[![Release][13]][14] [![Powered][17]][18] [![MIT licensed][11]][12] [![Build Status][3]][4] [![Go Report Card][5]][6] [![Downloads][15]][16] [![Docker][1]][2] [1]: https://images.microbadger.com/badges/image/xtaci/kcptun.svg [2]: https://microbadger.com/images/xtaci/kcptun [3]: https://travis-ci.org/xtaci/kcptun.svg?branch=master [4]: https://travis-ci.org/xtaci/kcptun [5]: https://goreportcard.com/badge/github.com/xtaci/kcptun [6]: https://goreportcard.com/report/github.com/xtaci/kcptun [7]: https://img.shields.io/badge/license-MIT-blue.svg [8]: https://raw.githubusercontent.com/xtaci/kcptun/master/LICENSE.md [11]: https://img.shields.io/badge/license-MIT-blue.svg [12]: LICENSE.md [13]: https://img.shields.io/github/release/xtaci/kcptun.svg [14]: https://github.com/xtaci/kcptun/releases/latest [15]: https://img.shields.io/github/downloads/xtaci/kcptun/total.svg?maxAge=1800 [16]: https://github.com/xtaci/kcptun/releases [17]: https://img.shields.io/badge/KCP-Powered-blue.svg [18]: https://github.com/skywind3000/kcp
Download precompiled Releases.
KCP Client: ./client_darwin_amd64 -r "KCP_SERVER_IP:4000" -l ":8388" -mode fast2
KCP Server: ./server_linux_amd64 -t "TARGET_IP:8388" -l ":4000" -mode fast2
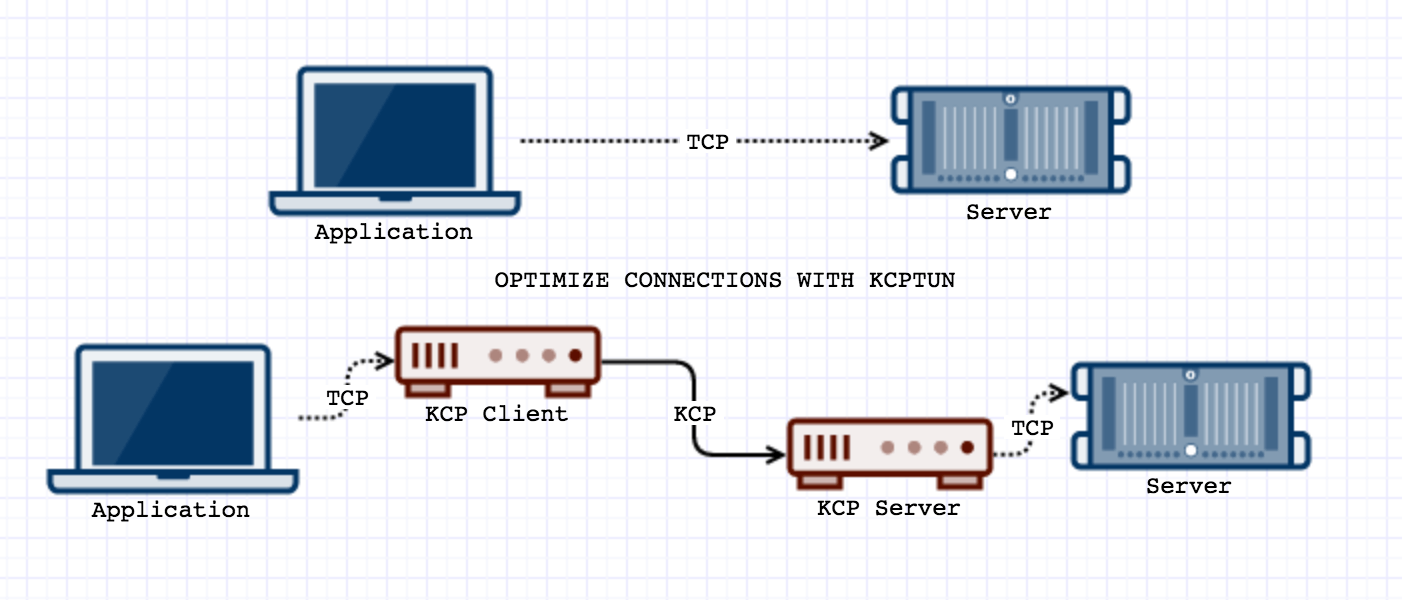
The above commands will establish port forwarding for 8388/tcp as:
Application -> KCP Client(8388/tcp) -> KCP Server(4000/udp) -> Server(8388/tcp)
$go get -u github.com/xtaci/kcptun/client
$go get -u github.com/xtaci/kcptun/server
All precompiled releases are genereated from build-release.sh script.
Q: I have a high speed network link, how to reach the maximum bandwidth?
