Simulation of Ben Eater's 8 Bit CPU Build Project https://eater.net/8bit
I was working on Ben Eater's 8-Bit CPU Project and created a web based simulator for the project.
A friend of mine made some fixes and optimized the way the microcode is used, which I then forked back to this repository. I have since made an assembler that generates CPU compatible code.
The assembler is loosely based around the style and syntax of the Z-80 assembly language. It currently supports the following:
Lines that start with ; are considered comments and ignored.
The A register (Accumulator) is the only register available in the ld command. The output register is considered
unique and populated via the out opcode which moves the contents of the Accumulator into the display register.
There are three situations for the use of the load command:
ld a,3 Loads the value 3 into the accumulator. Uses the LDI opcode.
ld a,(X) Loads the value at memory location (X) into the accumulator. Uses the LDA opcode
ld (X),a Loads the value in the accumulator into memory location (X). Uses the STA opcode.
There is basic support for labels and jumps which allows for conditional branching. Labels start with : . Memory
locations will be mapped by the assembler, allowing for code such as the following:
Start:
ld a,1
out
jmp Foo
Bar:
ld a,3
out
hlt
Foo:
sub (Decrement)
jz Bar
; This line is never executed
hlt
Decrement:
.byte 1
This program will output 1 then 2 then 3 since the zero flag is set. The following jumps are supported:
jmp Unconditional Jump
jc Jump if Carry-Flag is set
jz Jump if Zero-Flag is set
Variables may be declared after labels. The assembler will automatically assign a pointer and manage references when building the machine code. Variables must start with .byte after a label.
Counter:
.byte 3
Y:
.byte 6
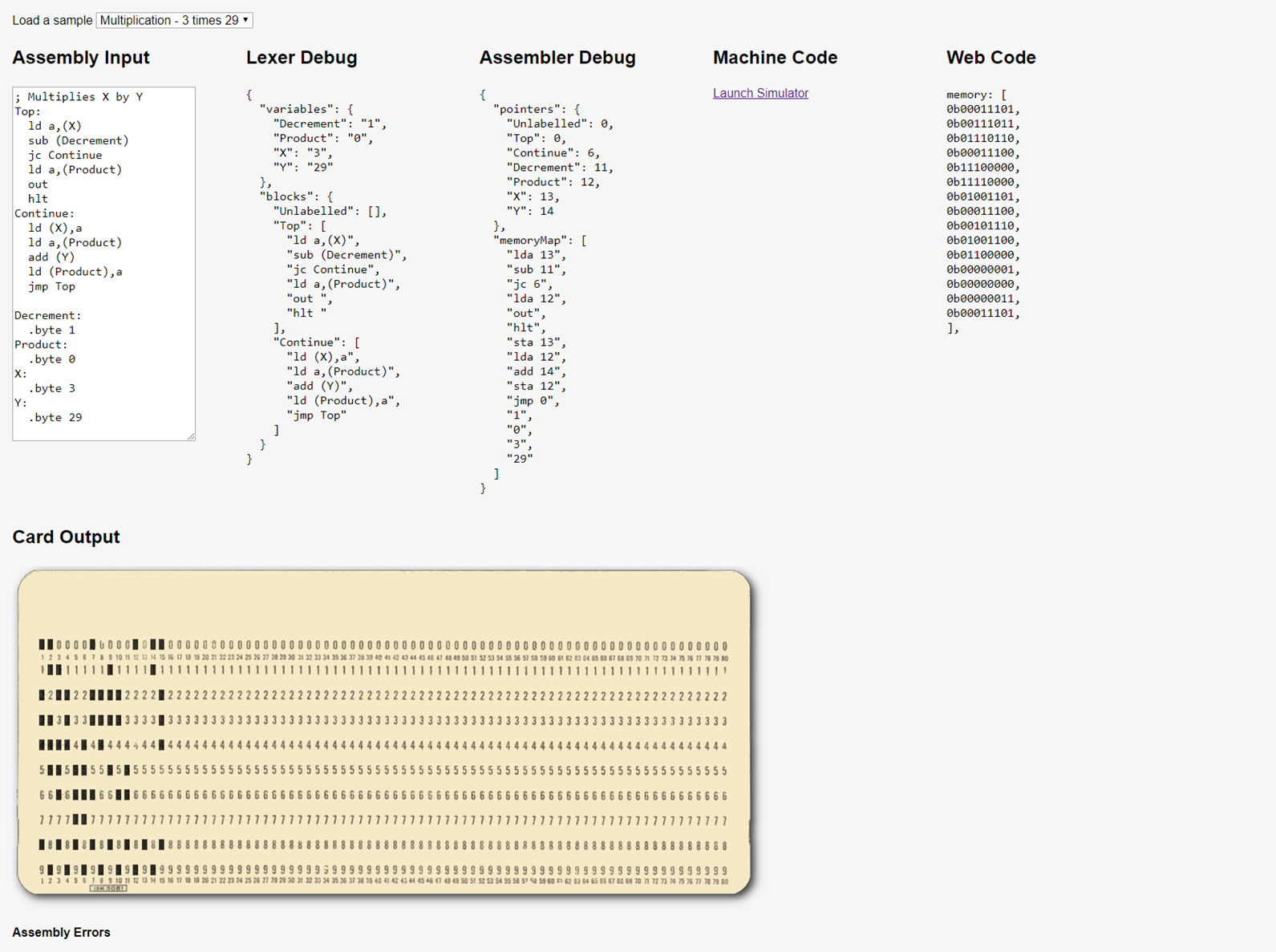
The following computes 3 * 29 and displays the output:
; Multiplies X by Y
Top:
ld a,(X)
sub (Decrement)
jc Continue
ld a,(Product)
out
hlt
Continue:
ld (X),a
ld a,(Product)
add (Y)
ld (Product),a
jmp Top
Decrement:
.byte 1
Product:
.byte 0
X:
.byte 3
Y:
.byte 29