Build a Traffic Sign Recognition Project
The goals / steps of this project are the following:
- Load the data set (see below for links to the project data set)
- Explore, summarize and visualize the data set
- Design, train and test a model architecture
- Use the model to make predictions on new images
- Analyze the softmax probabilities of the new images
1. Provide a Writeup / README that includes all the rubric points and how you addressed each one. You can submit your writeup as markdown or pdf. You can use this template as a guide for writing the report. The submission includes the project code.
You're reading it! and here is a link to my project code
1. Provide a basic summary of the data set. In the code, the analysis should be done using python, numpy and/or pandas methods rather than hardcoding results manually.
I used the pandas, matplot, and numpy libraries to calculate summary statistics of the traffic. signs data set:
- The size of training set is 34799
- The size of the validation set is 4410
- The size of test set is 12630
- The shape of a traffic sign image is (32, 32, 3)
- The number of unique classes/labels in the data set is 43
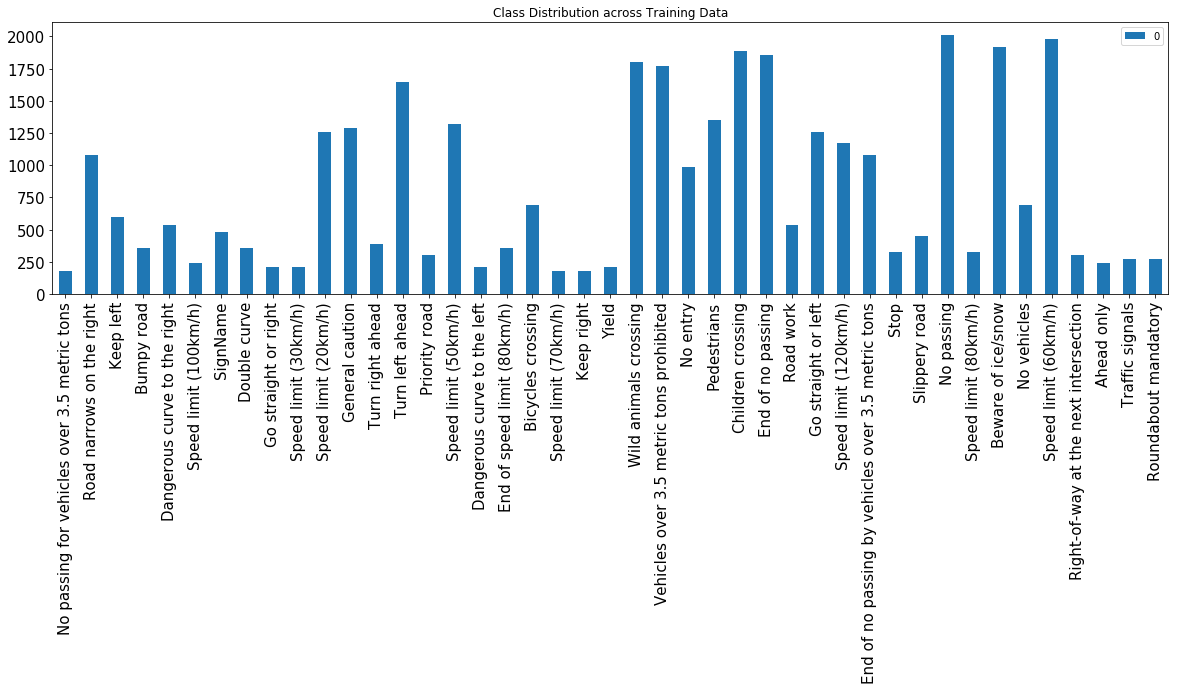
Here is an exploratory visualization of the data set. It is a bar chart showing how the data ...
1. Describe how you preprocessed the image data. What techniques were chosen and why did you choose these techniques? Consider including images showing the output of each preprocessing technique. Pre-processing refers to techniques such as converting to grayscale, normalization, etc. (OPTIONAL: As described in the "Stand Out Suggestions" part of the rubric, if you generated additional data for training, describe why you decided to generate additional data, how you generated the data, and provide example images of the additional data. Then describe the characteristics of the augmented training set like number of images in the set, number of images for each class, etc.)
The only pre-processing I used was normalization. I have tried to grayscale, blur, and other techniques, but it decreased the accuracy. I was able to achieve a good accuracy with normalization only.
Another technique that could improve the accuracy would generate more data out of the existing one, data augmentation, by rotating and reposition the figures in the original pictures.
2. Describe what your final model architecture looks like including model type, layers, layer sizes, connectivity, etc.) Consider including a diagram and/or table describing the final model.
My final model consists of the following layers:
| Layer | Description |
|---|---|
| Input | 32x32x3 RGB image |
| Convolution 5x5 | 1x1 stride, VALID padding, outputs 28x28x6 |
| RELU | |
| Max pooling 2x2 | 2x2 stride, outputs 14x14x6 |
| Convolution 5x5 | 1x1 stride, VALID padding, outputs 10x10x16 |
| RELU | |
| Max pooling 2x2 | 2x2 ksize, 2x2 stride, outputs 5x5x16 |
| Flatten | output 400 |
| Fully Connected 400 | output 120 |
| RELU | |
| Dropout | Keep_prob: 0.5 |
| Fully Connected 84 | output 10 |
| RELU | |
| Dropout | Keep_prob: 0.5 |
3. Describe how you trained your model. The discussion can include the type of optimizer, the batch size, number of epochs and any hyperparameters such as learning rate.
The data is divided into 3 sets, train, valid, and test. I trained the model with 34799 examples from the train set, and measured the accurcy using 12630 examples from the valid set. Hyperparameters;learning rate = 0.001, epoch = 120, and batch = 128.
