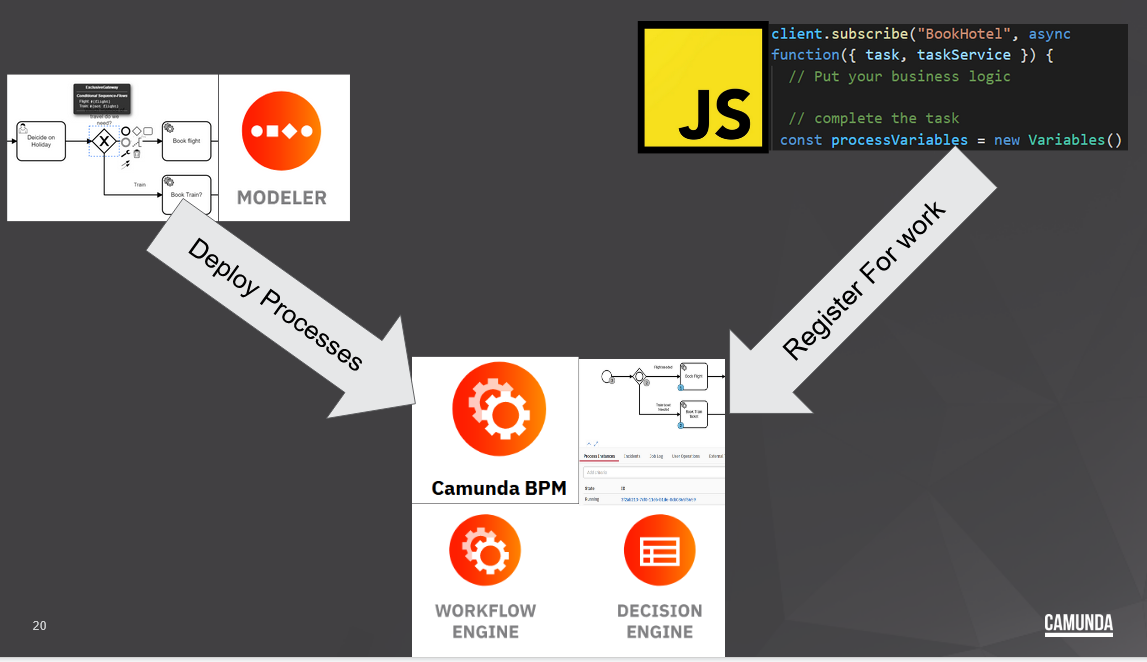
This is an example of how to model the Saga Pattern by taking a distributed group of microservices and have them orchestrated asynchronously using Camunda and BPMN.
It involves 3 groups of independend components.
- The Camunda Platform Run
- A BPMN model created by the Camunda Modeler
- JavaScript Microservice Workers
Camunda Run is at the center of everything. The modeles are deployed to it and the services are resigster for work to it.
