Python 2.x code to compute the location of a phone on a floor from a single RGB camera image. The approach was to first build a phone classifier and then use it to locate the phone via a sliding-window algorithm. More details can be found in this Jupyter Notebook.
On a Macbook Pro, set up the following conda environment:
conda create -n find_phone python=2.7 pandas scikit-learn Pillow matplotlib ipython-notebook
Train the object-detection model using:
python train_phone_finder.py ./data
The data set consists of approximately 100 jpeg images of the
floor from a factory building with a phone on it.
There is a file named labels.txt that contains
normalized coordinates of a phone for each picture.
The command above will show a collection
of 'cut-outs' from the image data set,
some of which contain a phone, and some of which don't,
along with the predicted label ('contains phone' or 'does not contain phone').
Test the model using:
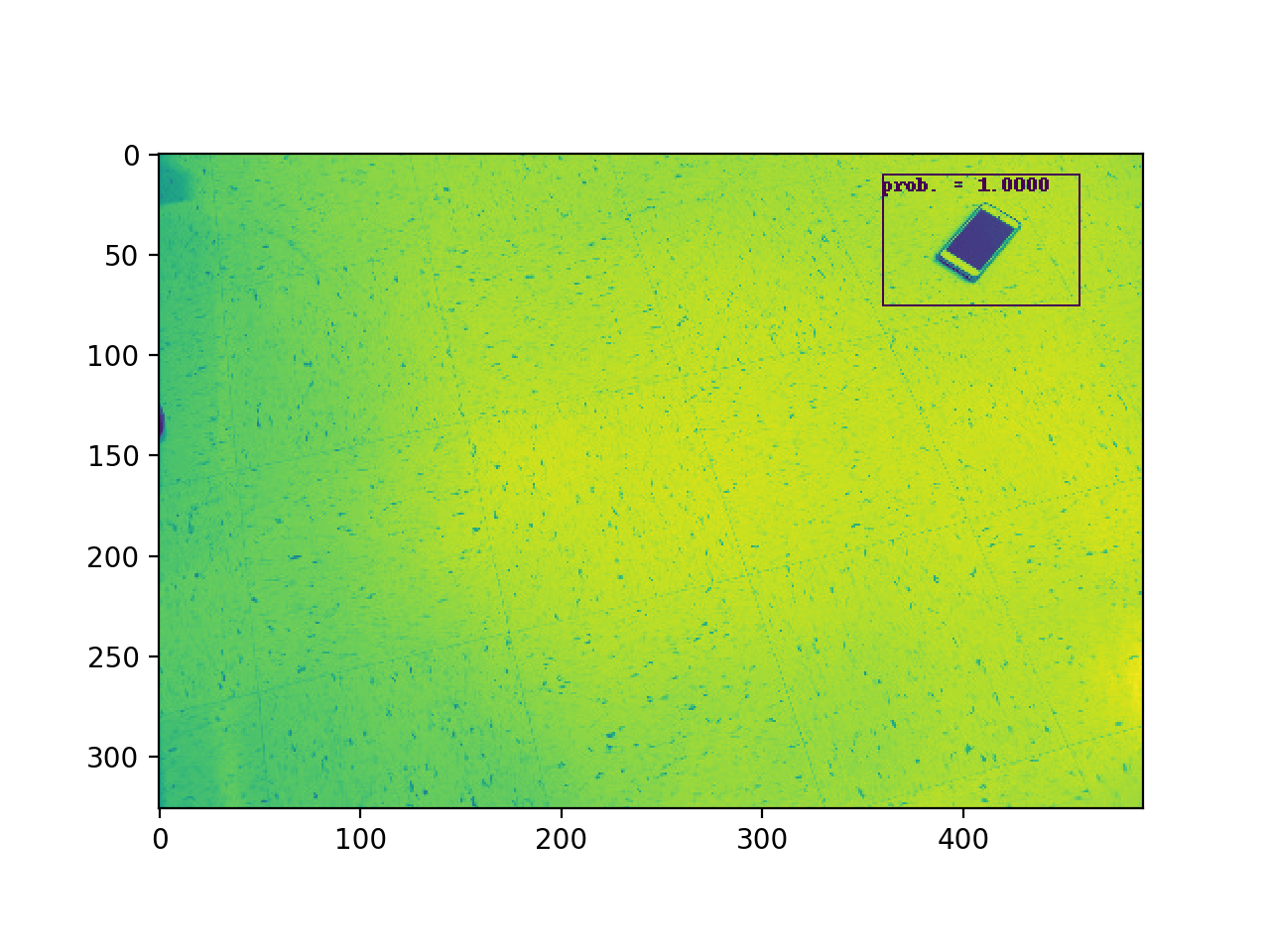
python find_phone.py ./data/x.jpg
which will print to the terminal the normalized coordinates of the phone in the test image and show the image with a box around the detected phone.
Use:
python find_phone_accuracy.py
to quantitively assess the accuracy of the phone-finding algorithm.