This is the implementation of my paper titled "A Light Weighted Deep Learning Framework for Multiple Sclerosis Lesion Segmentation" (https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/8985674) published in 2019 Fifth International Conference on Image Information Processing (ICIIP).
MS is a long-term, or persistent, condition that affects the central nervous system (CNS) which often leads to disability. The CNS is made up of optic nerve, brain and spinal cord. Hardening of tissue in the body is defined as sclerosis. In MS, scar tissue appears in the CNS. This leads to travelling of messages between the brain and rest of the body in an uneven way.
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) can reveal significant scars, also called lesions, on the brain or spinal cord.Lesions show up as white or dark spots, depending on the type of scan.
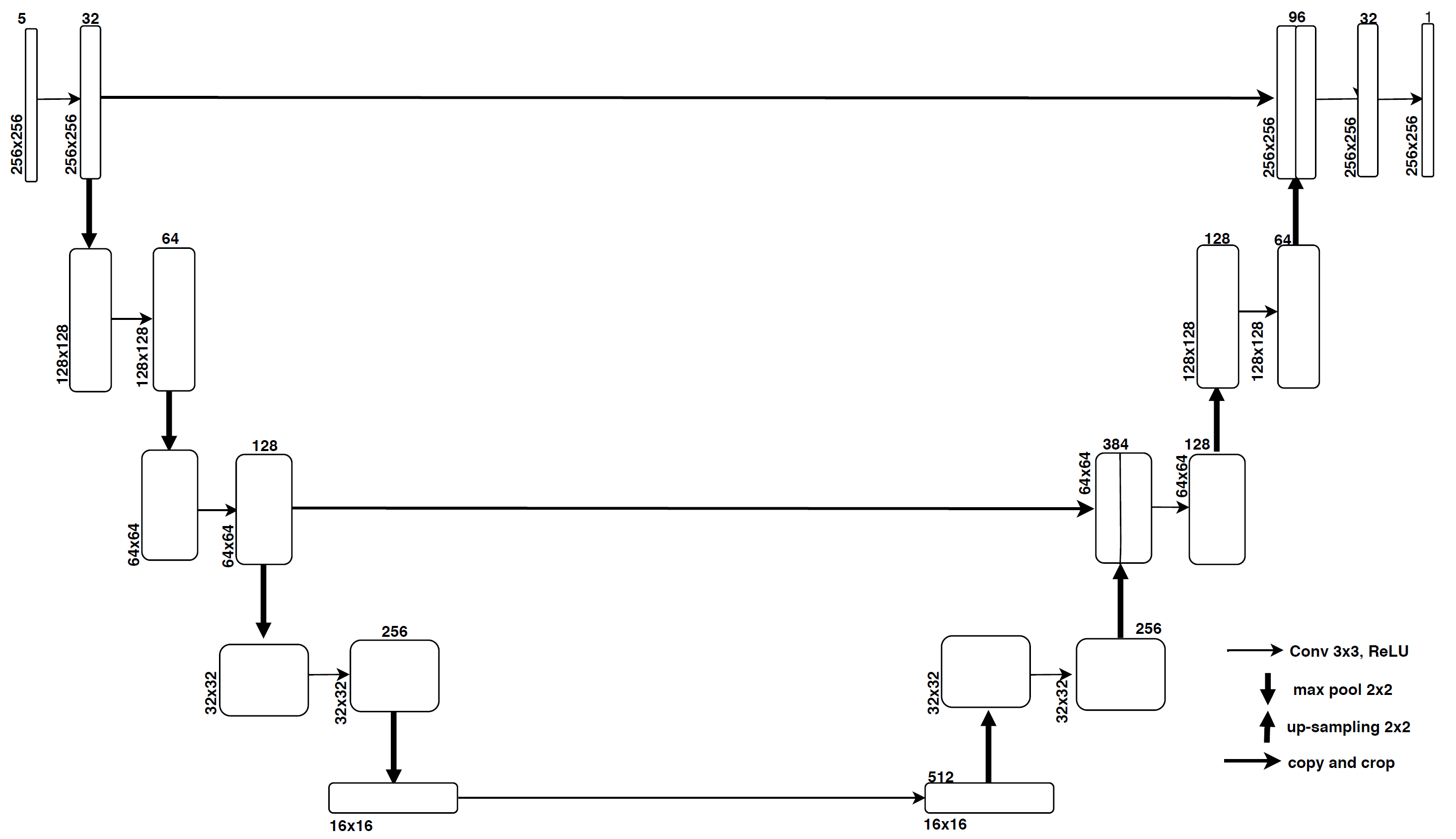
MICCAI 2016 Dataset : MRI Scans of 15 patients acquired in different image domains with 5 different modalities T1-w, MPRAGE, FLAIR, T1-w gadolinium enhanced and T2-w/DP contrast enhanced images. The scans were already provided with necessary pre-processing like image de-noising, intensity corrected and skull-stripped.
- Each slice in each modality are concatenated along its 3rd dimension and used as an input.
- Resizing the input image is (256 * 256 * 5).
- Removing Null Samples.
- Normalization and Standardization:
Normalisation(X) = X / max(X) + epsilon Standardization(X) = (X - mean(X))/(std(X) + epsilon) where epsilon = 0.00001 (a very small value) and X represents one channel of any modalityof size (h * w).
- Total number of samples : 2834
- Input size : (256 * 256 * 5) a.
- Weights Initialization : Xavier initialization.
- Mini batch size of 32
- Optimizer : Adam
- Learning rate : 0.001.
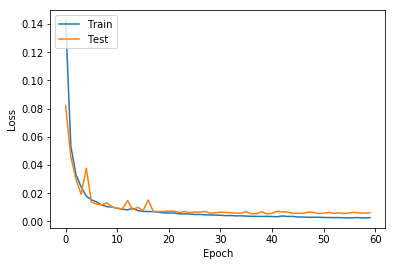
- Loss function : Binary Cross Entropy
- Epochs : 60
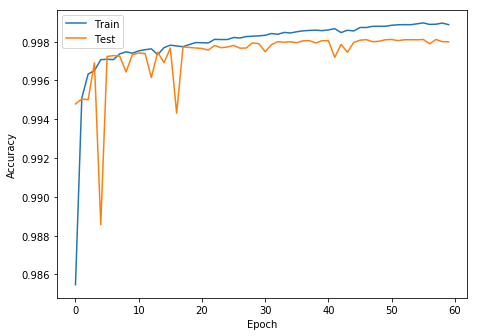
- Accuracy : 96.79%
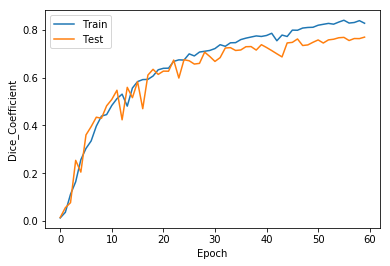
- DSC : 0.76
- Sensitivity : 0.65
- Specificity : 0.86