Android-Interview-Question-2022-2023
Android interview questions for junior and seniors.
Java
OOP Concept
-
Class
- Collection of objects is called class. It is a logical entity. A class can also be defined as a blueprint from which you can create an individual object. Class doesn't consume any space.
-
Object
- An object can be defined as an instance of a class, and there can be multiple instances of a class in a program.
-
Method
- A method is a collection of statements that perform some specific task, method can or can't return any result.
-
Abstraction
- Data abstraction is the process of hiding certain details and showing only essential information to the user.
- Abstract Classes
- Interfaces
- Data abstraction is the process of hiding certain details and showing only essential information to the user.
-
Encapsulation
- The meaning of Encapsulation, is to make sure that "sensitive" data is hidden from users.
- declare class variables as private
- provide public get and set methods to access and update the value of a private variable
- The meaning of Encapsulation, is to make sure that "sensitive" data is hidden from users.
-
Inheritence
- It is the mechanism in Java by which one class is allowed to inherit the features (fields and methods) of another class.
- Code Reusability
- Method Overriding
- Abstraction
-
Types of Inheritance
- Single Inheritance
- In single inheritance, subclasses inherit the features of one superclass. In the image below, class Fruit serves as a base class for the derived class Mango.
- Multilevel Inheritance
- Multilevel Inheritance, a derived class will be inheriting a base class, and as well as the derived class also acts as the base class for other classes. Class GrandFather serves as a base class for the derived class Father, which in turn serves as a base class for the derived class Son.
- Hierarchical Inheritance
- One class serves as a superclass (base class) for more than one subclass. Class Wheel serves as a base class for the derived classes Cycle, Bike, and Car.
- Multiple Inheritance
- One class can have more than one superclass and inherit features from all parent classes. Please note that Java does not support multiple inheritances with classes. In java, we can achieve multiple inheritances only through Interfaces. Class Car is derived from interfaces Wheel and Body.
- Hybrid Inheritance
- It is a mix of two or more of the above types of inheritance. Since java doesn’t support multiple inheritances with classes, hybrid inheritance is also not possible with classes. In java, we can achieve hybrid inheritance only through Interfaces.
- Single Inheritance
- It is the mechanism in Java by which one class is allowed to inherit the features (fields and methods) of another class.
-
Polymorephism
- When one object acquires all the properties and behaviors of a parent object, it is known as inheritance. It provides code reusability.
- Overloading
- Overriding
- When one object acquires all the properties and behaviors of a parent object, it is known as inheritance. It provides code reusability.
Architecture Pattern
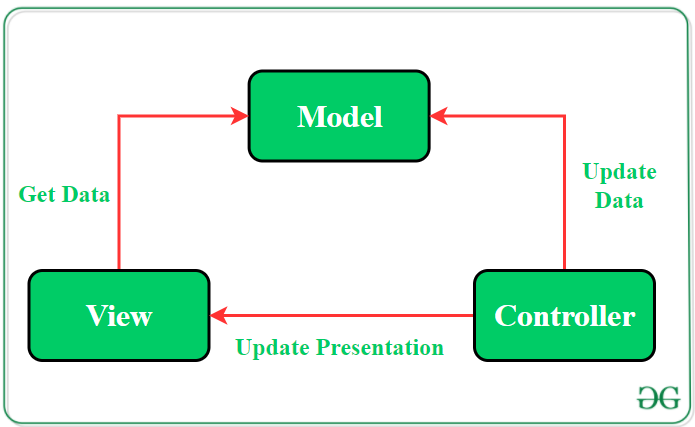
MVC(Model View Controller) https://bit.ly/geeksforgeeks-mvc
- The MVC pattern suggests splitting the code into 3 components. While creating the class/file of the application, the developer must categorize it into one of the following three layers:
-
Model
- This component stores the application data. It has no knowledge about the interface. The model is responsible for handling the domain logic(real-world business rules) and communication with the database and network layers.
-
View
- It is the UI(User Interface) layer that holds components that are visible on the screen. Moreover, it provides the visualization of the data stored in the Model and offers interaction to the user.
-
Controller
- This component establishes the relationship between the View and the Model. It contains the core application logic and gets informed of the user’s behavior and updates the Model as per the need.
