(This repo is a fork of https://github.com/ibm-cloud-architecture/node-web-app, all the credits goes to Roland Barcia and the team at the IBM Gragage.)
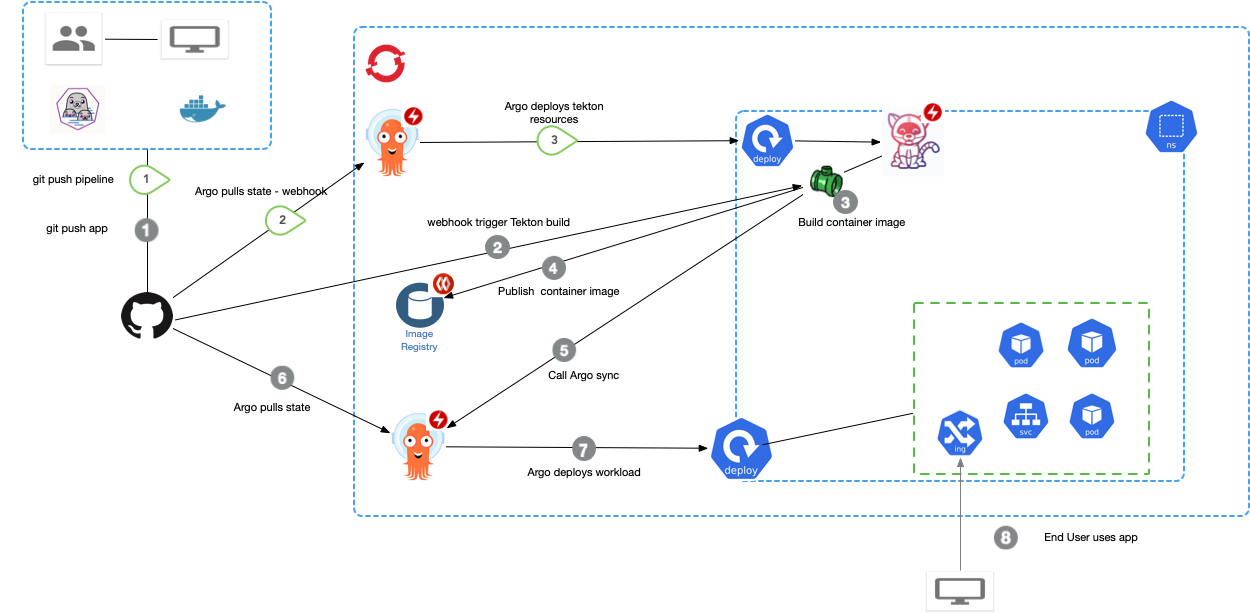
This git repo is a simple contains a simple node applicaiton that uses argocd to deploy its tekton pipeline to OpenSHift 4.3. It the uses Tekton to build an image, publish it to the Container Registry and executes an argo sync to deploy the app.
The Node Application is created following this tutorial simulating how a new user might learn to containerize a Node App. Dockerizing a Node.js web app
-
To run the application locally, Install Docker Desktop.
-
You can run the app locally if you have node installed
cd node-web-app/
npm install
node server.js- Since you have the code, docker build with a tag
docker build -t <your username>/node-web-app .- Run the application in a container.
docker run -p 49162:8082 -d <your username>/node-web-app- Check that the container is running.
docker ps- Test the Application
curl -i localhost:49162This change is required to run a build from the console without a Trigger Event.
You need your own 4.3 OpenShift Cluster. Here are some options.
I installed OpenShift 4.3 into AWS following these instructions.
You could use Code Ready Containers Locally.
This tutorial can work also on any Kubernetes, but you have to install Tekton and use the buildah task.
You need the following CLI's
Log into your OpenShift Cluster should automatically log you into kubernetes and tekton.
oc login --server=https://<OCP API Server> --token=<Your Auth Token>
Your ID should use an ID with admin access since you will be installing a set of tools.
You can also log into your OpenShift web console.
Install ArgoCD
kubectl create namespace argocd
kubectl apply -n argocd -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/argoproj/argo-cd/stable/manifests/install.yamlDownload ArgoCD CLI
brew install argocdChange the argocd-server service type to LoadBalancer:
kubectl patch svc argocd-server -n argocd -p '{"spec": {"type": "LoadBalancer"}}'Kubectl port-forwarding can also be used to connect to the API server without exposing the service.
