| release | ||
| dev |
A Clojure tools.build task library for interrogating your project's dependencies' licenses. Somewhat inspired by the (discontinued) lein-licenses Leiningen plugin, but with the added benefit of canonicalisation to SPDX License Expressions.
It also provides the ability to check your (Apache-2.0 licensed) project against the Apache Software Foundation's 3rd Party License Policy.
Note: tools-licenses assumes a "flat" project organisational structure, where each project is defined by a directory containing a deps.edn file, and all of its sub-directories. This may or may not work well with monolithic development models (such as Polylith), where all source code is managed out of a single, large, deeply-nested directory structure. That said, tools-licenses will do something, but whether that thing is what you're expecting and/or useful is quite another matter.
The author and contributors to tools-licenses are not lawyers, and neither they nor tools-licenses itself provide legal advice. This is simply a tool that might help you and your legal counsel perform licensing due diligence on your projects. If you need a primer on the legal aspects of open source software, the author has found the Blue Oak Council to be a useful resource.
This tool uses the lice-comb library, which has these system requirements:
-
JDK 11 or higher.
-
An internet connection.
-
Assumes Maven is installed and in the
PATH(but has fallback logic if it isn't available).
licenses- attempt to display the licenses used by all transitive dependencies of the projectcheck-asf-policy- attempt to check your project's probable compliance (or not) with the ASF's 3rd Party License Policy
tools.deps' license discovery logic (provided via the command clj -X:deps list) has several serious shortcomings, including:
- It only scans Maven POM files for license information, and silently ignores projects that don't have license tags in their POM file, or don't have a POM file at all. This is a problem because:
- git dependencies (whose use is encouraged by tools.deps/tools.build) don't need a POM file (and in practice most don't provide one)
- silently ignoring projects that lack a
pom.xmlfile (or have one that doesn't contain licensing information) may lull users into a false sense of security vis-a-vis license compliance - Clojars only recently started mandating license information in the POM files it hosts, and as of mid-2023 around 1/3 of all projects deployed hosted there do not include any licensing information in their POM files
- It's coupled to tools.deps and cannot easily be consumed as an independent library. It's also dependent on tools.deps state management (e.g. requires POM files to be downloaded locally).
- It doesn't canonicalise license information to SPDX License Expressions, or even (in some cases) SPDX License Identifiers.
- It only reports the first license for multi-licensed artifacts.
Why not scarletcomply/license-finder?
It uses tools.deps' license discovery logic under the covers, so has all of the same issues. It does provide a better user experience however (it's packaged as a tool, has more output options, etc.).
While Leiningen's original lein-licenses plugin was discontinued some years ago and finally archived in 2020, JohnnyJayJay has developed an alternative lein-licenses plugin that leverages the same underlying license detection library (lice-comb) as tools-licenses, thereby offering similar capabilities.
API documentation is available here, or here on cljdoc.
Add the tool as a Maven dependency to your deps.edn, in your build alias:
:aliases
:build
{:deps {com.github.pmonks/tools-licenses {:mvn/version "LATEST_CLOJARS_VERSION"}} ; Or use "RELEASE" to blindly follow the latest release of the tool
:ns-default your.build.ns}Require the namespace in your tools.build script (typically called build.clj), and add task functions that delegate to the tool:
(ns your.build.ns
(:require [tools-licenses.tasks :as lic]))
(defn licenses
"Attempts to list all licenses for the transitive set of dependencies of the
project, as SPDX license expressions."
[opts]
(lic/licenses opts))
; And, optionally:
(defn check-asf-policy
"Checks this project's dependencies' licenses against the ASF's 3rd party
license policy (https://www.apache.org/legal/resolved.html).
Note: only meaningful if this project is Apache-2.0 licensed."
