For both the browser as the NodeJS framework it adds features specifically for getting RDF resources.
Supports these features over standard fetch:
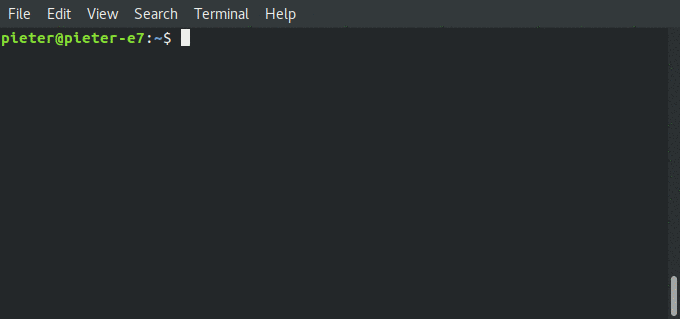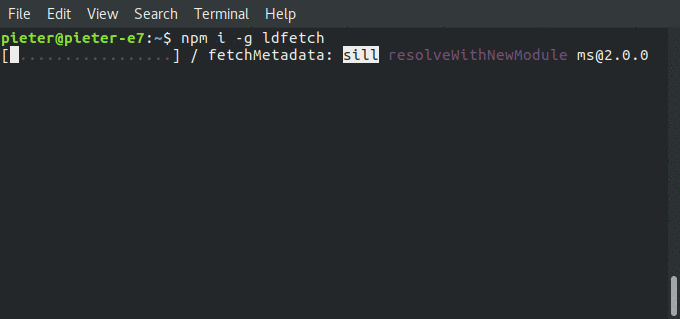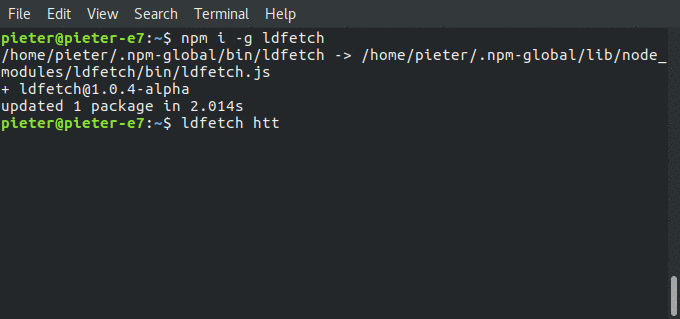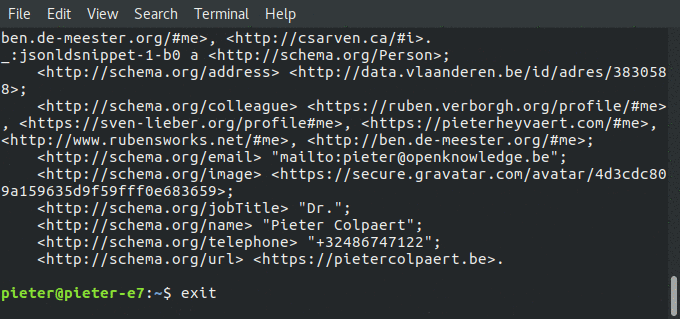
- Prefers to read TriG, yet also reads N3, Turtle, N-Triples, N-Quads, RDFa, JSON-LD snippets hidden in the HTML or just plain JSON-LD (uses content-negotiation to get an RDF representation)
- Returns the Triples/Quads containing the data in the RDFJS triple representation
- Returns the URL of the document after redirects
- Emits events for:
request,response,redirect,cache-hit,cache-missandparsed
Features for the NodeJS framework in specific:
- Automatically follows redirects
- Able to be configured with HTTP caching
- Able to limit the amount of concurrent requests and schedule these
Features for the Command Line:
- Writes data on any URL in TriG on stdout
- Extra features to automatically follow links (see
ldfetch --helpafternpm install -g ldfetch)
Install it in your project:
npm install ldfetchYou can also use JSON-LD framing from the CLI: ldfetch https://pietercolpaert.be/ --frame {} to return a JSON-LD object complying to your frame.
For full, well tested and modular SPARQL or GraphQL Web Querying, we refer to the Comunica project.
And using webpack you can compile it for browser purposes:
npm run build<script src="dist/main.js"></script>
<script>
let fetcher = new window.ldfetch();
let main = async function () {
let objects = await fetcher.get('http://ruben.verborgh.org').then(response => {
//LDFetch also exposes a frame function that can be used on the triples
//See https://json-ld.org/spec/latest/json-ld-framing/
return fetcher.frame(response.triples, {'@graph':{}});
});
console.log(objects);
}
try {
main();
} catch (e) {
console.error(e);
}
</script>A small example fetching the next page of a paged collection and returning the url
let ldfetch = require('../lib/ldfetch.js');
try {
let url = 'https://graph.irail.be/sncb/connections/';
let fetch = new ldfetch({}); //options: allow to add more headers if needed
let response = await fetch.get(url);
for (let i = 0; i < response.triples.length; i ++) {
let triple = response.triples[i];
if (triple.subject.value === response.url && triple.predicate.value === 'http://www.w3.org/ns/hydra/core#next') {
console.error('The next page is: ', triple.object.value);
}
}
fetch.frame(response.triples, {'http://www.w3.org/ns/hydra/core#next': {}}).then(object => {
console.error('Or you can also use the JSON-LD frame functionality to get what you want in a JS object', object);
});
} catch (e) {
console.error(e);
}If HTTP requests with specific headers are needed, the options object may be used by defining an object inside of it, named headers containing HTTP header names and values.
The response object will look like this:
{
"responseCode": 200,
"triples": [{},{},{}],
"url": "https://{url after redirects}"
}This library was developed by Pieter Colpaert and contributors. The source code is available under an MIT license.