A: Increase
-rcvwndon KCP Client and-sndwndon KCP Server simultaneously & gradually, the mininum one decides the maximum transfer rate of the link, aswnd * mtu / rtt; Then try downloading something and to see if it meets your requirements.
Q: I'm using kcptun for game, I don't want any lag happening.
A: Lag means packet loss for most of the time, lags can be improved by changing
-mode.
eg:
-mode fast3
Aggresiveness/Responsiveness on retransmission for embeded modes are:
fast3 > fast2 > fast > normal > default
$ ./client_darwin_amd64 -h
NAME:
kcptun - client(with SMUX)
USAGE:
client_darwin_amd64 [global options] command [command options] [arguments...]
VERSION:
20170120
COMMANDS:
help, h Shows a list of commands or help for one command
GLOBAL OPTIONS:
--localaddr value, -l value local listen address (default: ":12948")
--remoteaddr value, -r value kcp server address (default: "vps:29900")
--key value pre-shared secret between client and server (default: "it's a secrect") [$KCPTUN_KEY]
--crypt value aes, aes-128, aes-192, salsa20, blowfish, twofish, cast5, 3des, tea, xtea, xor, none (default: "aes")
--mode value profiles: fast3, fast2, fast, normal (default: "fast")
--conn value set num of UDP connections to server (default: 1)
--autoexpire value set auto expiration time(in seconds) for a single UDP connection, 0 to disable (default: 0)
--mtu value set maximum transmission unit for UDP packets (default: 1350)
--sndwnd value set send window size(num of packets) (default: 128)
--rcvwnd value set receive window size(num of packets) (default: 512)
--datashard value, --ds value set reed-solomon erasure coding - datashard (default: 10)
--parityshard value, --ps value set reed-solomon erasure coding - parityshard (default: 3)
--dscp value set DSCP(6bit) (default: 0)
--nocomp disable compression
--snmplog value collect snmp to file, aware of timeformat in golang, like: ./snmp-20060102.log
--snmpperiod value snmp collect period, in seconds (default: 60)
--log value specify a log file to output, default goes to stderr
-c value config from json file, which will override the command from shell
--help, -h show help
--version, -v print the version
$ ./server_darwin_amd64 -h
NAME:
kcptun - server(with SMUX)
USAGE:
server_darwin_amd64 [global options] command [command options] [arguments...]
VERSION:
20170120
COMMANDS:
help, h Shows a list of commands or help for one command
GLOBAL OPTIONS:
--listen value, -l value kcp server listen address (default: ":29900")
--target value, -t value target server address (default: "127.0.0.1:12948")
--key value pre-shared secret between client and server (default: "it's a secrect") [$KCPTUN_KEY]
--crypt value aes, aes-128, aes-192, salsa20, blowfish, twofish, cast5, 3des, tea, xtea, xor, none (default: "aes")
--mode value profiles: fast3, fast2, fast, normal (default: "fast")
--mtu value set maximum transmission unit for UDP packets (default: 1350)
--sndwnd value set send window size(num of packets) (default: 1024)
--rcvwnd value set receive window size(num of packets) (default: 1024)
--datashard value, --ds value set reed-solomon erasure coding - datashard (default: 10)
--parityshard value, --ps value set reed-solomon erasure coding - parityshard (default: 3)
--dscp value set DSCP(6bit) (default: 0)
--nocomp disable compression
--snmplog value collect snmp to file, aware of timeformat in golang, like: ./snmp-20060102.log
--snmpperiod value snmp collect period, in seconds (default: 60)
--log value specify a log file to output, default goes to stderr
-c value config from json file, which will override the command from shell
--help, -h show help
--version, -v print the version
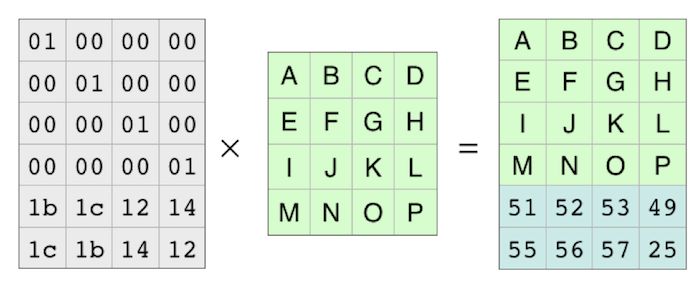
In coding theory, the Reed–Solomon code belongs to the class of non-binary cyclic error-correcting codes. The Reed–Solomon code is based on univariate polynomials over finite fields.
