This repository contains the source code implementation of the following papers:
-
''Harmony: Overcoming the hurdles of GPU memory capacity to train massive DNN models on commodity servers'', which appeared at VLDB 2022.
-
''Doing more with less: Training large DNN models on commodity servers for the masses'', which appeared at HotOS 2021.
This work was done as part of Microsoft Research's Project Fiddle. This source code is available under the MIT License.
-
harmony: the Harmony source code, with detailed instructions, various example scripts, as well as previous results. -
model_lib: the model libary containing model code that is not included in pytorch, such as the transformer library from huggingface. -
util_lib: the customized utility libary.
To run Harmony, the easiest way is to use the standard nvidia's container (nvcr.io/nvidia/pytorch:20.03-py3) which satisfies most dependencies. It can be launched by:
./launch.shOnce getting into the container, the remaining dependencies can be satisified by running:
./install.sh-
Harmony was developed in the environment of Python 3.6.9, PyTorch 1.5.0a0, CUDA 10.1.243, cuDNN 7.6.3, NCCL 2.4.8, Nvidia driver 418, Ubuntu 18.04.3 LTS.
-
Harmony was developed with Nivida GPUs.
-
Harmony does not modfiy PyTorch library and may remain portable to different versions.
-
GLUE (including MRPC): It can be downloaded by running this script and unpacked to a directorary
/data/glue/MRPC. -
WikiText-2 and WikiText-103: It can be downloaded from here and unpacked to a directorary
/data/wikitext-2-tokensand/data/wikitext-103-tokens. -
ImageNet: The ImageNet ILSVC 2012 can be downloaded by running this script and unpacked to a directory
/data/imagenet/.
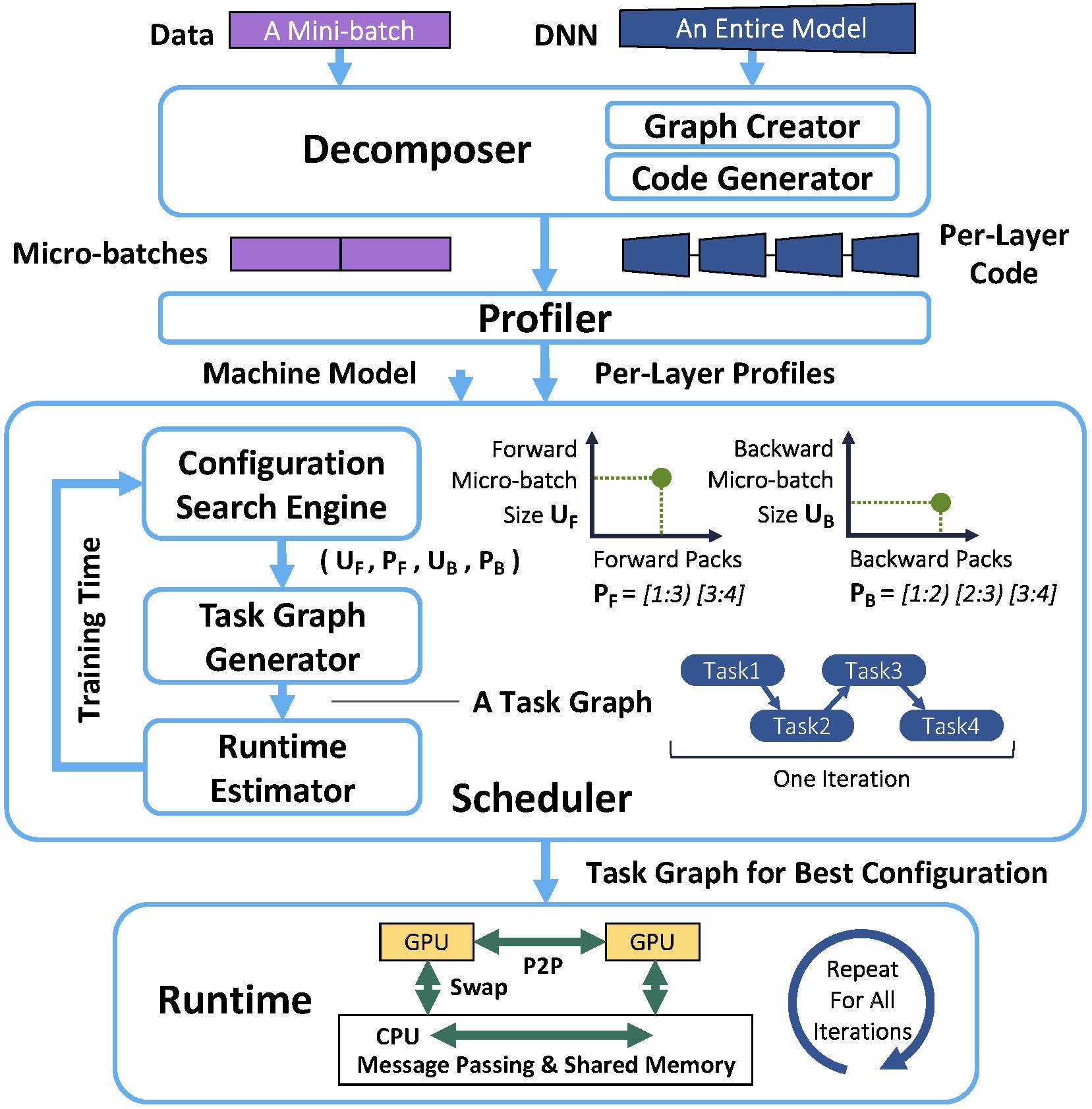
The end-to-end workflow of Harmony can be illustrated by the figure below:
For example, to run a BERT-Large with Harmony, we can go through following steps:
cd harmony/1_decomposer/bert_thomwolf && ./run_bert_large.shcd ../../2_profiler/bert_thomwolf && ./run_bert_large.shcd ../../3_scheduler && ./run_bert_large.shcd ../4_runtime/bert_thomwolf && ./run_bert_large.shMore examples can be found under harmony/1_decomposer, harmony/2_profiler, harmony/3_scheduler, and harmony/4_runtime.
