Fuzion is a simple and easy way to deploy and manage ZKsync paymasters. It is a web application that allows developers to deploy paymasters on ZKsync with a few clicks. The paymaster is designed in a composable way, making it easy to manage and update the paymaster.
I found that most of the projects just use the basic paymaster provided by ZKsync. But we can do a lot more with the paymaster and have to consider different use cases like user verification, payment processing, and other custom logic. So, I decided to build a platform that allows developers to deploy and manage paymasters easily. This will help developers to focus on their core product and not worry about the paymaster.
Deploy Paymaster on ZKsync with a few clicks. Just enter the required details and click on the create button.
Deployed paymasters can be managed easily. You can view the list of paymasters, details of the paymaster, and update the paymaster.
The Paymaster is designed in a composable way. It is divided into different modules like Validator, Payport, and Hook. This makes it easy to manage and update the Paymaster.
Anyone can create and register their own modules. These modules can be used in the Paymaster to add custom logic.
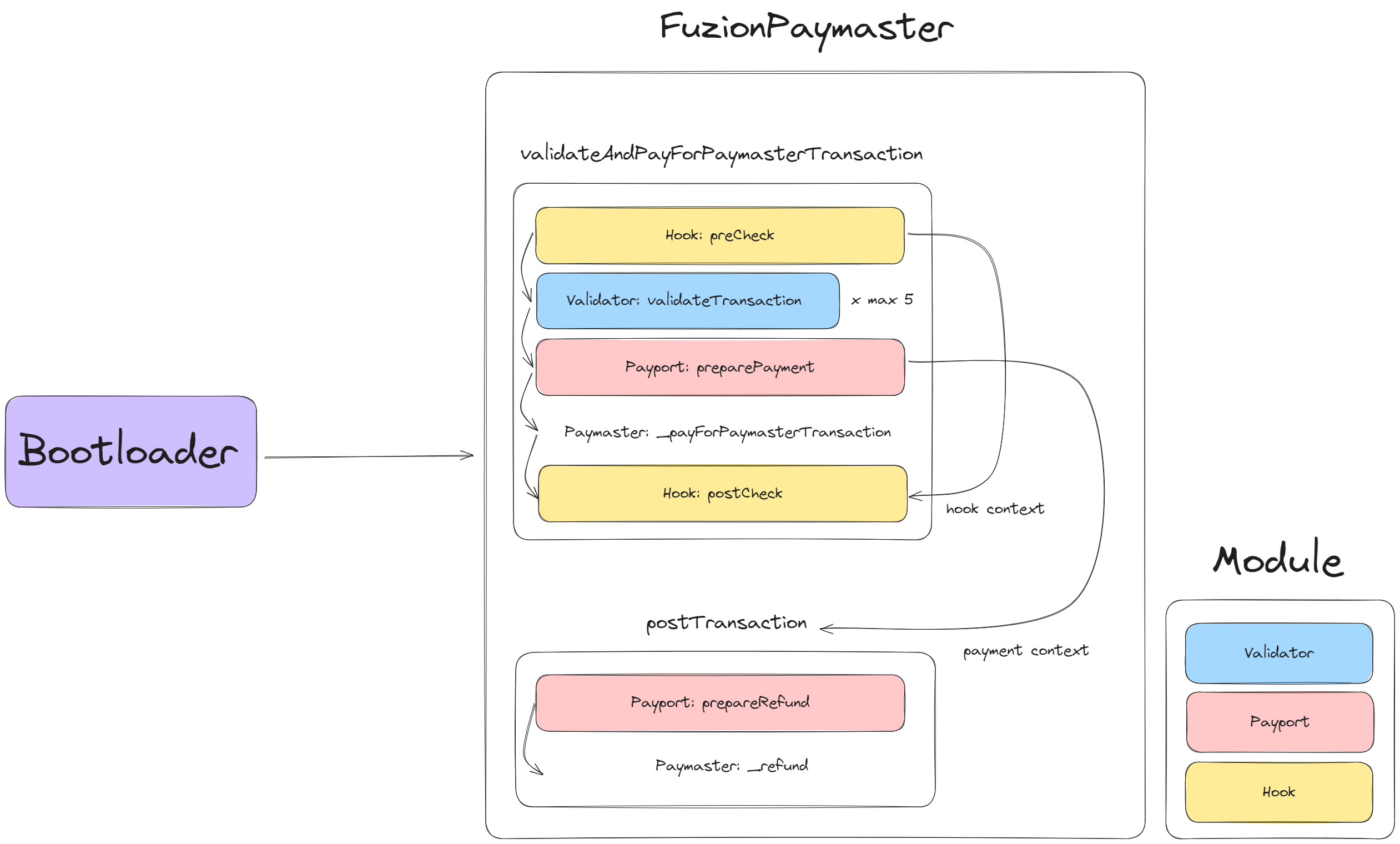
This diagram illustrates the structure of the FuzionPaymaster smart contract. The process is divided into two main stages: validateAndPayForPaymasterTransaction and postTransaction. Each stage involves various modules (Validator, Payport, Hook) that execute specific tasks. Below is a step-by-step explanation of how the function operates.
This function is responsible for validating the transaction and processing the payment. The process follows these steps:
-
Hook: preCheck
- In this step, a pre-check is performed to ensure the transaction meets initial conditions before processing.
-
Validator: validateTransaction
- This step validates the transaction up to 5 times using different Validator modules. This can include checking the transaction’s signature, nonce, gas requirements, and other parameters.
-
Payport: preparePayment
- Once the transaction is validated, this step prepares the payment by setting the payment context and gathering necessary information. The payment can be made in ETH or ERC20 tokens based on the paymaster input selector.
-
Paymaster: _payForPaymasterTransaction
- After preparing the payment, the payment is processed and transferred to the bootloader by the paymaster.
-
Hook: postCheck
- A post-check is conducted after the transaction is completed to ensure everything was processed correctly. Additional actions can be taken in this step.
This function handles any post-transaction tasks that might be necessary after a transaction is successfully processed:
-
Payport: prepareRefund
- If the payment was done in ERC20 tokens, maybe the refund is required because of overcharging or any other reason. This step prepares the refund by taking the payment data from the context.
-
Paymaster: _refund
- The refund is processed and transferred to the user by the paymaster.
- Validator (Blue): Validates the transaction through various checks.
- Payport (Pink): Prepares payments and refunds.
- Hook (Yellow): Manages pre- and post-transaction checks and allows for additional logic to be implemented.
The actual payment and refund are handled by the Paymaster contract. Because modules are designed to be called externally to prevent the storage collision and other possible errors by using the delegatecall method, the payment and refund are done by the Paymaster contract.
In the case of modular account, the user can choose which module to call when initiating the transaction. But in the case of the paymaster, the paymaster contract is the one that calls the modules and pays for the transaction. Thus, the paymaster contract needs to know which module to call not the user. That's why the default modules are defined in the FuzionPaymaster contract. It should be controlled by the admin of the paymaster not the user.
- Basic UI Design
- Wallet Connection and Login
- Design Paymaster Structure
- Paymaster Deployment on web app
- Paymaster List by User
- Paymaster Details
- Paymaster Module Registration
- Paymaster Update
- Clone the repository
git clone https://github.com/piatoss3612/ZKsync-fuzion.git- Install the dependencies
cd frontend && yarn install- Run the application
yarn dev- Open the application in the browser
http://localhost:3000This project is licensed under the MIT License - see the LICENSE file for details.
If you have any suggestions or improvements, feel free to create an issue or a pull request. This project is open for contributions. 🚀