It is able to detect and correct multiple symbol errors. By adding t check symbols to the data, a Reed–Solomon code can detect any combination of up to t erroneous symbols, or correct up to ⌊t/2⌋ symbols. As an erasure code, it can correct up to t known erasures, or it can detect and correct combinations of errors and erasures. Furthermore, Reed–Solomon codes are suitable as multiple-burst bit-error correcting codes, since a sequence of b + 1 consecutive bit errors can affect at most two symbols of size b. The choice of t is up to the designer of the code, and may be selected within wide limits.
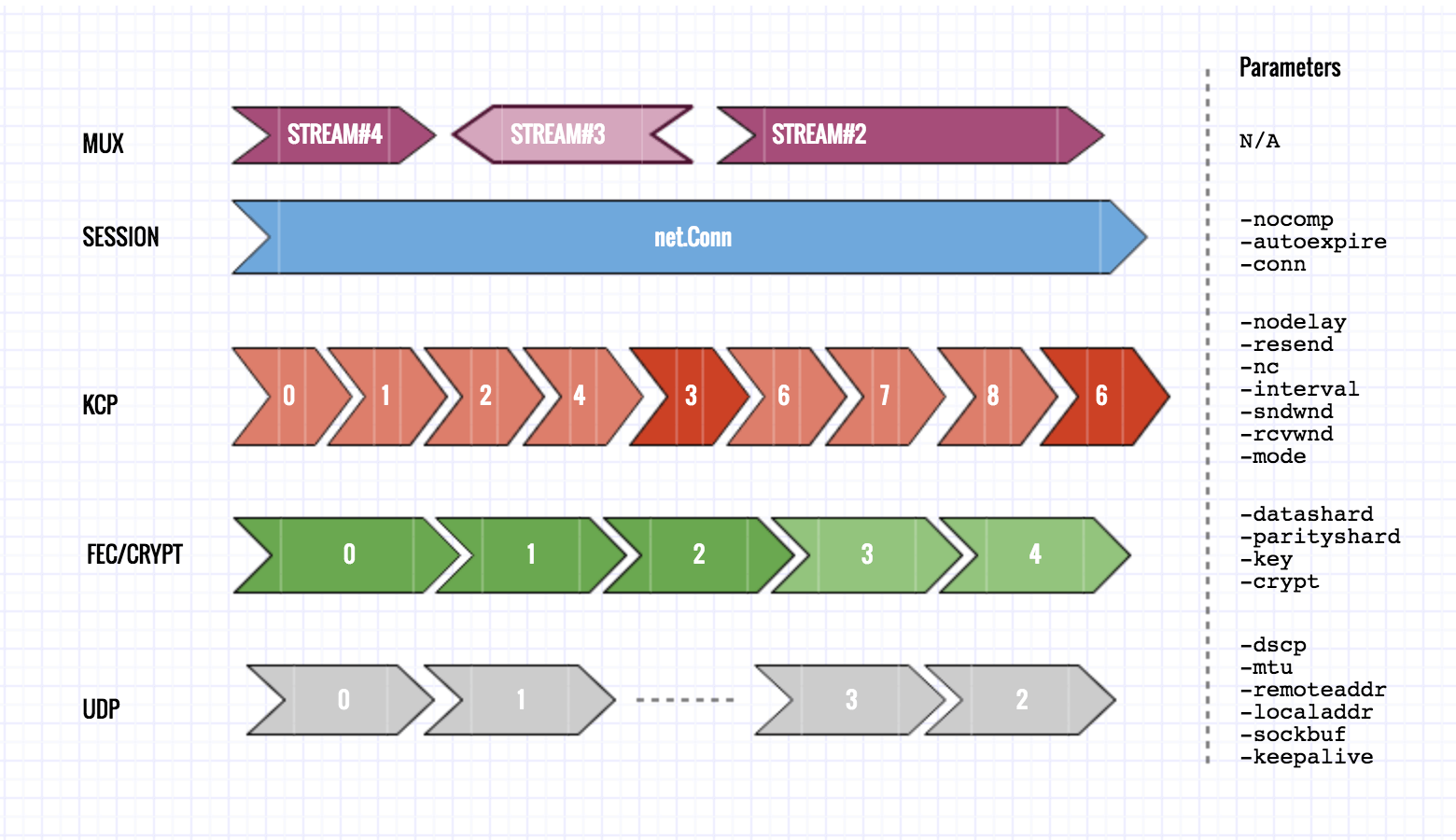
Setting parameters of RS-Code with -datashard m -parityshard n on both KCP Client & KCP Server.
Differentiated services or DiffServ is a computer networking architecture that specifies a simple, scalable and coarse-grained mechanism for classifying and managing network traffic and providing quality of service (QoS) on modern IP networks. DiffServ can, for example, be used to provide low-latency to critical network traffic such as voice or streaming media while providing simple best-effort service to non-critical services such as web traffic or file transfers.
