Traffic analysis using networks of Automatic Number Plate Recognition cameras.
ANPRX is available through pypi:
pip install anprx
See requirements.txt for a complete list of dependencies.
Important: OSMnx requires the Rtree package which is a python wrapper for libspatialindex. To get osmnx to work properly, which this package heavily relies on, download and install libspatialindex first.
- Obtain a model of the drivable street network, using osmnx and networkx, that encompasses the traffic cameras (coordinate points).
from anprx.core import Point
from anprx.core import get_surrounding_network
# Using the same dummy location twice
locations = [ Point(lat = 54.974537,
lng = -1.625644),
Point(lat = 54.974537,
lng = -1.625644)]
network = get_surrounding_network(locations)- Instantiate camera objects whose observed network edge is implicitly estimated. If the camera's address has been annotated by a human, you can use it to remove candidate edges with a different address.
import networkx as nx
from anprx.core import Camera
# With address filtering - only nearby edges with the
# given address are considered
mock_camera1 = Camera(
network = network,
id = "c1",
point = locations[0],
address = "Pitt Street, Newcastle Upon Tyne, UK")
# Without address filtering - all nearby edges are considered
mock_camera2 = Camera(
network = network,
id = "c2",
point = locations[1])
# chosen edge
mock_camera1.edge
mock_camera2.edge
# proportion of valid points for each candidate edge
mock_camera1.p_cedges
mock_camera2.p_cedges
# then you can compute routes between cameras
route = nx.shortest_path(network,
source = mock_camera1.edge.u,
target = mock_camera2.edge.v,