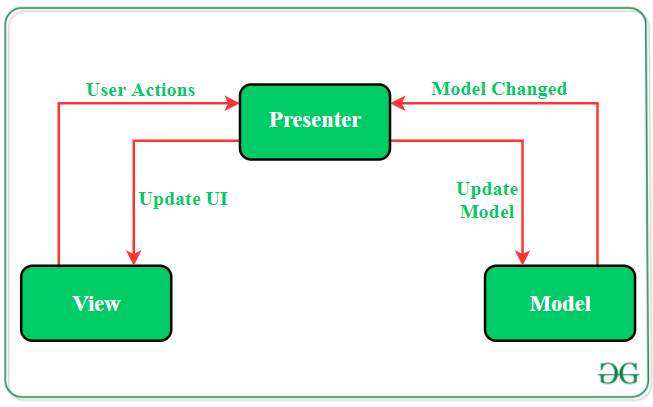
MVP(Model View Presenter) https://bit.ly/geeksforgeeks-mvp
- MVP pattern overcomes these challenges of MVC and provides an easy way to structure the project codes. The reason why MVP is widely accepted is that it provides modularity, testability, and a more clean and maintainable codebase. It is composed of the following three components:
-
Model
- Layer for storing data. It is responsible for handling the domain logic(real-world business rules) and communication with the database and network layers.
-
View
- UI(User Interface) layer. It provides the visualization of the data and keep a track of the user’s action in order to notify the Presenter.
-
Presenter
- Fetch the data from the model and applies the UI logic to decide what to display. It manages the state of the View and takes actions according to the user’s input notification from the View.
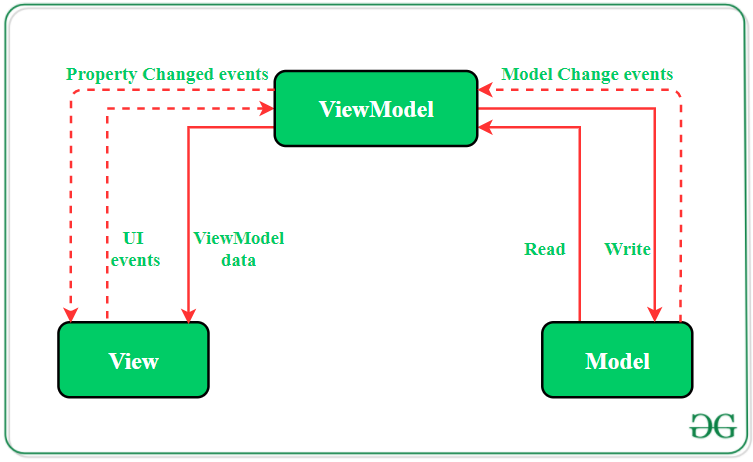
MVVM(Model View ViewModel) https://bit.ly/geeksforgeeks-mvvm
- MVVM pattern is the industry-recognized software architecture pattern that overcomes all drawbacks of MVP and MVC design patterns. MVVM suggests separating the data presentation logic(Views or UI) from the core business logic part of the application.
-
Model
- This layer is responsible for the abstraction of the data sources. Model and ViewModel work together to get and save the data.
-
View
- The purpose of this layer is to inform the ViewModel about the user’s action. This layer observes the ViewModel and does not contain any kind of application logic.
-
ViewModel
- It exposes those data streams which are relevant to the View. Moreover, it serves as a link between the Model and the View.
Agile Methodology https://bit.ly/5280software-agile-methodology
- The Agile model is a project management methodology purposely adopted for the development of sophisticated software. The framework allows for iterations, which helps a lot in minimizing mistakes and errors that commonly occur.
- The model divides the project into a series of development cycles or short time boxes, which are assigned to each professional on the project team. It is a collaborative approach the allows a response to rapid change. It is flexible enough to accommodate changes in project requirements throughout the mobile app development lifecycle.
-
Scrum
- Focuses on the management aspects of software development in intricate knowledge work, research and advanced technologies with an emphasis on teamwork, iteration and accountability.
Unit Testing https://bit.ly/geeksforgeeks-unit-test
- Unit testing is done to ensure that developers write high-quality and errorless code. It is advised to write Unit tests before writing the actual app, you will write tests beforehand and the actual code will have to adhere to the design guidelines laid out by the test. In this article, we are using JUnit to test our code. JUnit is a “Unit Testing” framework for Java Applications which is already included by default in android studio. It is an automation framework for Unit as well as UI Testing. It contains annotations such as @Test, @Before, @After, etc.
Android
-
Android is an open source and Linux-based Operating System for mobile devices such as smartphones and tablet computers. Android was developed by the Open Handset Alliance, led by Google, and other companies.
