Peng Hu*, Liangli Zhen*, Dezhong Peng, Pei Liu, Scalable deep multimodal learning for cross-modal retrieval[C], International ACM SIGIR Conference on Research and Development in Information Retrieval (SIGIR), 2019: 635-644. (*denotes equal contribution, PyTorch Code)
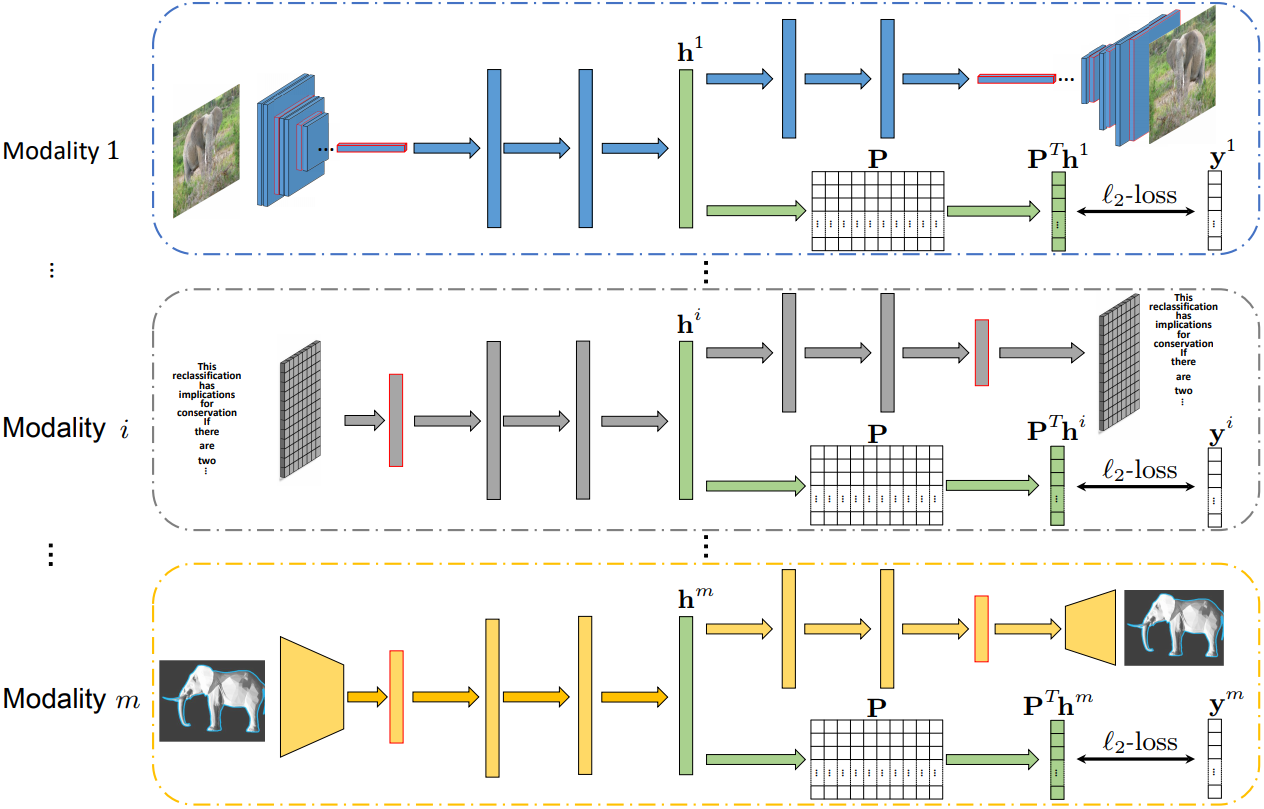
Cross-modal retrieval takes one type of data as the query to retrieve relevant data of another type. Most of existing cross-modal retrieval approaches were proposed to learn a common subspace in a joint manner, where the data from all modalities have to be involved during the whole training process. For these approaches, the optimal parameters of different modality-specific transformations are dependent on each other and the whole model has to be retrained when handling samples from new modalities. In this paper, we present a novel cross-modal retrieval method, called Scalable Deep Multimodal Learning (SDML). It proposes to predefine a common subspace, in which the between-class variation is maximized while the within-class variation is minimized. Then, it trains
The general framework of the proposed SDML method. The m modality-specific neural networks (one network for
each modality) can be trained separately since they do not share any trainable parameters.
If you find SDML useful in your research, please consider citing:
@inproceedings{hu2019deep,
author = {Hu, Peng and Zhen, Liangli and Peng, Dezhong and Liu, Pei},
title = {Scalable Deep Multimodal Learning for Cross-Modal Retrieval},
booktitle = {Proceedings of the 42Nd International ACM SIGIR Conference on Research and Development in Information Retrieval},
series = {SIGIR'19},
year = {2019},
isbn = {978-1-4503-6172-9},
location = {Paris, France},
pages = {635--644},
numpages = {10},
url = {http://doi.acm.org/10.1145/3331184.3331213},
doi = {10.1145/3331184.3331213},
acmid = {3331213},
publisher = {ACM},
address = {New York, NY, USA},
keywords = {cross-modal retrieval, multimodal learning, representation learning},
}