weight = 'length')- Visualise the camera's placement on the road network, including nearby nodes, and the likelihood of candidate edges.
from anprx.plot import plot_camera
plot_camera(mock_camera1)
plot_camera(mock_camera2)| Mock camera on Pitt Street with address filtering | Mock camera on Pitt Street without address filtering |
|---|---|
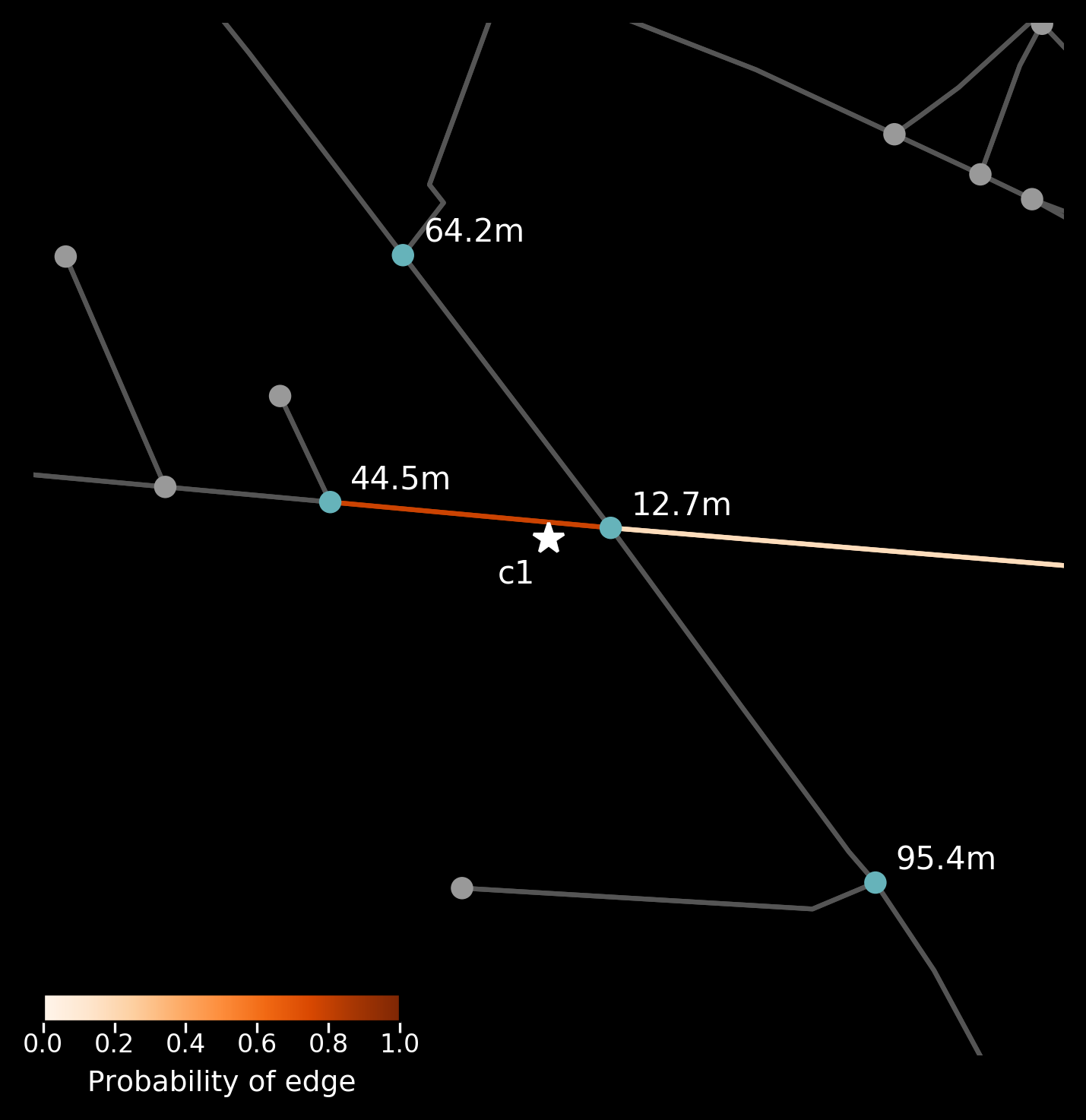 |
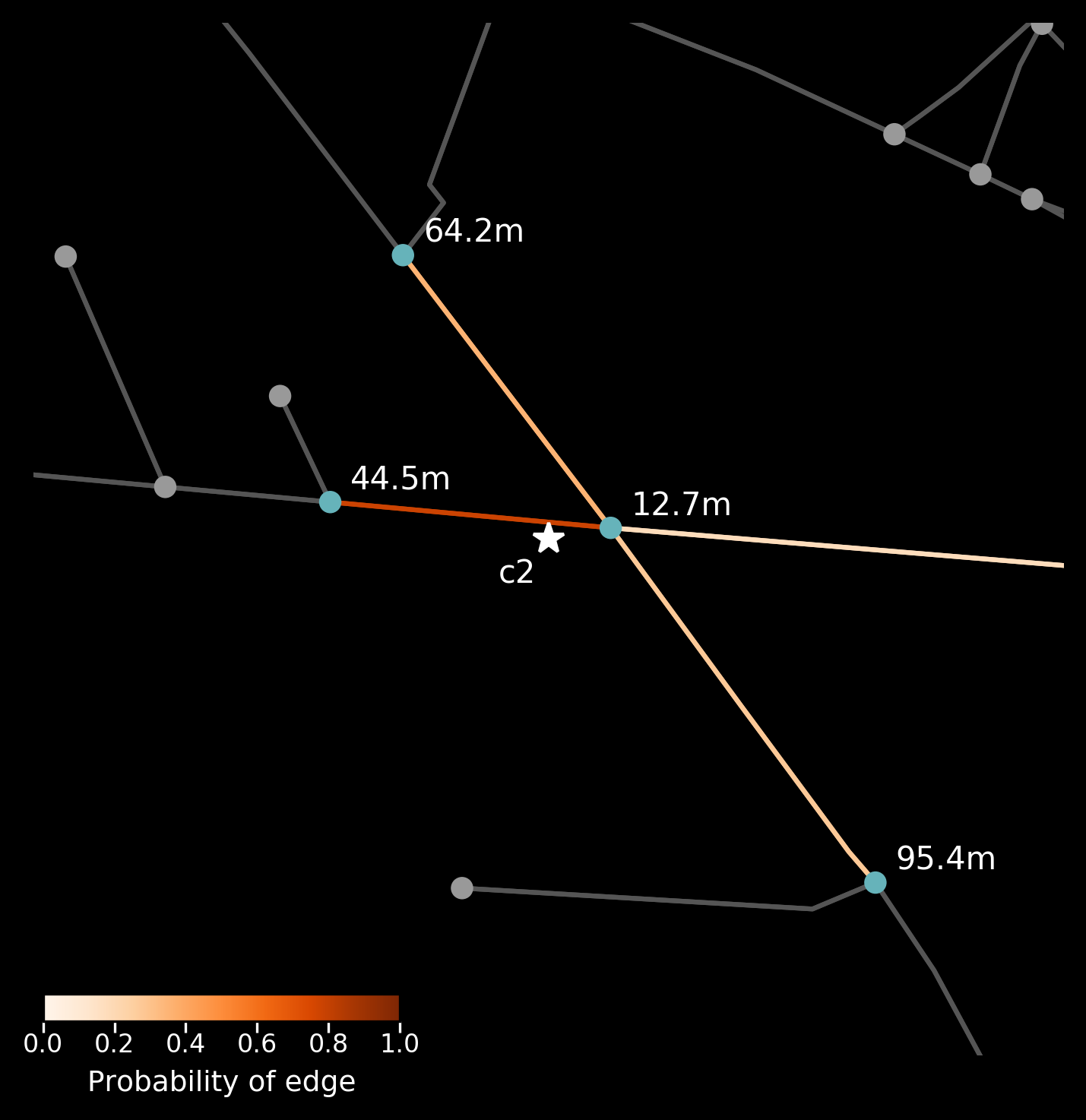 |
- Produce a video animation explaining how the edge estimation algorithm works.
from anprx.animate import animate_camera
# saved to ~/.anprx/images/c1.mp4
anim1 = animate_camera(mock_camera1,
progress = True,
save_mp4 = True)
# saved to ~/.anprx/images/c2.mp4
anim2 = animate_camera(mock_camera2)- Enrich the road network by adding further attributes to the edges of the network (address details, elevation, bearing).
import osmnx as ox
from anprx.core import enrich_network
network = enrich_network(network,
elevation_api_key = "dummy",
postcode_delim = ' ')
elevations = nx.get_edge_attributes(network, 'elevation')
bearings = nx.get_edge_attributes(network, 'bearing')
postcodes = nx.get_edge_attributes(network, 'postcode')
suburbs = nx.get_edge_attributes(network, 'suburb')
importance = nx.get_edge_attributes(network, 'importance')
road_types = nx.get_edge_attributes(network, 'type')
# you can use osmnx to plot the network and colour the edges by attribute
edges_color = ox.get_node_colors_by_attr(network, 'bearings', cmap='plasma')
fig, ax = ox.plot_graph(network, edge_color = egdes_color)Among others:
- Filter/compress the road network based on edge attributes.
- Batch analysis of ANPR data: trip identification and inference.
All modules and methods are documented in anprx.readthedocs.io