-
Android offers a unified approach to application development for mobile devices which means developers need only develop for Android, and their applications should be able to run on different devices powered by Android.
-
The first beta version of the Android Software Development Kit (SDK) was released by Google in 2007 where as the first commercial version, Android 1.0, was released in September 2008.
-
Kotlin https://bit.ly/digitalocean-kotlin
- QUESTION: How do you declare variables in Kotlin?
val s: String = "Hi"
var x = 5 - QUESTION: What’s the difference between val and var declaration? How to convert a String to an Int?
- val(Immutable Variables) variables cannot be changed. They’re like final modifiers in Java. A var(Mutable Variables) can be reassigned. The reassigned value must be of the same data type.
- We use the toInt() method to convert the String to an Int.
- QUESTION: What’s Null Safety and Nullable Types in Kotlin?
- Kotlin puts a lot of weight behind null safety which is an approach to prevent the dreaded Null Pointer Exceptions by using nullable types which are like String?, Int?, Float? etc. These act as a wrapper type and can hold null values. A nullable value cannot be added to another nullable or basic type of value. To retrieve the basic types we need to use safe calls that unwrap the Nullable Types. If on unwrapping, the value is null we can choose to ignore or use a default value instead.
- QUESTION: What is the Elvis Operator?
- The Elvis Operator is used to safely unwrap the value from the Nullable. It’s represented as ?: over the nullable type. The value on the right hand side would be used if the nullable type holds a null.
var str: String? = null
var str2: String? = "May be declare nullable string"
var len1: Int = if (str != null) str.length else -1 NotElvis Implemented
var len2: Int = str2?.length ?: -1 Elvis Implemented
- The Elvis Operator is used to safely unwrap the value from the Nullable. It’s represented as ?: over the nullable type. The value on the right hand side would be used if the nullable type holds a null.
- QUESTION: What’s a const? How does it differ from a val?
- By default val properties are set at runtime. Adding a const modifier on a val would make a compile-time constant. A const cannot be used with a var or on its own. A const is not applicable on a local variable.
- QUESTION: How is !!different from ?. in unwrapping the nullable values? Is there any other way to unwrap nullable values safely?
- !! is used to force unwrap the nullable type to get the value. If the value returned is a null, it would lead to a runtime crash. Hence a !! operator should be only used when you’re absolutely sure that the value won’t be null at all. Otherwise, you’ll get the dreaded null pointer exception. On the other hand, a ?. is an Elvis Operator that does a safe call. We can use the lambda expression let on the nullable value to unwrap safely.
- QUESTION: How is a function declared? Why are Kotlin functions known as top-level functions?
- A function’s return type is defined after the : Functions in Kotlin can be declared at the root of the Kotlin file.
fun sumOf(a: Int, b: Int): Int{
return a + b
} - QUESTION: What’s the difference between == and === operators in Kotlin?
- == is used to compare the values are equal or not. === is used to check if the references are equal or not.
- QUESTION: List down the visibility modifiers available in Kotlin. What’s the default visibility modifier?
- public(default)
- internal
- protected
- private
- QUESTION: Can we inherite normal class ?
- NO. By default classes are final in Kotlin. To make them non-final, you need to add the
openmodifier.
open class A{ }
- NO. By default classes are final in Kotlin. To make them non-final, you need to add the
- QUESTION: What are the types of constructors in Kotlin? How are they different? How do you define them in your class?
- Constructors in Kotlin are of two types:
- Primary - These are defined in the class headers. They cannot hold any logic. There's only one primary constructor per class.
- Secondary - They're defined in the class body. They must delegate to the primary constructor if it exists. They can hold logic. There can be more than one secondary constructors.
class User(name: String, isAdmin: Boolean){ constructor(name: String, isAdmin: Boolean, age: Int) :this(name, isAdmin) { this.age = age } } - QUESTION: What’s init block in Kotlin?
initis the initialiser block in Kotlin. It's executed once the primary constructor is instantiated. If you invoke a secondary constructor, then it works after the primary one as it is composed in the chain.
- QUESTION: How does string interpolation work in Kotlin? Explain with a code snippet?
- String interpolation is used to evaluate string templates. We use the symbol $ to add variables inside a string.
val name = "Journaldev.com"
val desc = "$name now has Kotlin Interview Questions too. ${name.length}"
- QUESTION: How do you declare variables in Kotlin?