To conduct the experiments in the VLDB paper, the scripts are provided as below:
-
Figure 8
cd harmony/4_runtime/bert_thomwolf && ./run_bert_large__fig8.sh
-
Figure 10
cd harmony/4_runtime/bert_thomwolf && ./run_bert96__fig10.sh cd harmony/4_runtime/gpt2_huggingface && ./run_gpt2_xl__fig10_fig12.sh cd harmony/4_runtime/vgg_resnet_torch && ./run_vgg416__fig10.sh cd harmony/4_runtime/vgg_resnet_torch && ./run_resnet1026__fig10.sh
-
Figure 12
cd harmony/4_runtime/gpt2_huggingface && ./run_gpt2_xl__fig10_fig12.sh
-
Figure 13
cd harmony/4_runtime/bert_thomwolf && ./run_bert_large__fig13.sh
-
Figure 17 and Figure 18
cd harmony/4_runtime/gpt2_huggingface && ./run_gpt2_billions__fig17_fig18.sh
-
Figure 21
cd harmony/4_runtime/gpt2_huggingface && ./run_gpt2_medium__fig21.sh
-
Table 1
cd harmony/3_scheduler && ./run_four_models__tab1.sh
For experiments of Figure 17 and Figure 18, three prerequisits exist to run largest models saturating the CPU memory capacity. (Tested on Ubuntu 18.04.)
-
Raise the limitation of pinned memory
Step 1: open /etc/security/limits.conf
sudo vim /etc/security/limits.conf
Step 2: make memlock unlimited
#<domain> <type> <item> <value> # #* soft core 0 #root hard core 100000 #* hard rss 10000 #@student hard nproc 20 #@faculty soft nproc 20 #@faculty hard nproc 50 #ftp hard nproc 0 #ftp - chroot /ftp #@student - maxlogins 4 * - memlock unlimited root - memlock unlimited # End of fileStep 3: verify
ulimit -a -
Step 1: Open /etc/fstab
sudo vim /etc/fstab
Step 2: Locate /dev/shm and use the tmpfs size option to specify max size
# /etc/fstab: static file system information. # # Use 'blkid' to print the universally unique identifier for a # device; this may be used with UUID= as a more robust way to name devices # that works even if disks are added and removed. See fstab(5). # # <file system> <mount point> <type> <options> <dump> <pass> # / was on /dev/sda1 during installation UUID=4e3b7d44-77c9-4cc8-be72-fa2ff836ac2f / ext4 errors=remount-ro 0 1 /swapfile none swap sw 0 0 # resize /dev/shm tmpfs /dev/shm tmpfs defaults,size=750g 0 0Step 3: To make change effective immediately, remount the /dev/shm filesystem:
mount -o remount /dev/shm
Step 4: Verify
df -h
-
Step 1: Open sysctl.conf
sudo vim /etc/sysctl.conf
Step 2: Add this line vm.swappiness = 0
################################################################### # Protected links # # Protects against creating or following links under certain conditions # Debian kernels have both set to 1 (restricted) # See https://www.kernel.org/doc/Documentation/sysctl/fs.txt #fs.protected_hardlinks=0 #fs.protected_symlinks=0 vm.swappiness = 0Step 3: Restart machine
sudo reboot nowAfter all experiments, restore swapping to disk
# vm.swappiness = 0 # comment out -
Setup Container
Finally, we need to unlock the resource limitation of container by setting options in
launch.shas below. Assume that the machine has 750GB CPU memory and 8 GPUs.nvidia-docker run \ ... --memory=750g \ --memory-swap=750g \ --memory-swappiness=0 \ --memory-reservation=750g \ --shm-size=750g \ --ulimit memlock=750000000000:750000000000 \ --gpus '"device=0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7"' \ ...
This project has adopted the Microsoft Open Source Code of Conduct. For more information see the Code of Conduct FAQ or contact opencode@microsoft.com with any additional questions or comments.
Copyright (c) Microsoft Corporation. All rights reserved.
Licensed under the MIT License.
If you find the code helpful, citing our papers would be appreciated : )
@article{VLDB22Harmony,
title = {{Harmony: Overcoming the Hurdles of GPU Memory Capacity to Train Massive DNN Models on Commodity Servers}},
author = {Youjie Li and Amar Phanishayee and Derek Murray and Jakub Tarnawski and Nam Sung Kim},
journal = {The 48th International Conference on Very Large Databases (VLDB'22)},
year = {2022},
address = {Sydney, Australia},
month = sep
}
@inproceedings{HotOS21Harmony,
title = {{Doing More with Less: Training Large DNN Models on Commodity Servers for the Masses}},
author = {Youjie Li and Amar Phanishayee and Derek Murray and Nam Sung Kim},
booktitle = {Workshop on Hot Topics in Operating Systems (HotOS’21)},
year = {2021},
address = {Ann Arbor, MI, USA},
month = jun
}