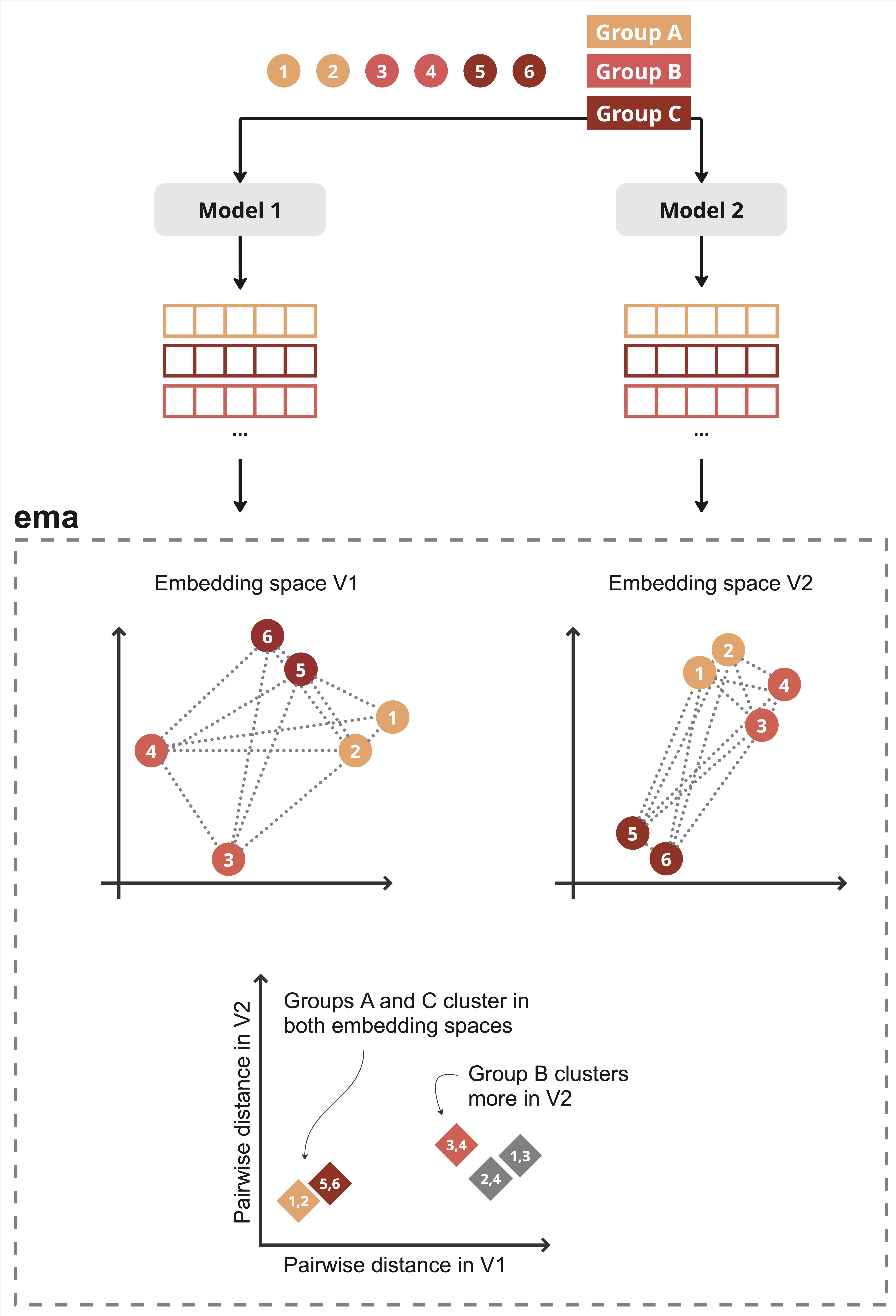
ema-tool is a Python library designed to facilitate the initial comparison of diverse embedding spaces in biomedical data. By incorporating user-defined metadata on the natural grouping of data points, ema-tool enables users to compare global statistics and understand the differences in clustering of natural groupings across different embedding spaces.
More information about the ema-tool can be found in our pre-print on bioRxiv: ema-tool: a Python Library for the Comparative Analysis of Embeddings from Biomedical Foundation Models.
Given a set of samples and metadata, and at least two embedding spaces, the ema-tool provides visualisations to compare the following aspects of the embedding spaces:
- Unsupervised Clusters: ema-tool provides a simple interface to cluster samples in the embedding space using the KMeans algorithm and compare against user-defined metadata.
- Dimensionality Reduction: ema-tool allows users to reduce the dimensionality of the embedding space using PCA, t-SNE, or UMAP.
- Pairwise Distances: ema-tool computes pairwise distances between samples in the embedding space. Different distance metrics are available, including Euclidean, Cosine, and Mahalanobis.
The following figure provides an overview of the ema-tool workflow:
You can install the ema library through pip, or access examples locally by cloning the github repo.
pip install ema-emb
git clone https://github/pia-francesca/ema
cd ema # enter project directory
pip3 install . # install dependencies
jupyter lab colab_notebooks # open notebook examples in jupyter for local exploration
To get started with the ema-tool, load the metadata and embeddings, and initialize the EmbeddingHandler object. The following code snippet demonstrates how to use the ema-tool to compare two embedding spaces:
# import ema object
from ema.ema import EmbeddingHandler
# load metadata and embeddings
metadata = pd.read_csv(FP_METADATA)
emb_esm1b = np.load(FP_EMB_ESM1b)
emb_esm2 = np.load(FP_EMB_ESM2)
# initialize embedding handler
emb_handler = EmbeddingHandler(metadata)
# add embeddings to the handler
emb_handler.add_emb_space(embeddings=emb_esm1b, emb_space_name='esm1b')
emb_handler.add_emb_space(embeddings=emb_esm2, emb_space_name='esm2')
# start analysis
emb_hander.plot_emb_hist()Two examples of how to use the ema-tool library is provided in the following colab notebooks:
To allow a flexible use, ema-tool does not include the scripts for generating the embeddings. However, here are some links to external scripts for generating protein embeddings from fasta files using the following models:
If you have any questions or suggestions, please feel free to reach out to the authors: francesca.risom@hpi.de.
This project is licensed under the MIT License - see the LICENSE file for details.