💾⏰💪
Thanks for your interest in this open source project. This repo is the go implementation of the Spacemesh p2p full node software.
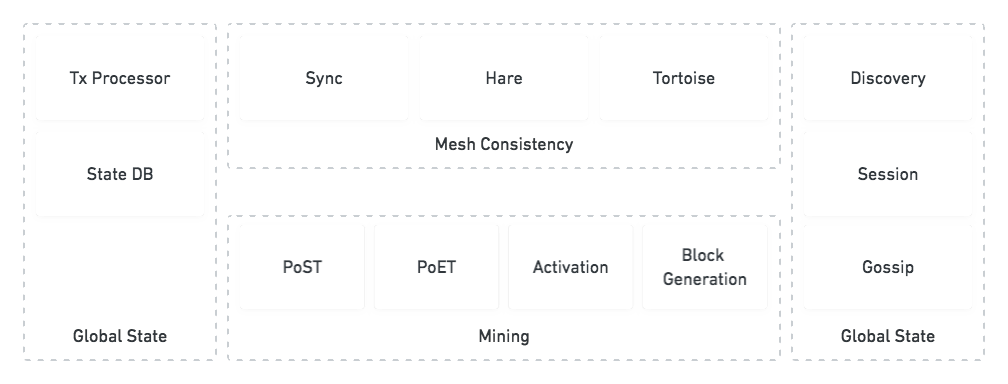
Spacemesh is a decentralized blockchain computer using a new race-free consensus protocol that doesn't involve energy-wasteful proof of work.
We aim to create a secure and scalable decentralized computer formed by a large number of desktop PCs at home.
We are designing and coding a modern blockchain platform from the ground up for scale, security and speed based on the learnings of the achievements and mistakes of previous projects in this space.
To learn more about Spacemesh head over to https://spacemesh.io.
To learn more about the Spacemesh protocol watch this video.
Spacemesh is designed to create a decentralized blockchain smart contracts computer and a cryptocurrency that is formed by connecting the home PCs of people from around the world into one virtual computer without incurring massive energy waste and mining pools issues that are inherent in other blockchain computers, and provide a provably-secure and incentive-compatible smart contracts execution environment.
Spacemesh is designed to be ASIC-resistant and in a way that doesn’t give an unfair advantage to rich parties who can afford setting up dedicated computers on the network. We achieve this by using a novel consensus protocol and optimize the software to be most effectively be used on home PCs that are also used for interactive apps.
Provide dapp and app developers with a robust way to add value exchange and other value related features to their apps at scale. Our goal is to create a truly decentralized cryptocurrency that fulfills the original vision behind bitcoin to become a secure trustless store of value as well as a transactional currency with extremely low transaction fees.
go-spacemesh is designed to be installed and operated on users' home PCs to form one decentralized computer. It is going to be distributed in the Spacemesh App but people can also build and run it from source code.
We are working hard towards our first major milestone - a public permissionless testnet running the Spacemesh consensus protocol.
Thank you for considering to contribute to the go-spacemesh open source project!
We welcome contributions large and small and we actively accept contributions.
-
go-spacemesh is part of The Spacemesh open source project, and is MIT licensed open source software.
-
We welcome collaborators to the Spacemesh core dev team.
-
You don’t have to contribute code! Many important types of contributions are important for our project. See: How to Contribute to Open Source?
-
To get started, please read our contributions guidelines.
-
Browse Good First Issues.
-
Get ethereum awards for your contribution by working on one of our gitcoin funded issues.
Please read the Spacemesh full FAQ.
git clone git@github.com:spacemeshos/go-spacemesh.gitor fork the project from https://github.com/spacemeshos/go-spacemesh
Since the project uses Go Modules it is best to place the code outside your $GOPATH. Read this for alternatives.
Building is supported on OS X, Linux, FreeBSD, and Windows.
Install Go 1.18 or later for your platform, if you haven't already.
On Windows you need to install make via msys2, MingGW-w64 or mingw
Ensure that $GOPATH is set correctly and that the $GOPATH/bin directory appears in $PATH.
Before building we need to set up the golang environment. Do this by running:
make installTo build go-spacemesh for your current system architecture, from the project root directory, use:
make build(On FreeBSD, you should instead use gmake build. You can install gmake with pkg install gmake if it isn't already installed.)
