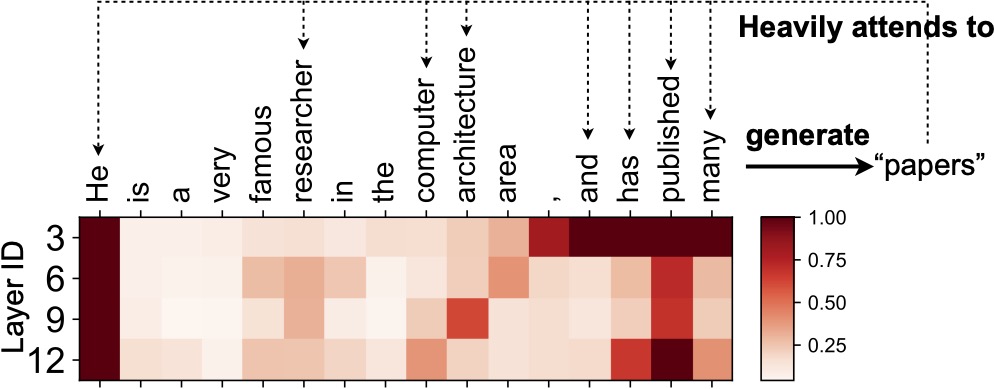
We present SpAtten, an efficient algorithm-architecture co-design that leverages token sparsity, head sparsity, and quantization opportunities to reduce the attention computation and memory access. Inspired by the high redundancy of human languages, we propose the novel KV token pruning to prune away unimportant tokens in the sentence. We also propose head pruning to remove unessential heads. Cascade pruning is fundamentally different from weight pruning since there is no trainable weight in the attention mechanism, and the pruned tokens and heads are selected on the fly. To efficiently support them on hardware, we design a novel top-k engine to rank token and head importance scores with high throughput. Furthermore, we propose KV progressive quantization that first fetches MSBs only and performs the computation; if the confidence is low, it fetches LSBs and recomputes the attention outputs, trading computation for memory reduction.
conda create -yn spatten python=3.8
conda activate spatten
pip install torch torchvision torchaudio
pip install transformers==4.33.0 accelerate datasets evaluate wandb scikit-learn scipy sentencepiece
python setup.py developCUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0 python run_spatten_llama.py --enable_spattenThis repo also contains the RTL-level simulation model of SpAtten in spatten_hardware/hardware/ for accurate performance evaluation on generative models like GPT-2 and a fast behavior model in spatten_hardware/simulator for quick evaluation on BERT.
-
Note that there is a known issue with the latest Verilator that may cause random assertion failure on startup of simulation. Use v4.218 as a workaround.
-
C/C++ build tools for verilator and ramulator.
gcc,g++>=12,cmake -
Workload information in CSV format. There are some examples in hardware/workloads
Build the ramulator2
$ cd spatten_hardware/hardware/third_party/ramulator2
$ mkdir build
$ cd build
$ cmake .. -DCMAKE_BUILD_TYPE=RelWithDebInfo
$ make
$ cd ../../../..
Build the Verilog (DPI) interface for ramulator
$ cd hardware/dpi
$ make
$ cd ../../..
Use the python script to run SpAtten simulation with a workload file
python3 run_spatten_hardware.py hardware/workloads/summary-gpt2-small-wikitext2-per8.csv
The evaluation results is located in the working directory spatten.workdir/summary.txt
SpAtten uses a specialized pipeline to support efficient attention and focus on memory traffic optimizations for decoding models like GPT2 and LLMs.
This repo contains the following major modules in SpAtten, and the main pipeline implementation is in SpAttenController.scala.
- A parallelized top-k unit (10) that dynamically decides the values to fetch: TopK.scala, which uses QuickSelect.scala to choose the k-th largest element from attention prob
- A matrix fetcher ((3) and (6) in the figure) that loads the key/value matrix from DRAM and convert the bitwidth when necessary: MatrixFetcher.scala
- The Q*K (7) and Prob*V (11) unit and the corresponding key / value buffers: DotProduct.scala, MultiplyValue.scala, Buffer.scala, BufferManager.scala
- A progressive quantization module (9) to decide whether or not to load the LSBs of keys: RequantDecision.scala
We will release the code and data soon, please stay tuned.
- Release core code of SpAtten, including Llama-2, MPT, Falcon, and Pythia.
- Release SpAtten perplexity evaluation code
- Release SpAtten Llama Chatbot demo.
- Release a docker image for hardware simulation.
If you find SpAtten useful or relevant to your project and research, please kindly cite our paper:
@article{wang2021spatten,
title={SpAtten: Efficient Sparse Attention Architecture with Cascade Token and Head Pruning},
author={Wang, Hanrui and Zhang, Zhekai and Han, Song},
journal={HPCA},
year={2021}
}