[opts]
(lic/check-asf-policy opts))You may also wish to configure a logging implementation for your build alias, since this tool can emit logging output (mostly from the Java libraries it uses). For example (using log4j2, though you may choose any logging implementation you like that supports SLF4J):
:build
{:deps {com.github.pmonks/tools-licenses {:mvn/version "LATEST_CLOJARS_VERSION"} ; Or use "RELEASE" to blindly follow the latest release of the tool
org.apache.logging.log4j/log4j-api {:mvn/version "2.21.1"}
org.apache.logging.log4j/log4j-core {:mvn/version "2.21.1"}
org.apache.logging.log4j/log4j-jul {:mvn/version "2.21.1"} ; Java utils clogging bridge
org.apache.logging.log4j/log4j-jcl {:mvn/version "2.21.1"} ; Apache commons clogging bridge
org.apache.logging.log4j/log4j-slf4j2-impl {:mvn/version "2.21.1"} ; SLF4J clogging bridge
org.apache.logging.log4j/log4j-1.2-api {:mvn/version "2.21.1"}} ; log4j1 clogging bridge
:ns-default your.build.ns}Then add this log4j2.xml file in the root directory of your project (or another directory, which would then need to be added to the :paths of your build alias):
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<Configuration status="WARN" strict="true">
<Properties>
