Note: This project is a experimential project that leverages the concepts of CQRS and Event Sourcing. However, the events as written in this project are the results of the Strategic Design and this project can be used during the Tactical Design phase
Seed project (boilerplate) for RESTful API that leverages the concept of Domain Driven Design (DDD) along with CQRS and Event Sourcing
This API project utilises information from multiple sources to create the fine-tuned API product with the following objectives
- To build a maintainable enterprise grade application
- The application that follows
SOLIDprinciples as much as possible - To build an application that benefits most of the stakeholders in an organisation
- To decouple the read and the write side of the application. Thus, they can be scaled indenpendently
- To build the CQRS and Event Sourcing system
This project uses DDD with Onion Architecture as illustrated in below images
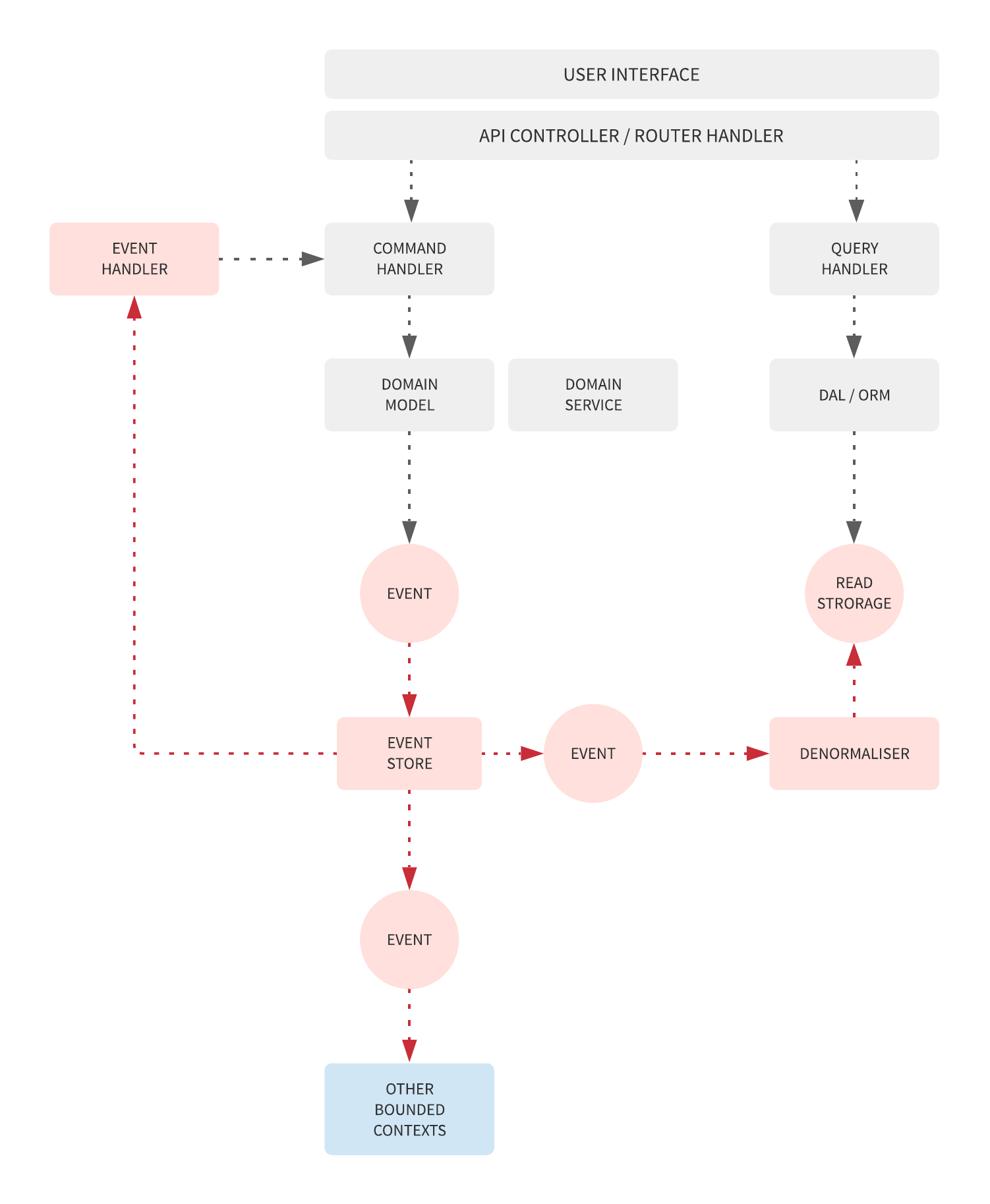
Below image illustrates the more detailed architecture
In CQRS & Event Sourcing systems, the main idea is to implement different data models for read and write sides of the application.
The workflow is that the write side sends the commands to the command handlers through commandBus to alter the information. The succeeded commands will then generate resulting events which are then stored in the event store. Finally, the event handlers subscribe to events and generate the denormalised data ready for the query. Please note that the events could also be handled by multiple event handlers. Some of them may handle notification tasks.
The only source of truth of Event Sourcing systems is the event store while the data in the read store is simply a derivative of the events generated from the write side. This means we can use totally different data structure between the read and the write sides and we can replay the events from the event store from the whenever we want the regenerate the denormalised data in whatever shapes we want.
In this example, we use MongoDB as an event store and Redis as the read store.
The commands are sent by the frontend to the commandBus which then selects appropriate command handlers for the commands. The command handlers then prepare the Aggregate Root and apply the business logic suitable for them. If the commands succeed, they result in events which will then be sent to the eventBus to the event handlers. In this example, the eventBus is implemented using Redis Pub/Sub.
To read more about CQRS and Event Sourcing. Please check this link
- Node.js
- TypeScript
- MongoDB with MongoDB native driver as an event store (mongodb package on NPM)
- InversifyJS as an IoC container
- Express (via Inversify Express Utils) as an API framework
- Redis as a read store
- Redis Pub/Sub as the message bus
This project follows the standard CQRS & Event Sourcing applications available on GitHub. Highly inspired by Greg Young's SimpleCQRS project (written in ASP.NET C#).
Below is the list of components in this project
- Domain Model (Aggregate Root)
Contains the business logic required for the application - Commands
The command class which implementsICommandinterface. This reflects the intention of the users to alter the state of the application - CommandHandlers
The command processor managed byCommandBus. It prepares the Aggregate Root and applies business logic on it. - CommandBus
The command management object which receieves incoming commands and select appropriate handlers for them. Please note that in order to use the command handlers. They must be registered to theCommandBusfirst atentrypoint.tsfile. - Events
The resulting objects from describing the changes generated by succeeding commands which are sent through theEventBus. This class implementsIEventinterface. - Event Store The storage that stores events. This is the only source of truth of the system (The sequence of events generated by the application).
- EventBus
The bus that contains the events where event handlers subscribe to. In this example,Redis Pub/Subis used to implement this bus.RabbitMQ - Event Handlers
The event processor. This could be the projector or the denormaliser that generates the data for the read side on the read storage.
To run the project, make sure you have these dependencies installed on your system
- Node.js v8 or later
- Typescript with
tsccommand - Nodemon
- ts-node
- MongoDB
- Redis Server and Clients (redis-cli)
You also need to setup and initialise MongoDB database. Then, copy the .env_example file into .env file by firing the command
cp .env_template .envDo adjust the DB_NAME and MONGODB_URI to match your configuration then run
yarn dev