DiffServ uses a 6-bit differentiated services code point (DSCP) in the 8-bit differentiated services field (DS field) in the IP header for packet classification purposes. The DS field and ECN field replace the outdated IPv4 TOS field.
setting each side with -dscp value, Here are some Commonly used DSCP values.
No matter what encryption you are using for application layer, if you specify -crypt none to kcptun,
the header will be PLAINTEXT to everyone; I suggest -crypt aes-128 for encryption at least .
-crypt and -key must be the same on both KCP Client & KCP Server.
NOTICE: -crypt xor is also insecure, do not use this unless you know what you are doing.
Benchmarks for crypto algorithms supported by kcptun:
BenchmarkAES128-4 200000 11182 ns/op
BenchmarkAES192-4 200000 12699 ns/op
BenchmarkAES256-4 100000 13757 ns/op
BenchmarkTEA-4 50000 26441 ns/op
BenchmarkSimpleXOR-4 3000000 441 ns/op
BenchmarkBlowfish-4 30000 48036 ns/op
BenchmarkNone-4 20000000 106 ns/op
BenchmarkCast5-4 20000 60222 ns/op
BenchmarkTripleDES-4 2000 878759 ns/op
BenchmarkTwofish-4 20000 68501 ns/op
BenchmarkXTEA-4 20000 77417 ns/op
BenchmarkSalsa20-4 300000 4998 ns/op
Routers, mobile devices are sensitive to memory consumption; by setting GOGC environment(eg: GOGC=20) will lower memory consumption. Reference: https://blog.golang.org/go15gc
kcptun has builtin snappy algorithms for compressing streams:
Snappy is a compression/decompression library. It does not aim for maximum compression, or compatibility with any other compression library; instead, it aims for very high speeds and reasonable compression. For instance, compared to the fastest mode of zlib, Snappy is an order of magnitude faster for most inputs, but the resulting compressed files are anywhere from 20% to 100% bigger.
Reference: http://google.github.io/snappy/
Compression may save bandwidth for PLAINTEXT data, such as HTTP data.
Compression is enabled by default, you can disable it by setting -nocomp on both KCP Client & KCP Server.
// Snmp defines network statistics indicator
type Snmp struct {
BytesSent uint64 // raw bytes sent
BytesReceived uint64
MaxConn uint64
ActiveOpens uint64
PassiveOpens uint64
CurrEstab uint64 // count of connections for now
InErrs uint64 // udp read errors
InCsumErrors uint64 // checksum errors from CRC32
KCPInErrors uint64 // packet iput errors from kcp
InSegs uint64
OutSegs uint64
InBytes uint64 // udp bytes received
OutBytes uint64 // udp bytes sent
RetransSegs uint64
FastRetransSegs uint64
EarlyRetransSegs uint64
LostSegs uint64 // number of segs infered as lost
RepeatSegs uint64 // number of segs duplicated
FECRecovered uint64 // correct packets recovered from FEC
FECErrs uint64 // incorrect packets recovered from FEC
FECSegs uint64 // FEC segments received
FECShortShards uint64 // number of data shards that's not enough for recovery
}Sending a SIGUSR1 signal to KCP Client or KCP Server will dump SNMP information to console, just like /proc/net/snmp. You can use this information to do fine-grained tuning.
https://github.com/skywind3000/kcp/blob/master/README.en.md#protocol-configuration
-mode manual -nodelay 1 -interval 20 -resend 2 -nc 1
Low-level KCP configuration can be altered by using manual mode like above, make sure you really UNDERSTAND what these means before doing ANY manual settings.
You can support this project by the following methods:
-
Vultr promotion code:
http://www.vultr.com/?ref=6897065 -
Paypal
https://www.paypal.me/xtaci
Your name or github name will be listed on this page by default.
- https://github.com/skywind3000/kcp -- KCP - A Fast and Reliable ARQ Protocol.
- https://github.com/klauspost/reedsolomon -- Reed-Solomon Erasure Coding in Go.
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Differentiated_services -- DSCP.
- http://google.github.io/snappy/ -- A fast compressor/decompressor.
- https://www.backblaze.com/blog/reed-solomon/ -- Reed-Solomon Explained.
- http://www.qualcomm.cn/products/raptorq -- RaptorQ Forward Error Correction Scheme for Object Delivery.
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/PBKDF2 -- Key stretching.
- http://blog.appcanary.com/2016/encrypt-or-compress.html -- Should you encrypt or compress first?
- https://github.com/hashicorp/yamux -- Connection multiplexing library.
- https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc6937 -- Proportional Rate Reduction for TCP.
- https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc5827 -- Early Retransmit for TCP and Stream Control Transmission Protocol (SCTP).
- http://http2.github.io/ -- What is HTTP/2?
- http://www.lartc.org/ -- Linux Advanced Routing & Traffic Control
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Noisy-channel_coding_theorem -- Noisy channel coding theorem