This is a Spring Boot application that contains the Camunda Engine, The Camunda Webapps and The REST API.
You can deploy processes to it via the modeler, start process instance, administrate them and step through them as an end user.
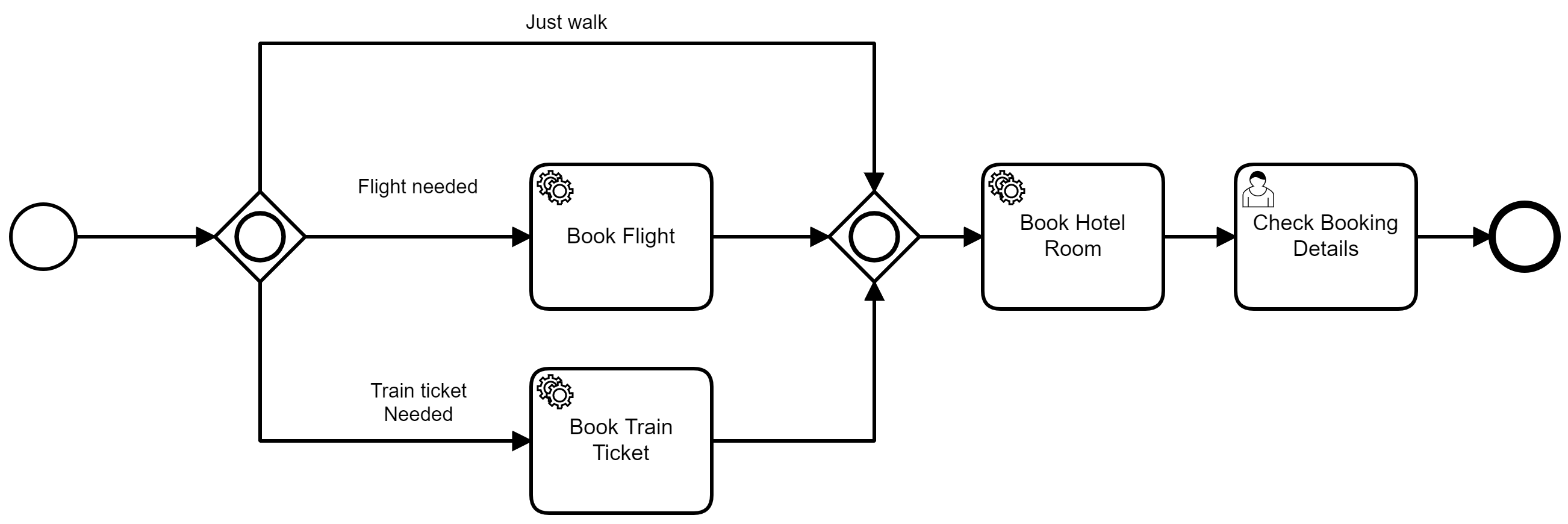
There are two process modeles in this repo. The first shows how a series of services and be used to book a holiday.
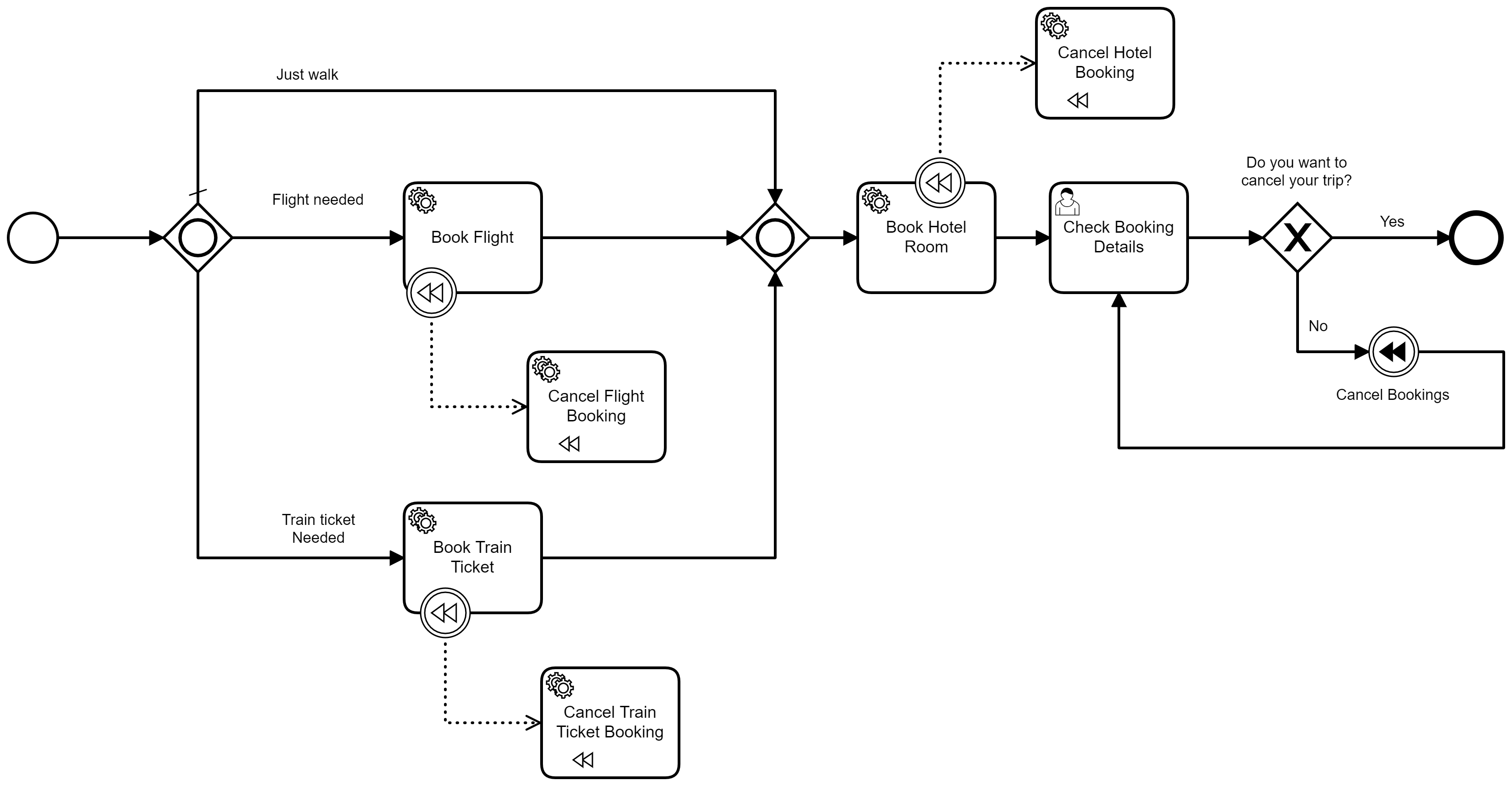
The second model has the same hotel booking feature, with the addtion of being able to reverse the actions made based on the user's choice.
