With this extension you can easily display and scroll any text on your LCD without worrying about the text length or the number of lines. Also it is possible to create a constant prefix and postfix to make data display easy and fast.
This small library extends RPLCD with the following functions:
- Scrolling text
- Pagination
- Prefix
- Postfix
- Structuring
This extension was created based on another project which implements the use of a HD44780 LCD. The idea was to make it easy to use an LCD without having to take formatting into account.
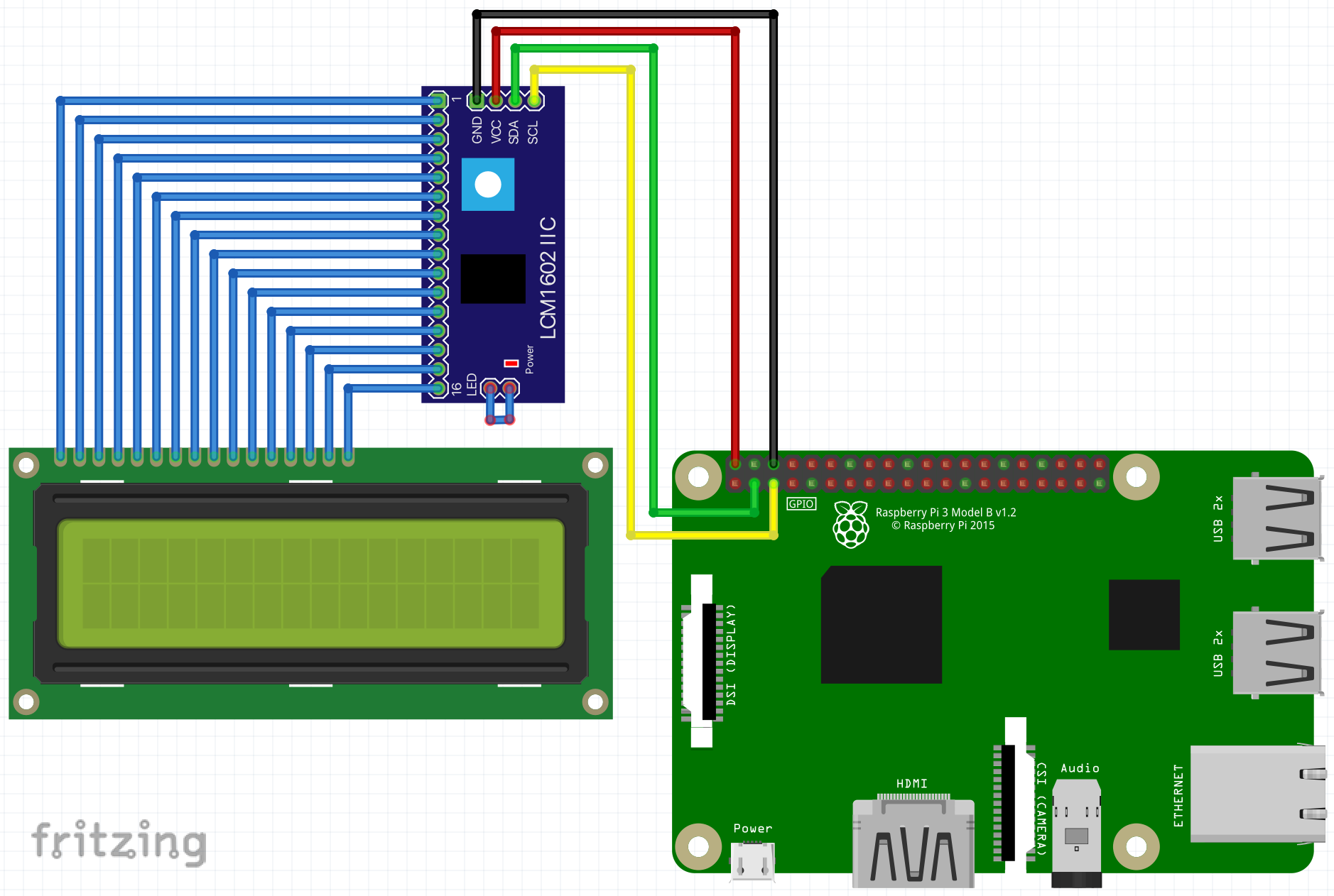
The display was connected to a Raspberry Pi via an I2C extender.
