The Hantek DSO 2000 series provides a convenient SCPI interface; sadly using that to fetch data is rather slow., with 2 channels at 4MSamples taking (measured!) 300 seconds - mostly because of USB latency for each 4KB packet.
Here is a C file that compiles to a shared library which, if LD_PRELOADed to the binary (see below), provides a faster (and easier) way to fetch data -- just connect the script and press the SAVE TO USB button!
Currently, this patch only works for the 2022-07-27 and the 2023-03-27 version of the firmware (the two latest ones).
The patch checks the binary for a few signature bytes (eg. the firmware string "3.0.0(230327.00)"), so it should be fairly safe - it should just not patch anything on the wrong version, and not break anything.
With the patch active on your DSO and your PC connected via USB, wait for the "USB connection" icon in the bottom right corner of the DSO screen.
Pressing the SAVE TO USB button now will disable your USB console, so that the USB serial port can be used for data transfer. The scope will show the message Activating quick fetch mode. as confirmation.
Next you run the script:
receiver-src/hantek-dso-fetch.pl --cont --file /tmp/my-hantek-data.%d.csv
Now you're ready to go -- use your DSO as usual, and when you see a waveform you want to transfer to the PC just press the SAVE TO USB button. The scope locks updates (RUN/STOP will turn red), and the script will show a line about the transfer being started and then being done.
My machine with a DSO2D15 (no overclocking) needs approximately 15 seconds to transfer 2 channels with 4MSamples each - that's 20 times as fast as the SCPI way, being CPU bound on the scope (and ~30%) on my laptop.
If your script isn't running when you press the button, you'll see a notification about that; and, in case there are any communication problems (there shouldn't, though you could cause one eg. by stopping the script in the middle of a data transfer), an error message (eg. a transmission timeout) will be displayed.
--contmakes the script wait for multiple data transfers; without that, it will only fetch one.--nowtells the script to immediately fetch a dump, ie. to not wait for aSAVE TO USBkey press. This is currently implemented only with USB IP connections.--file(or just another argument) specifies where to save the CSV; a%dwill be replaced by the (unix) timestamp, so that multiple transfers won't collide with each other.--sepdefaults to aTab; by using a comma (,) you could get a "real" CSV (which I wouldn't recommend - comma vs. decimal point is likely to go wrong in your spreadsheet or data analysis software.)--deviceallows you to switch to another USB serial device instead of/dev/ttyACM0.
The script also accepts a --run argument; the string passed in will be run via the shell when a file has been received.
receiver-src/hantek-dso-fetch.pl -f /tmp/my-hantek-data.%d.wav --cont --run receiver-src/notify-script.sh
There's an example script that tries to play some audio file (via paplay) and shows a notification, so that you (working with the DSO!) immediately know that the data has been received.
The output is a CSV (really TSV ;) file with two comment lines; here's an example:
# CH1: scale 0.500000, offset 50
# CH2: scale 0.500000, offset -51
index time raw.CH1 raw.CH2 volt.CH1 volt.CH2
0 0 52 -50 0.04 0.02
1 2e-07 52 -50 0.04 0.02
2 4e-07 52 -50 0.04 0.02
The header lines are optimized for R.
You can also get a WAV file, by simply specifying the file extension .wav:
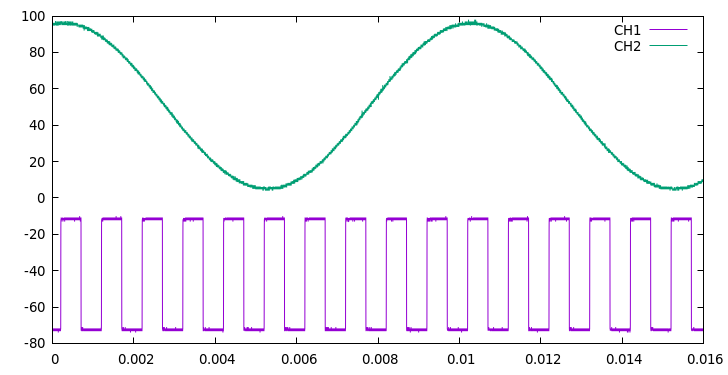
Here's an 2 x 40 KSamples example using gnuplot:
F=/tmp/test-1664046008.csv # specify your file here
gnuplot -p -e " plot '$F' using 2:3 with lines title 'CH1', '$F' using 2:4 with lines title 'CH2'"
Both the DSO patch and the fetch script use timeouts - when you see errors or are in doubt, wait two minutes (timeout is 60 seconds) and restart the local script. It will slurp up all data still in the USB pipeline, while the DSO patch will have stopped sending as soon as no receiver was available any more.
No problem. Just don't press the SAVE TO USB button after booting the DSO (then the console will still be active), or if you already used the quick fetch functionality, just stop the script and press the button 3 times in 4 seconds -- that will show a message and reactivate the USB console.
Pressing the button once more will switch to the quick fetch functionality and so will stop your USB console again.
Another (better!) way is to use /DavidAlfa/s kernel image that supports USB networking - then you can let the script fetch data via IP, and can SSH into the DSO in parallel!
BE CAREFUL -- YOU NEED TO KNOW WHAT YOU'RE DOING! YOU CAN BRICK YOUR DSO IF YOU DO SOMETHING STUPID!
Better just not do that but wait for one of David's great update packages.
You need a cross-compiler for ARM (see below); switch to the patch-src/ directory and run make.
You need a USB console (Thanks, David!!); then, by (temporarily) disabling the serial console via killall -STOP getty, run
cd /root
rz --verbose --overwrite --binary < /dev/ttyGS0 > /dev/ttyGS0
on the DSO and make sz in the patch-src/ directory to transfer the file.
Use vi /dso/app/app and insert the export... line near the end of the file; see here for the patched version:
cd $APP_DIR
export LD_PRELOAD=/lib/libdl.so.2:/dso/lib/libanolis.so.0:/root/quick-fetch.so
./$APP_REL_NAME&
Reboot the scope, and you're done!
Use this in your /etc/apt/sources.list.d/arm-hantek-env.list:
deb [ arch=armel check-valid-until=no ] https://snapshot.debian.org/archive/debian/20211213T205517Z/ testing main
deb [ arch=armel check-valid-until=no ] https://snapshot.debian.org/archive/debian/20211213T205517Z/ unstable main
and install gcc-9-cross-base=9.5.0-1cross1, libc6-armel-cross=2.33-1cross1, libc6-dev-armel-cross=2.33-1cross1.
A previous version used the USB storage interface for transferring data; but that precluded using the USB console, and had a longer latency because the data needed full preparation on the DSO before being transferred to the PC.
The current solution just does the DSO and local CSV printing in parallel and is therefore faster.
Furthermore, I suggest switching the kernel image - /DavidAlfa/ has one that also supports USB networking, so you can SSH into the DSO!