<Property name="filename">build.log</Property>
</Properties>
<Appenders>
<Appender type="File" name="File" fileName="${filename}">
<Layout type="PatternLayout" pattern="%d %p %C{1.} [%t] %m%n" />
</Appender>
</Appenders>
<Loggers>
<!-- These libraries tend to be exceptionally noisy, even at WARN -->
<Logger name="org.apache" level="FATAL">
<AppenderRef ref="File"/>
</Logger>
<Logger name="org.eclipse" level="FATAL">
<AppenderRef ref="File"/>
</Logger>
<Root level="WARN">
<AppenderRef ref="File"/>
</Root>
</Loggers>
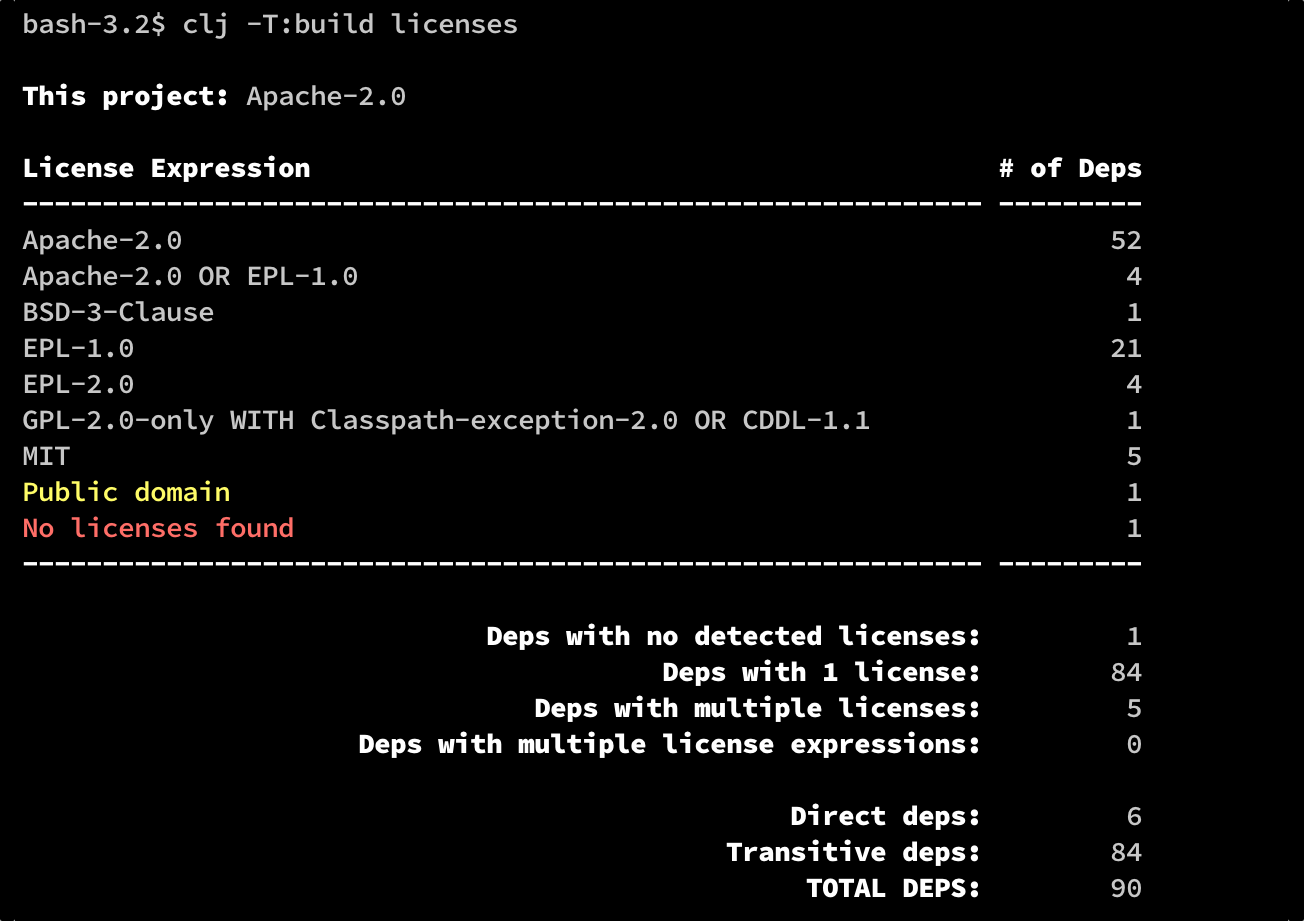
</Configuration>Example summary output:
Other invocation possibilities:
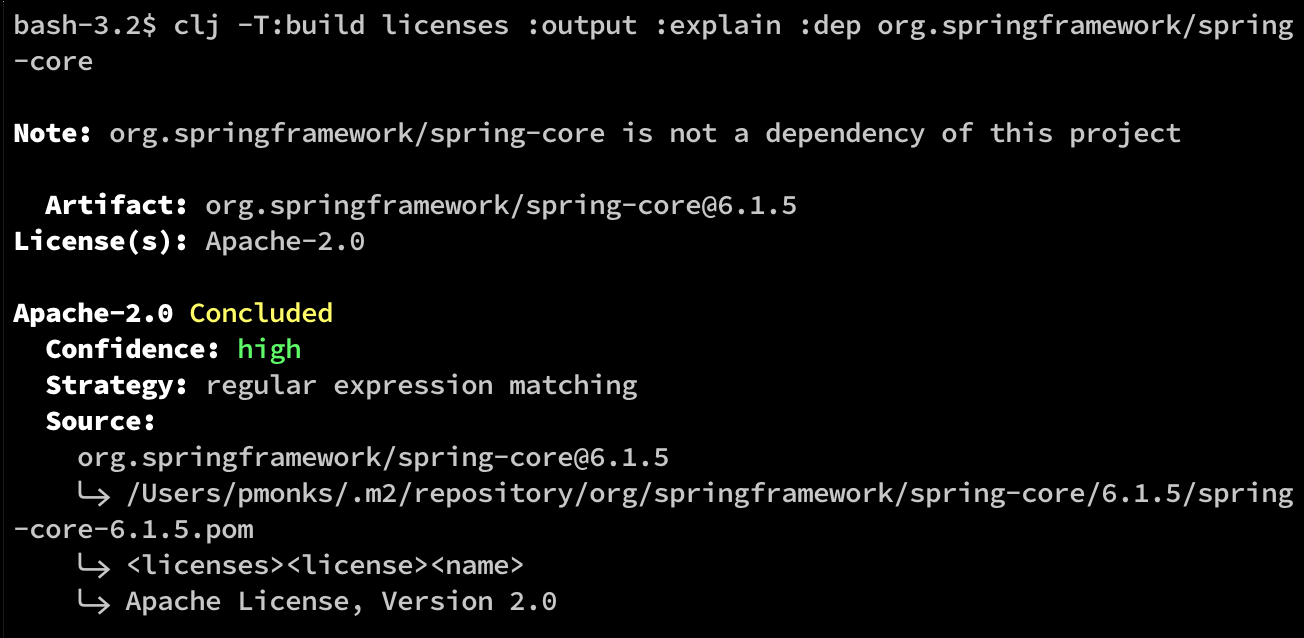
clj -T:build licenses :output :summary- the default (see above)clj -T:build licenses :output :detailed- detailed per-dependency license informationclj -T:build licenses :output :edn- detailed per-dependency license information in EDN formatclj -T:build licenses :output :explain :dep <dep symbol>- an explanation of how the tool arrived at the given license(s) for a single dep (expressed as a tools.dep symbol). For example:
If you see Unidentified (<some text>) licenses in the output, but the license is listed in the SPDX license list, please raise an issue here.
