Code for habr article on hyperparameter optimization methods review. In this article I also compared hyperopt, skopt and optuna frameworks on sentiment-analysis NLP task.
torch.nn.LSTM-based model with parameters grid:
params_grid = {
'hidden_size': [64, 128, 256, 512],
'num_layers': [1, 2],
'dropout': [0.5],
'bidirectional': [True, False],
'batch_size': [64, 256],
'lr': [1e-3, 1e-2, 1e-1]
}
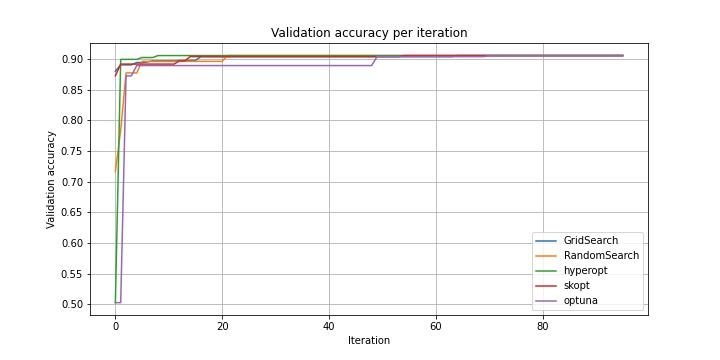
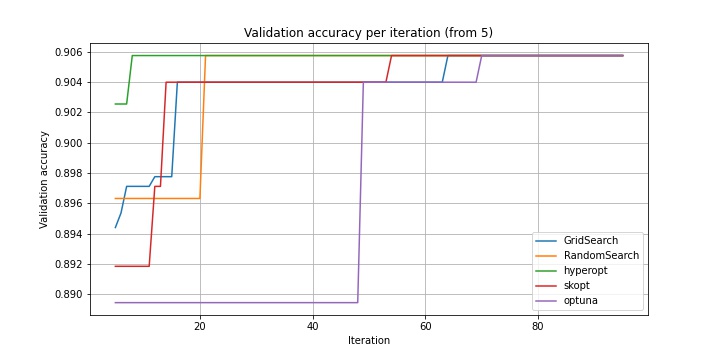
| Optimizer | hidden_size | num_layers | bidirectional | batch_size | lr | Val loss | Val accuracy | Test accuracy | Time (s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
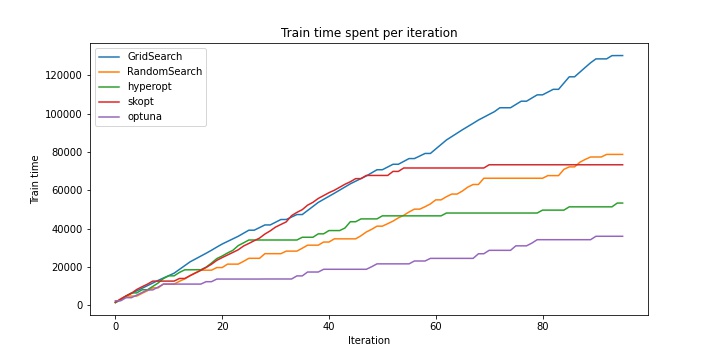
| GridSearch | 256 | 2 | + | 256 | 0.01 | 0.63 | 0.906 | 0.897 | 130357 |
| RandomSearch | 256 | 2 | + | 256 | 0.01 | 0.63 | 0.906 | 0.897 | 78777 |
| hyperopt | 256 | 2 | + | 256 | 0.01 | 0.63 | 0.906 | 0.897 | 68920 |
| scikit-optimize (LCB) | 256 | 2 | + | 256 | 0.01 | 0.63 | 0.906 | 0.897 | 73423 |
| scikit-optimize (gp_hedge) | 64 | 2 | + | 256 | 0.01 | 0.69 | 0.904 | 0.900 | 61869 |
| optuna | 256 | 2 | + | 256 | 0.01 | 0.63 | 0.906 | 0.897 | 40681 |
In my experiments I used python==3.6.6. Needed packages can be installed via pip install -r requirements.txt.
-
If you want just to play with obtained train/val/test accuracies, losses and times, you need to unpack
checkpoints_results_only.zipto your project directory. Then you may usehyperparams.ipynb. -
If you want retrain all the models and run the whole pipeline, you need to unpack the dataset archive to 'data' in your project directory, and unpack embeddings to your project directory. Then run
python3 train_all.py <n_epochs> <device>. When all the models will be trained, you may use hyperparams.ipynb.