Based on ~5978 tweets from Dutch politiciants, this LSTM-based classifier tries to indentify what the intention of the tweet was, based on 18 classes. This reaches approximately 47% accoracy. .
- prof. Marcel Broersma, principal investigator, University of Groningen, Faculty of Arts
- dr. Marc Esteve del Valle, second principal investigator, University of Groningen, Faculty of Arts
- MSc Herbert Teun Kruitbosch, data scientist, University of Groningen, Data science team
- dr. Erik Tjong Kim Sang, data scientist, eScience Center
(The data science team is a group of 10 data scientists and alike that assist researchers from all faculties with data science and scientific programming, as part of the universities Center of Information Technology)
We have 5978 tweets which are annotated in 18 categories are:
- SHARING FROM OWN NEWS OUTLET
- SHARING FROM OTHER OUTLETS
- SHARING FROM NON-MEDIA
- LIVE REPORTING
- SELF PROMOTION
- OTHERS PROMOTION
- OPINION, CRITIQUE, INTERPRETATION
- ARGUING
- REQUEST JOURN INPUT
- REQUEST NON-JOURN INPUT
- RETWEET REQUEST
- ADVICE
- ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
- PERSONAL
- ERROR CORRECTION
- JOURNALISTIC REFLECTION
- OTHER
- UNKNOWN
These categories have the distribution of Figure 1.
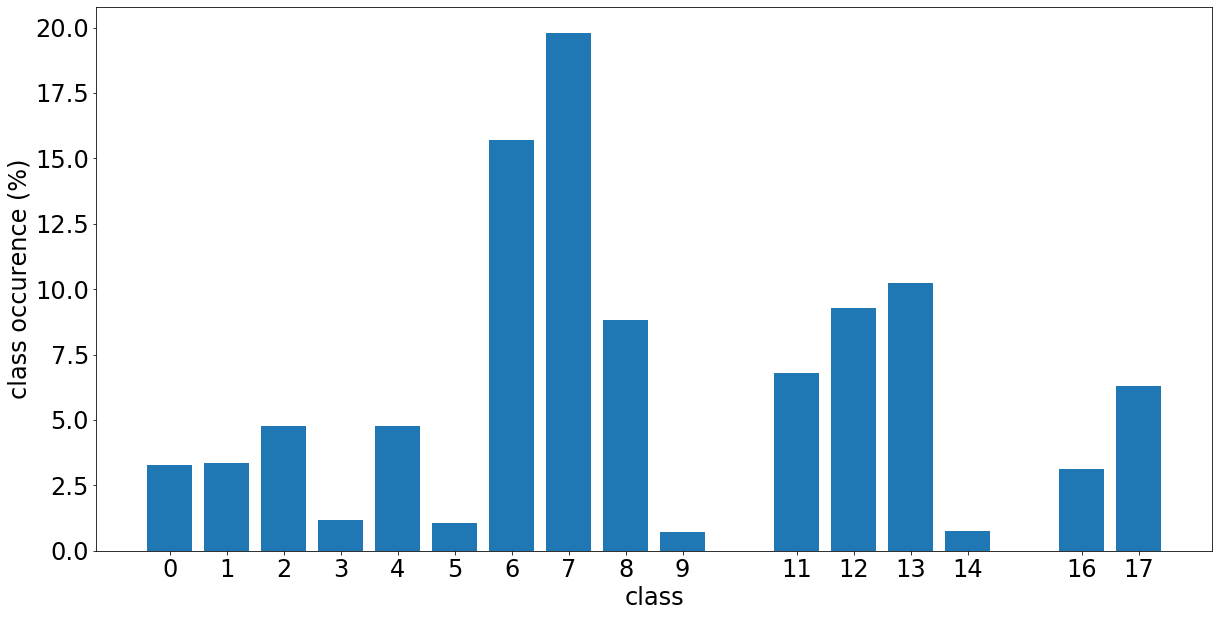
|
| Figure 1. Class distribution |
The 1000 most recent tweets were used as a test-set to avoid train-test contamination because tweets might be similar in the same time frame.
The data is owned by the principal investogator and hence not included in this git-repository.
We've used an ensemble of three models which performed the best in sample out of 10 trained models. Each model was a character-level LSTM.
This classifier obtained 47% accuracy on an out of data sample, Figure 2 and 3 show the confusion matrix and top-n accuracies.