4. Describe the approach taken for finding a solution and getting the validation set accuracy to be at least 0.93. Include in the discussion the results on the training, validation and test sets and where in the code these were calculated. Your approach may have been an iterative process, in which case, outline the steps you took to get to the final solution and why you chose those steps. Perhaps your solution involved an already well known implementation or architecture. In this case, discuss why you think the architecture is suitable for the current problem.
My final model results were:
- validation set accuracy of 93.1%
- test set accuracy of 91.4%
If an iterative approach was chosen:
- What was the first architecture that was tried and why was it chosen?
I used the original LeNet architecture, with two added dropouts at the fc1, and fc2.
- What were some problems with the initial architecture?
Initially, the model was overfitting the train data. When I measured the test data, the accuracy was around 75%.
- How was the architecture adjusted and why was it adjusted?
Typical adjustments could include choosing a different model architecture, adding or taking away layers (pooling, dropout, convolution, etc), using an activation function or changing the activation function. One common justification for adjusting an architecture would be due to overfitting or underfitting. A high accuracy on the training set but low accuracy on the validation set indicates over fitting; a low accuracy on both sets indicates under fitting.
To fix the overfitting issue, I added two dropout layers, I was able to reach 91% accuracy.
- Which parameters were tuned? How were they adjusted and why? I found the best hyperparameter combinations:
Epochs = 120 Batch size = 128 Learning rate = 0.001 Keep Prob = 0.5
1. Choose five German traffic signs found on the web and provide them in the report. For each image, discuss what quality or qualities might be difficult to classify.
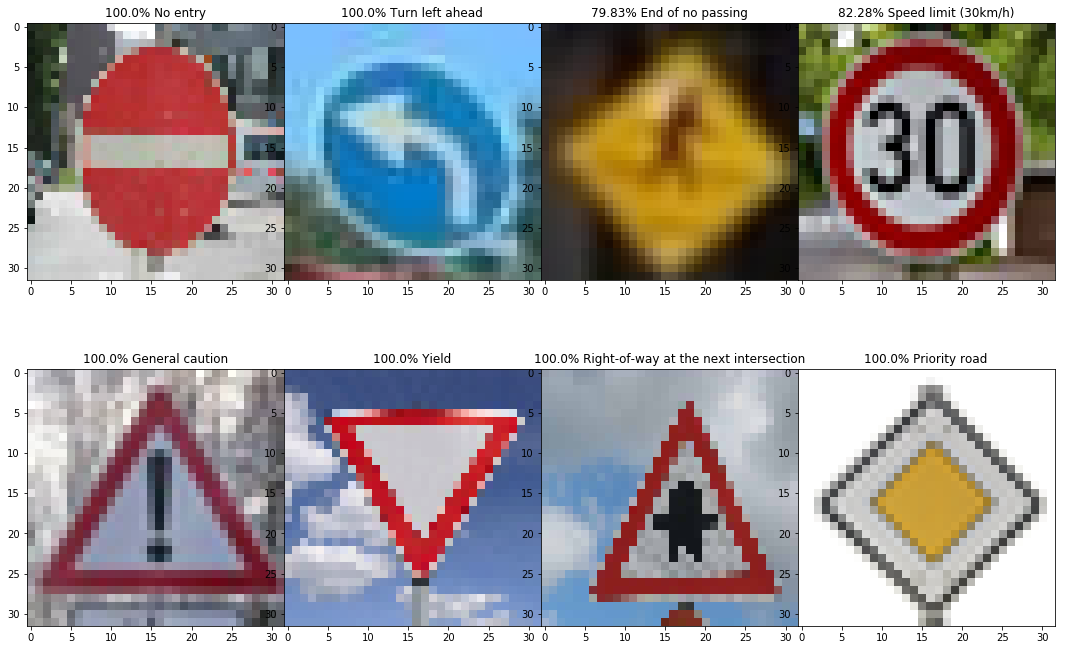
Here are five German traffic signs that I found on the web:
2. Discuss the model's predictions on these new traffic signs and compare the results to predicting on the test set. At a minimum, discuss what the predictions were, the accuracy on these new predictions, and compare the accuracy to the accuracy on the test set (OPTIONAL: Discuss the results in more detail as described in the "Stand Out Suggestions" part of the rubric).
Here are the results of the prediction:
| Image | Prediction |
|---|---|
| No entry | No entry |
| Turn left ahead | Turn left ahead |
| Pedestrains | End of no passing |
| Speed limit (30km/h) | Speed limit (30km/h) |
| General caution | General caution |
| Yield | Yield |
| Right-of-way at the next intersection | Right-of-way at the next intersection |
The model was able to correctly guess 7 of the 8 traffic signs, which gives an accuracy of 75%.
3. Describe how certain the model is when predicting on each of the five new images by looking at the softmax probabilities for each prediction. Provide the top 5 softmax probabilities for each image along with the sign type of each probability. (OPTIONAL: as described in the "Stand Out Suggestions" part of the rubric, visualizations can also be provided such as bar charts)
The model is relatively accurate in predicting the new image set. 6 of the images predicted with 100% probabilty, you can see from the signes picture above. The other two images, the predictions were above 79%:
| Probability | Prediction |
|---|---|
| .82 | Speed limit (30km/h) |
| .17 | Speed limit (50km/h) |
| .0 | No vehicles |
| .0 | Speed limit (80km/h) |
| .0 | Speed limit (70km/h) |
| Probability | Prediction |
|---|---|
| .79 | End of no passing |
| .08 | End of speed limit (80km/h) |
| .07 | Vehicles over 3.5 metric tons prohibited |
| .02 | End of all speed and passing limits |
| .006 | End of no passing by vehicles over 3.5 metric tons |