The parent project is used, among other things, to display photovoltaic data. The following demonstrates the result of using this extension module in the parent project.
The following requirements must be met in software and hardware.
- Python version >= 3.7
- RPLCD library from dbrgn (https://github.com/dbrgn/RPLCD)
Can be installed via PIP (https://pypi.org/project/RPLCD)
- LCD HD44780 - 2004 or 1602
- I2C extender for HD44780
- Raspberry Pi or other device capable of addressing the I2C display, depending on the required software prerequisites
The I2C expander can be connected as follows using a Rasbperry Pi as an example:
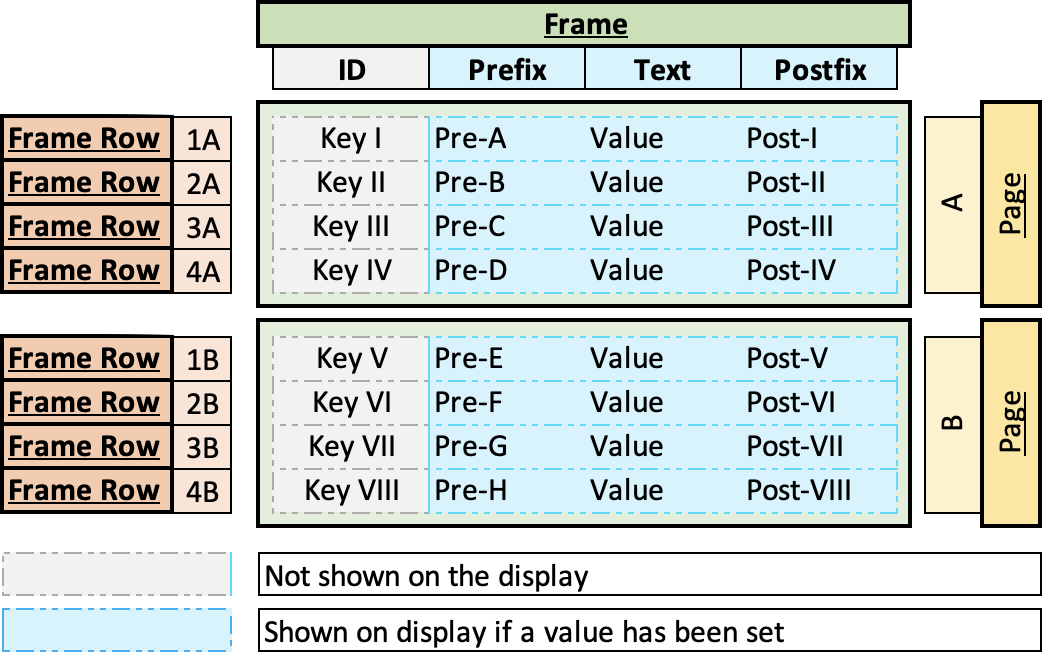
The following figure illustrates the concept of this library extension using the example of a 2004 HD44780 LCD.
A frame is used to hold the information to be displayed. The frame consists of frame rows. The maximum number of frame rows that a frame can show depends on the number that the hardware - HD44780 Display - can display. In this example, four.
If there are more rows than the frame can display, the library manages this by automatically grouping the rows into pages. In the example above, there are eight frame rows, so two pages.
A frame row contains the actual information and texts that are shown on the display. The frame row consists of four parts:
-
ID
Each frame row gets its own ID, which you can easily address and whose values can be changed according to your needs. The ID can be configured optionally. If an ID is not needed for the row, you do not have to specify one. In this case a random GUID will be taken. -
Prefix
Displays, like the one above, are often used to show data like sensor values, etc. The prefix allows you to keep a constant text like "Temp. " - for temperature - in front of your current value. You then only need to change the temperature value and not the whole line.
(This field is optional and need not be used if it is not needed) -
Text
This is the actual value you want to show on the display. -
Postfix
The postfix allows you to put a constant text like "°C " - for temperature - directly after your current value. You then only need to change the temperature value and not the whole line.