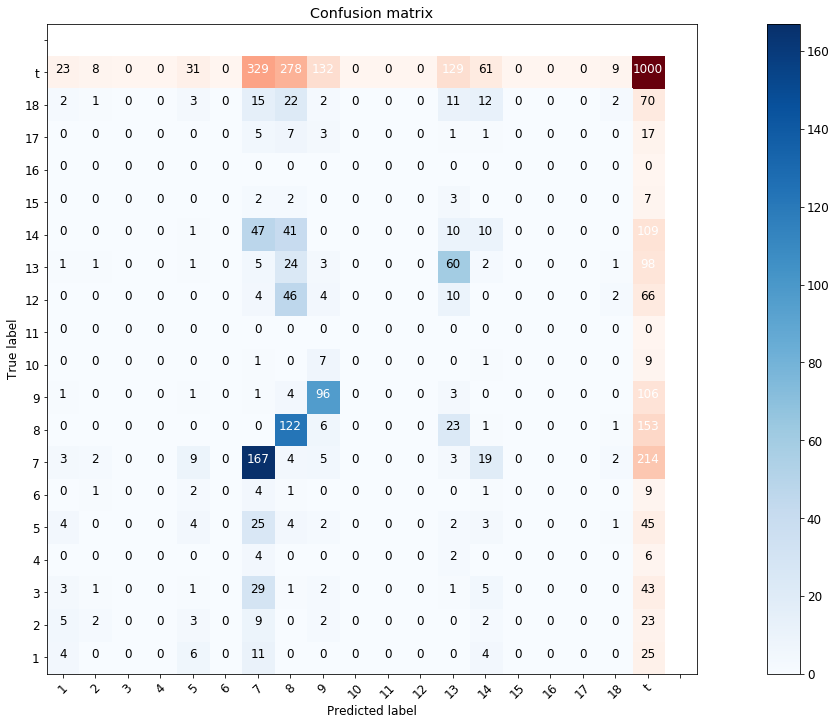
|
| Figure 2. Prediction confusion matrix |
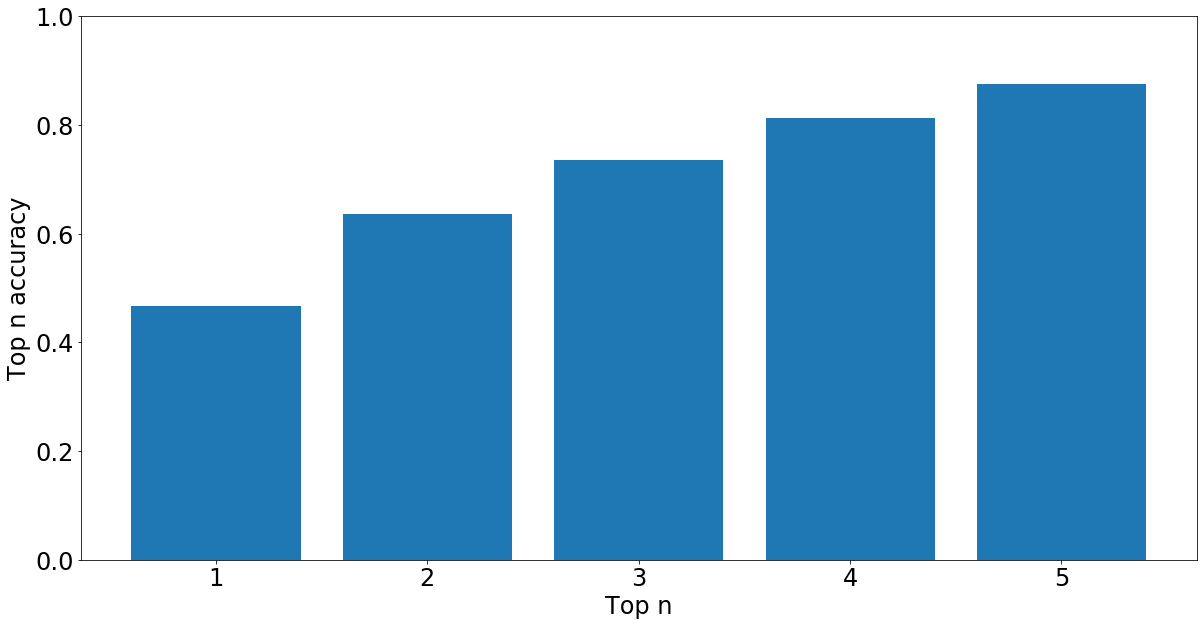
|
| Figure 3. Top-n classification accuracy |
The twitterlib provides:
- methods to scrape twitter by simulating a web browser session:
twitterlib.collection.scrape - models to predict meta-information of a tweet using TF-IFD and logistic regression or a Convolutional LSTM.
We've applied our method in Google Colab using this notebook.