The primary purpose of this project is to show how a proxy can be used to front a MongoDB cluster, as long as the cluster is sharded and the Mongos processes sit between the proxy and the Mongod shards (proxying a simple non-sharded replica set will not work). There can be a variety of reasons why a proxy is used between a MongoDB database and its clients, which requires host and/or port translation, including:
- Bridging from one network to another (eg. internet to intranet or vice versa)
- Providing a place in the deployment topology where additional monitoring can occur for increased observability.
- Providing an additional layer of security and access control in the deployment topology
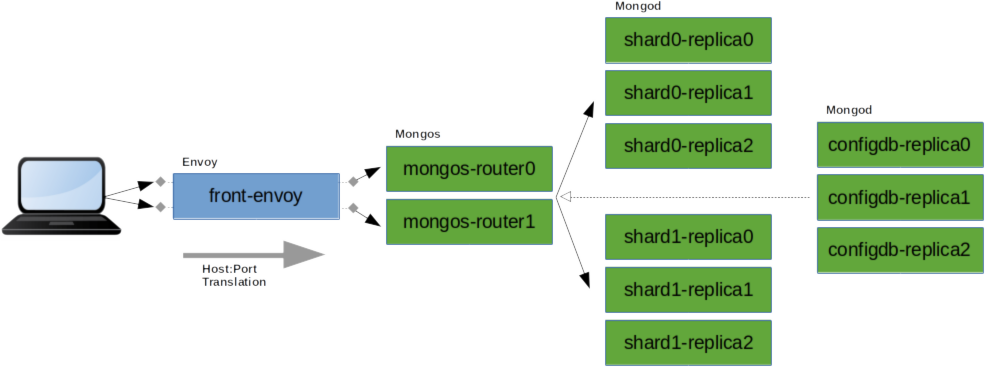
This example uses a Docker Compose project to launch the MongoDB cluster topology shown below, with Envoy proxy endpoints positioned in front of the Mongos processes.
Each element in the topology (9 Mongod processes, 2 Mongos processes, 1 Envoy process) runs in its own Docker container and all the containers are visible to each other on the same internal network. Once running, the MongoDB cluster is accessible directly from your laptop/PC, via localhost forwarded ports which connect to the Envoy proxy endpoints.
- Your workstation is running a recent version of Linux, Windows or Mac OS X
- Docker is already installed on your workstation
- Docker Compose is already installed on your workstation
- The MongoDB Shell is already installed on your workstation to you to issue commands to the running database cluster from your workstation (alternatively use the MongoDB Compass graphical tool to connect to the cluster)
- Launch a command line terminal in the base envoy-sharded-mongodb folder and execute the following command to build and start all the containers in the Docker Compose project:
docker-compose up --build -d
- Show all the running docker containers for this Docker Compose project:
docker-compose ps
- Connect to the MongoDB cluster from the MongoDB Shell (the Shell should connect to the first of the two configured Envoy proxy endpoints, which then connects to the first Mongos, which then connects to the Mongod shards):
mongosh --port 27000
sh.status()
Note: Use port 27001 instead, above, if you want to connect to the second Envoy endpoint which will connect to the second Mongos. Attempting to configure Envoy to load balance across the two Mongos proxies, to represent them as a single endpoint, will break the MongoDB wire protocol communication between the Shell and the Mongos processes.
- To show the container logs for the Envoy proxy, run:
docker-compose logs front-envoy
- To show the container logs for one of the Mongos servers, run:
docker-compose logs mongos-router0
- To execute a terminal session directly in the Envoy proxy's container and then view the Envoy access logs for requests sent to the two Mongos processes, run:
docker-compose exec front-envoy /bin/bash
cat /tmp/access0.log
cat /tmp/access1.log
- To execute a terminal session directly in one of the Mongos containers and then execute the MongoDB Shell directly accessing the local Mongos process, run:
docker-compose exec mongos-router0 /bin/bash
mongosh
- To execute a terminal session directly in one of the Mongod containers and then view the Mongod process' logs, run:
docker-compose exec shard0-replica0 /bin/bash
cat /data/db/mongod.log
-
To view the Envoy proxy's collected runtime statistics, in a browser go to: http://localhost:8001/stats
-
To shutdown and remove all the Docker Compose project's running containers (ready for you to rebuild and run again), run:
docker-compose down