The importand addtion is the use of compensation in the process. A Compensation Throw Event is thrown and any task that had been previously completed and has a Compensation Catch Eventattached to it will running the Compensation Tasklinked to it. Thus implementing the Saga Pattern.
You can find out more details about compensation and BPMN in the docs.
These are independent services written in java script which subscripe to the Camunda Patform for a Topic. The services will then be given any work for that topic. It works be defining the topic as part of the model and then having the worker subscripte to the topic of the same name.
The model semandics are descriped as follows:
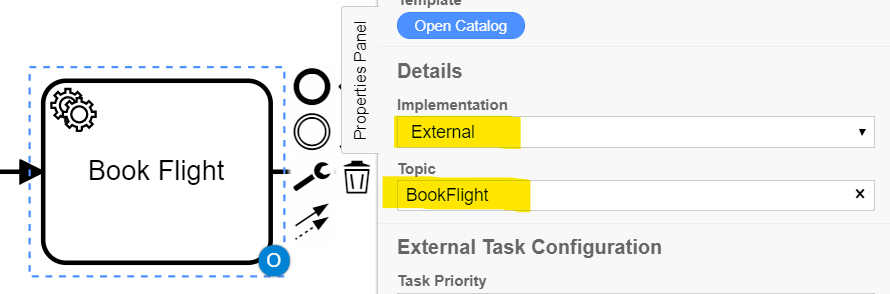
The Worker then needs to subscribe to the same topic - In this case it's BookFlight
// susbscribe to the topic: 'BookFlight'
client.subscribe("BookFlight", async function({ task, taskService }) {
// Put your business logic
await new Promise(r => setTimeout(r, 2000));
// complete the task
// Create variables to be returned to the process
const processVariables = new Variables();
processVariables.set("FlightBookingStatus", "Confirmed");
processVariables.set("FlightBookingID", create_UUID());
// Complete the task
await taskService.complete(task, processVariables);
});Workers can often subscribe to more than one topic, especially in the case where the work falls into the same context or responsibility. In this example the worker responsible for making a booking is also responsibile for canceling a booking. So the worker has a second subscription.
// susbscribe to the topic: 'CancelFlightBooking'
client.subscribe("CancelFlightBooking", async function({ task, taskService }) {
// Just a little sleep method to show that some work is doing done
await new Promise(r => setTimeout(r, 2000));
// create variables to be sent back
const processVariables = new Variables();
processVariables.set("FlightBookingStatus", "Canceled");
// complete task
await taskService.complete(task, processVariables);
});As I mentioned there are three components and each needing to be installed (but it's all pretty easy)
You can choose here to either follow the instructions to intall Camunda Platform Run on the docs page OR You can start is up using docker with the following command
docker pull camunda/camunda-bpm-platform:run-latest
docker run -d --name camunda -p 8080:8080 camunda/camunda-bpm-platform:run-latest The process models are part of this repo in the ./Models/ folder. You deploy them by downloading the Camunda Modeler, opening them up and useing the depoly button. if successful, you should see them in Camunda cockpit.
There are 3 micoservices built using the offical External Task Client.
NodeJS >= v10 is required
npm install -s camunda-external-task-client-jsOr:
yarn add camunda-external-task-client-jsIf successful you'll see the node_module folder appear.
For each of the services open up a terminal window in the directory containing the workers run the workers with node:
node ./BookHotel.jsnode ./FlightBooking.jsnode ./TrainBooking.jsOptimize and Cawemo