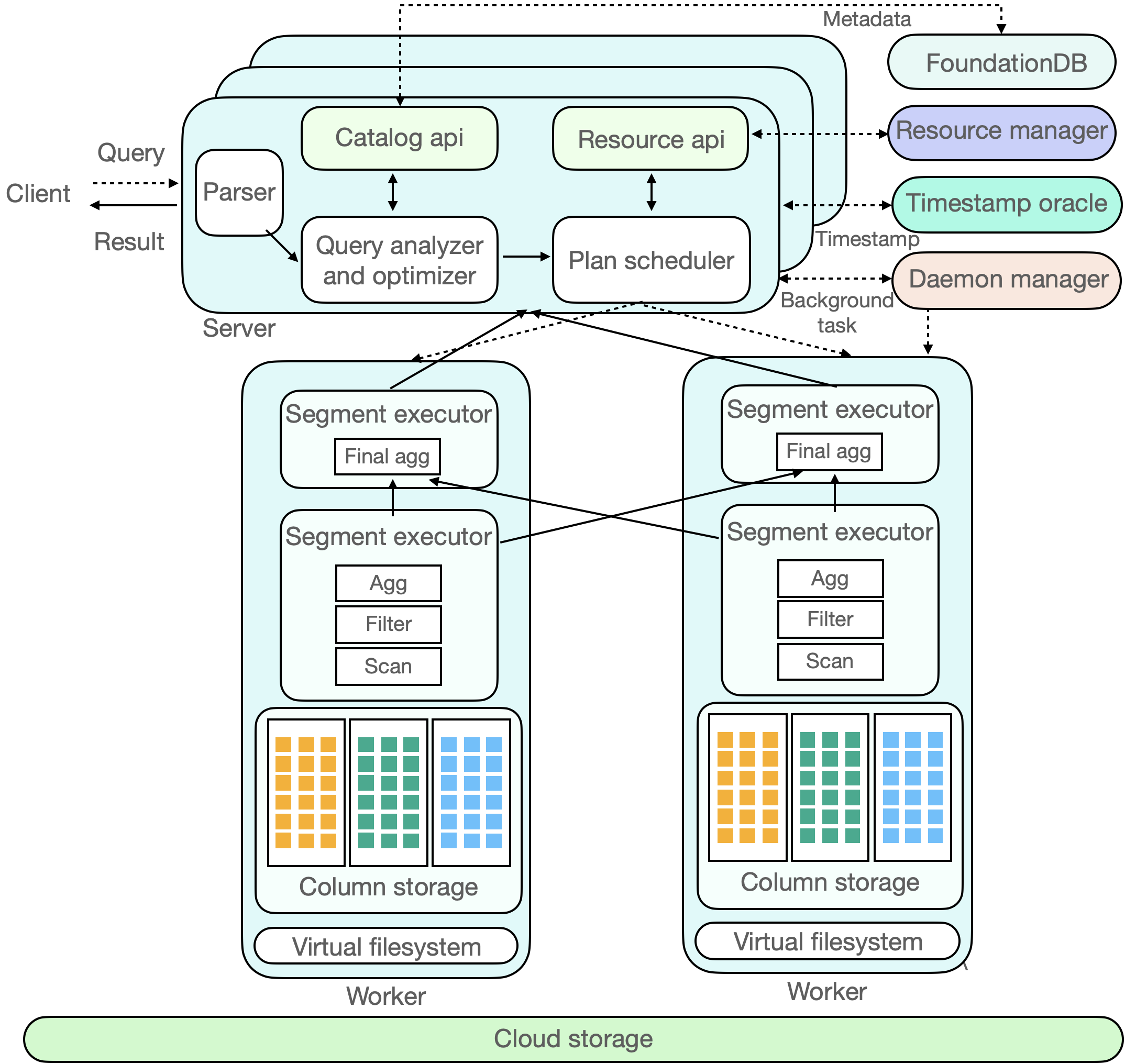
ByConity is a data warehouse designed for changes in modern cloud architecture. It adopts a cloud-native architecture design to meet the requirements of data warehouse users for flexible scaling, separation of reads and writes, resource isolation, and strong data consistency. At the same time, it provides excellent query and write performance.
ByConity is using a large number of mature OLAP technologies, such as column storage engine, MPP execution, intelligent query optimization, vectorized execution, Codegen, indexing, and data compression; it also makes special technological innovations for the cloud scenarios and storage-computing separation architecture.
ByConity is built on top of ClickHouse. We appreciate the excellent work of the ClickHouse team.
You can quickly bring up a ByConity playground by following this simple guide.
A minimal ByConity cluster include:
- A FoundationDB database cluster to store meta data.
- A HDFS cluster to store data.
- A ByConity server to receive request from clients.
- A ByConity read worker to carry execution of read requests forward from server.
- A ByConity write worker to carry execution of write requests forward from server.
- A ByConity TSO server to provide timestamp
- A ByConity daemon manager to manage background jobs that run in server
The easiest way to build ByConity is built in docker
It can also be built the following operating systems:
- Linux
The following packages are required:
- Git
- CMake 3.17 or newer
- Ninja
- C++ compiler: clang-11 or clang-12
- Linker: lld
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get install git cmake ccache python3 ninja-build libssl-dev libsnappy-dev apt-transport-https
# install llvm 12
sudo apt install lsb-release wget software-properties-common gnupg # pre-requisites of llvm.sh
wget https://apt.llvm.org/llvm.sh
chmod +x llvm.sh
sudo ./llvm.sh 12
git clone --recursive https://github.com/ByConity/ByConity.git byconity
cd byconity
mkdir build && cd build
export CC=clang-12
export CXX=clang++-12
cmake ..
ninja
Then you can find the binary in the programs folder
clickhouse-client # byconity client
clickhouse-server # byconity server
clickhouse-worker # byconity worker
tso_server # byconity tso
daemon_manager # byconity daemon manager
resource_manager # byconity resource manager
Assuming you have FoundationDB and HDFS set up and running locally:
- Modify the template config
- Run the local deployment script to run all the components
The config templates can be found in deploy/template. You should replace the following in in byconity-server.xml and byconity-worker.xml:
Path_To_FDBwith path to your FoundationDBfdb.clusterfile pathHOST:PORTwith the host and port of your name node in your HDFS cluster
<catalog_service>
<type>fdb</type>
<fdb>
<cluster_file>/Path_To_FDB/fdb.cluster</cluster_file>
</fdb>
</catalog_service>
...
<tso_service>
<port>49963</port>
<type>fdb</type>
<fdb>
<cluster_file>/Path_To_FDB/fdb.cluster</cluster_file>
</fdb>
<tso_window_ms>3000</tso_window_ms>
<tso_max_retry_count>3</tso_max_retry_count>
</tso_service>
...
<hdfs_nnproxy>hdfs://HOST:PORT</hdfs_nnproxy>
- Make sure you have
python3.9andtmuxinstalled - Install missing libraries if any. For example:
pip3.9 install psutils
- Run tmux in another terminal
- Run the deploy script in a separate terminal.
template_pathsandprogram_dirargs are compulsorycd ByConity/deploypython3.9 deploy.py --template_paths template/byconity-server.xml template/byconity-worker.xml --program_dir /home/ByConity/build/programs- There are other arguments for the script. For example, you can run 2 servers with argument
-s 2