(This field is optional and need not be used if it is not needed)
- Install the required libraries from Software Prerequisites.
- Download this repository and extract it.
- Copy the module
HD44780.pyto your project - Import the module:
from HD44780 import HD44780
- Instantiate the class (Sample with a HD44780 2004 LCD - 20 columns / 4 rows):
lcd = HD44780("PCF8574", 0x27, 20, 4)
- Create a frame:
sampleFrame = lcd.Frame()
- Create frame row/s:
sampleFrameRowDate = sampleFrame.addWithGuid("-", "Date: ") sampleFrameRowTime = sampleFrame.addWithGuid("-", "Time: ")
- Show the frame on the display:
lcd.scrollFrame(sampleFrame)
Find a detailed sample script in the folder sample of this repository.
You should be able to run it from scratch with just adapting the LCD I2C settings in the config.py file.
- Example of a standard scrolling text

- Example of a text scrolling in

- Example of a text scrolling in and out

The interfaces for integration in your own code are described below.
-
HD44780(CharLCD)
This is the main class that inheritsRPLCD.i2c CharLCDfrom RPLCD-
__init__(i2c_expander, address, cols, rows, dotsize=8, expander_params=None, port=1, charmap='A00', linebreaks=True, backlight=True)The constructor of this module passes the provided parameters to the parent class
RPLCD.i2c CharLCDfrom the RPLCD library. The parameters of the I2C expander (i2c_expander), the I2C address of the expander (address) and the number of columns (cols) and rows (rows) of the physical display must be provided. All other parameters are optional and have the default value of the parentRPLCD.i2c CharLCDclass. -
writeFrame(framebuffer, pageNumber=1, scrollingFrame=False)Shows the specified frame as
framebufferon the display. If the number of frame rows is larger than the number of rows the display can show, pages are automatically created in the background. The page to be displayed can be specified by the parameterpageNumber.
The parameterscrollingFrameis only needed in the combination by the call through the functionscrollFrame. Otherwise it must always be False for a correct output.
This function only displays the content of a frame and does not include a scrolling feature. For this, the functionscrollFramemust be called. -
scrollFrame(framebuffer, scrollIn=False, scrollToBlank=False, scrollIfFit=False, delay=0.5, showFirstFrameAfterScroll=True)This is the main function that should be used to display the frame content provided in the frame as
framebufferon the LCD.
The remaining parameters provide the following functionality:-
scrollIn
IfTrue, the text is scrolled in from the right side of the LCD. Otherwise, the beginning of the text is displayed before scrolling starts. -
scrollToBlank
IfTrue, the text is scrolled out to the left until it is no longer visible. Otherwise, the scrolling stops as soon as the text is completely displayed. -
scrollIfFit
Specifies whether the text should be scrolled by the parametersscrollInandscrollToBlankif the text can also be displayed completely in the LCD row without scrolling. -
delay
Specifies the time in seconds to wait between scrolling and before displaying the inserted characters. Defines the scrolling speed. -
showFirstFrameAfterScroll
Specifies whether the display should be reset to the output - before/at the start of scrolling - when the function is ended.
-
-
-
Frame()Instantiate this class for getting a object that represents a frame that holds the frame rows.
FrameRow
This is a structure that that have the following attributes as String:idtextprefixpostfix
-
add(id, text="", prefix="", postfix="")Adds a frame row with a specific
idto the parent frame. All other fields are optional to allow you to provide a blank frame row. -
addWithGuid(text, prefix="", postfix="")Adds a frame row to the parent frame without the need to specific
id. In case a frame row does not need to be addressed by an ID, then this function can be used, which uses a generated GUID as a reference in the background. -
getFrame(id, createEmptyRowIfIdNotExist=True)Returns a frame row requested by the
idparameter. If the requestedidis not found in the parent frame, it can be created if thecreateEmptyRowIfIdNotExistparameter is specified asTrue. -
removeByIndex(id)This function
-
clear()This function clears all attributes to an empty string except the
id -
updateFrameRow(frameRow)This function will update the provided frame row in the parent frame.
All changes to this project are described in the CHANGELOG.md.
This code is licensed under the license specified in the LICENSE file.