This repository presents an implementation of the boosting algorithm based on the Multiplicative Weights Update.
It was developed for an assignment for the Algorithms and Uncertainty course @ PUC-Rio (2022.2).
The goal of the project is to classify/distinguish a pair of digits in the 28x28 MNIST dataset. For example, if we chose the classes "5" and "6", our goal is to correctly classify the instances of those classes in the test dataset.
For the implementation of this assignment, we had two main steps.
In order to evaluate the boosting algorithm in action, we first train single-pixel classifers for each pixel of the 28x28 the image. Thus, we train 784 classifiers that only receive the information of a single pixel of each of the images of the train dataset (classifier i will be trained with the pixel i of every image in the train dataset).
Since very little information is provided, many single-pixel classifiers will have close to 0.5 accuracies, while a few classifiers that see relevant pixels may have a better accuracy.
The classifiers were trained using sklean Decision Trees. The MNIST dataset used was the one available in Keras datasets.
The comparrison of accuracies among the single-pixel classifiers can be seen in the image below.
Having trained the single-pixel classifiers, we use the boosting algorithm following the Multiplicative Weight Update method to create a better combined classifier.
At each iteration the algorithm finds a gamma-weak classifier for an distribution p over the training data. After that, we update an reward array r with a value r(i) = 1 if the sample i was mislabeled by the classifier, and r(i) = 0 otherwhise. Finally, we send the reward array r to the MWU algorithm to get a new distribution p.
This steps happens until a defined time T or until there are no more gamma-weak classifiers for the distribution p.
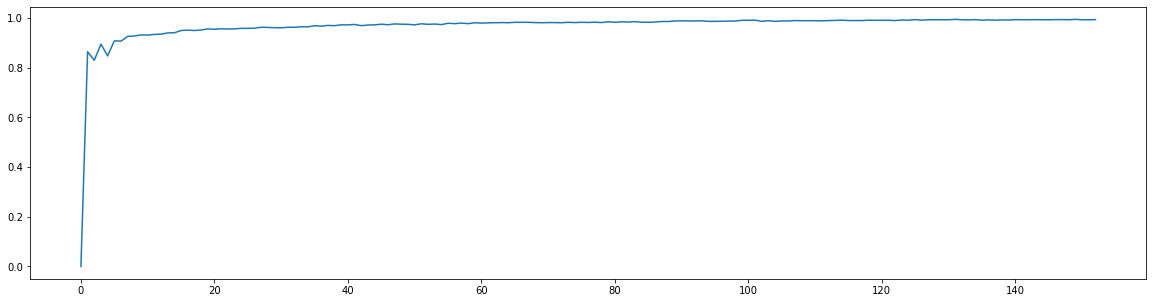
The accuracy of the combined classifier at each iteraction of the boosting algorithm is displayed in the image below.
In our experiment, the boosted classifier got a final accuracy of 0.962, while the best single-pixel classifier had a 0.864 accuracy.