This will build the go-spacemesh binary, saving it in the build/ directory.
To build a binary for a specific architecture directory use:
make darwin | linux | freebsd | windowsPlatform-specific binaries are saved to the /build directory.
To build code without using make the CGO_LDFLAGS environment variable must be set
appropriately. The required value can be obtained by running make print-ldflags or
make print-test-ldflags.
This can be done in 3 ways:
- Setting the variable in the shell environment (e.g., in bash run
CGO_LDFLAGS=$(make print-ldflags)). - Prefixing the key and value to the
gocommand (e.g.,CGO_LDFLAGS=$(make print-ldflags) go build). - Using
go env -w CGO_LDFLAGS=$(make print-ldflags), which persistently adds this value to Go's environment for any future runs.
There's a handy shortcut for the 3rd method: make go-env or make go-env-test.
go-spacemesh is p2p software which is designed to form a decentralized network by connecting to other instances of go-spacemesh running on remote computers.
To run go-spacemesh you need to specify the parameters shared between all instances on a specific network.
You specify these parameters by providing go-spacemesh with a json config file. Other CLI flags control local node behavior and override default values.
-
Build go-spacemesh from source code.
-
Download the testnet's json config file. Make sure your local config file suffix is
.json. -
Start go-spacemesh with the following arguments:
./go-spacemesh --listen [a_multiaddr] --config [configFileLocation] -d [nodeDataFilesPath]
Example:
Assuming
tn1.jsonis a testnet config file saved in the same directory as go-spacemesh, use the following command to join the testnet. The data folder will be created in the same directory as go-spacemesh. The node will use TCP port 7513 and UDP port 7513 for p2p connections:./go-spacemesh --listen /ip4/0.0.0.0/tcp/7513 --config ./tn1.json -d ./sm_data
-
Build the CLI Wallet from source code and run it:
-
Use the CLI Wallet commands to setup accounts, start smeshing and execute transactions.
./cli_wallet-
Run go-spacemesh to join a testnet without mining (see above).
-
Run the CLI Wallet to create a coinbase account. Save your coinbase account public address - you'll need it later.
-
Stop go-spacemesh and start it with the following params:
./go-spacemesh --listen [a_multiaddr] --config [configFileLocation] -d [nodeDataFilesPath] --coinbase [coinbase_account] --start-mining --post-datadir [dir_for_post_data]
Example:
./go-spacemesh --listen /ip4/0.0.0.0/tcp/7513 --config ./tn1.json -d ./sm_data --coinbase 0x36168c60e06abbb4f5df6d1dd6a1b15655d71e75 --start-mining --post-datadir ./post_data
-
Use the CLI wallet to check your coinbase account balance and to transact
NOTE: if tests are hanging try running ulimit -n 400. some tests require that to work.
make testor
make coverWe've enabled continuous integration on this repository in GitHub. You can read more about our CI workflows.
A Dockerfile is included in the project allowing anyone to build and run a docker image:
docker build -t spacemesh .
docker run -d --name=spacemesh spacemeshOn Windows you will need the following prerequisites:
- Powershell - included by in Windows by default since Windows 7 and Windows Server 2008 R2
- Git for Windows - after installation remove
C:\Program Files\Git\binfrom System PATH (if present) and addC:\Program Files\Git\cmdto System PATH (if not already present) - Make - after installation add
C:\Program Files (x86)\GnuWin32\binto System PATH - Golang
- GCC. There are several ways to install gcc on Windows, including Cygwin. Instead, we recommend tdm-gcc which we've tested.
Close and reopen powershell to load the new PATH. You can then run the command make install followed by make build as on UNIX-based systems.
- You can run a local Spacemesh Testnet with 6 full nodes, 6 user accounts, and 1 POET support service on your computer using docker.
- The local testnet full nodes are built from this repo.
- This is a great way to get a feel for the protocol and the platform and to start hacking on Spacemesh.
- Follow the steps in our Local Testnet Guide
- Please visit our wiki
- Browse project go docs
- Spacemesh Protocol video overview
- Introduce yourself and ask anything on Discord.
- DM @teamspacemesh