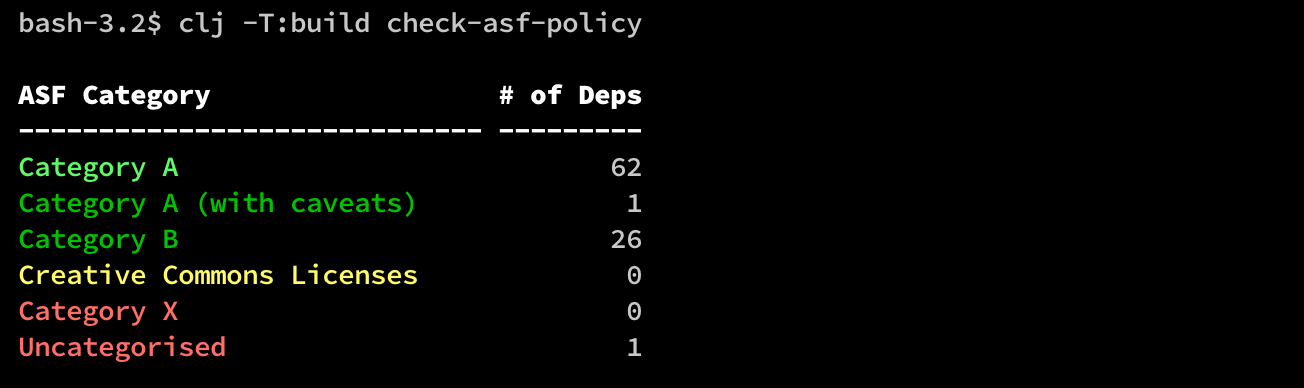
Example summary output:
Other invocation possibilities:
clj -T:build check-asf-policy :output :summary- the default (see above)clj -T:build check-asf-policy :output :detailed- detailed per-dependency ASF category informationclj -T:build check-asf-policy :output :edn- detailed per-dependency ASF category information in EDN format
This project uses the git-flow branching strategy, and the permanent branches are called release and dev. Any changes to the release branch are considered a release and auto-deployed (JARs to Clojars, API docs to GitHub Pages, etc.).
For this reason, all development must occur either in branch dev, or (preferably) in temporary branches off of dev. All PRs from forked repos must also be submitted against dev; the release branch is only updated from dev via PRs created by the core development team. All other changes submitted to release will be rejected.
tools-licenses uses tools.build. You can get a list of available tasks by running:
clojure -A:deps -T:build help/doc
Of particular interest are:
clojure -T:build test- run the unit testsclojure -T:build lint- run the linters (clj-kondo and eastwood)clojure -T:build ci- run the full CI suite (check for outdated dependencies, run the unit tests, run the linters)clojure -T:build install- build the JAR and install it locally (e.g. so you can test it with downstream code)
Please note that the deploy task is restricted to the core development team (and will not function if you run it yourself).
Copyright © 2021 Peter Monks
Distributed under the Mozilla Public License, version 2.0.
SPDX-License-Identifier: MPL-2.0