kubectl port-forward svc/argocd-server -n argocd 8080:443The API server can then be accessed using the http://localhost:8080
Login Using the CLI, using the username admin and the password from below:
kubectl -n argocd get secret argocd-initial-admin-secret -o jsonpath="{.data.password}" | base64 -dChange the password using the command:
argocd login localhost:8080
argocd account update-passwordRegister a cluster docker-desktop to deploy apps to
argocd cluster add docker-desktopkubectl apply -f https://storage.googleapis.com/tekton-releases/pipeline/previous/v0.24.1/release.yamlkubectl apply -f https://storage.googleapis.com/tekton-releases/triggers/latest/release.yaml
kubectl apply -f https://storage.googleapis.com/tekton-releases/triggers/latest/interceptors.yamlkubectl apply --filename https://storage.googleapis.com/tekton-releases/dashboard/latest/tekton-dashboard-release.yamlThe Dashboard can be accessed through its ClusterIP Service by running kubectl proxy. Assuming tekton-pipelines is the installed namespace for the Dashboard, run the following command:
kubectl proxyBrowse http://localhost:8001/api/v1/namespaces/tekton-pipelines/services/tekton-dashboard:http/proxy/ to access your Dashboard.
kubectl create namespace node-web-projectAfter tekton builds the application and pushes the container image into the Image Repository, tekton needs to trigger a new OpenShift Deployment. There is a special task that allows Tekton to trigger a argocd sync. You have to install the Argo CD Tekton Task.
kubectl apply -n argocd -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/tektoncd/catalog/main/task/argocd-task-sync-and-wait/0.1/argocd-task-sync-and-wait.yaml
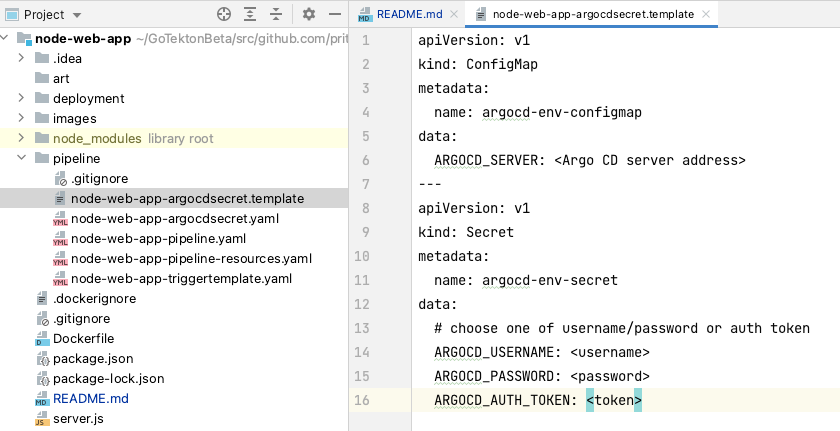
There is a file called node-web-app-argocdsecret.template which contains
argocd-env-configmap:ConfigMapwithARGOCD_SERVERused for server addressargocd-env-secret:SecretwithARGOCD_USERandARGOCD_PASSWORDused for authentication
Create a copy of that file as yaml.
cd pipeline/
cp node-web-app-argocdsecret.template node-web-app-argocdsecret.yamlIn the newly created file, replace the value for ARGOCD_SERVER (localhost:8080) to your server. Either enter your ARGOCD_AUTH_TOKEN or User and Password Base 64 encoded.
There is a file called node-web-app-serviceaccount.template which contains
dockerhub-user-pass:Secretwith${DOCKER_USERNAME}and${DOCKER_PASSWORD}used for authenticationcdcon-app-builder:ServiceAccountusing the secretdockerhub-user-pass
Create a copy of that file as yaml.
cd pipeline/
cp node-web-app-serviceaccount.template node-web-app-serviceaccount.yamlIn the newly created file, replace the value for DOCKER_USERNAME and DOCKER_PASSWORD with your docker credentials.
-
node-web-app-pipeline-resources.yaml: Pipeline Resources are configured for the pipeline. We will create two resources (
gitandimage), which will need the name of the git repository, and the name of the Container Image using the Docker Hub. Note, the resources here allow us to run a Pipeline from the Tekton Dashboard or CLI. It hard codes default values. They will be overridden by Trigger Template when builds are done via a git push. -
node-web-app-pipeline.yaml: Our Pipeline for building, publishing, and deploying our application. There are two Tasks. We make use of the shared tasks rather than creating our own. Tasks:
- the
build-and-publish-imageuses the ClusterTask buildah (podman build system). argocd-sync-deploymentuses the ArgoCD task we installed earlier
- the
-
node-web-app-triggertemplate.yaml: Now that the pipeline is setup, there are several resources created in this file. They create the needed resources for triggering builds from an external source, in our case a Git webhook. You can learn more about Tekton Triggers here. We have created the following.
-
A TriggerTemplate is used to create a template of the same pipeline resources, but dynamically genertaed to not hard code image name or source. It also creates a PipelineRun Template that will be created when a build is triggered.
-
A TriggerBinding that binds the incoming event data to the template (this will populate things like git repo name, revision,etc....)
-
An EventListener that will create a pod application bringing together a binding and a template.
-
An OpenShift Route to expose the Event Listener. Your will create a GIT Webhook that will callback this Route.
-
You can learn about Tekton Resources and OpenShift Pipleines
We can use ArgoCD to deploy the Tekton build for the app. IN a real project, having your pipeline in a separate repo might be better. You can create an argo cd app via the GUI or commandline.
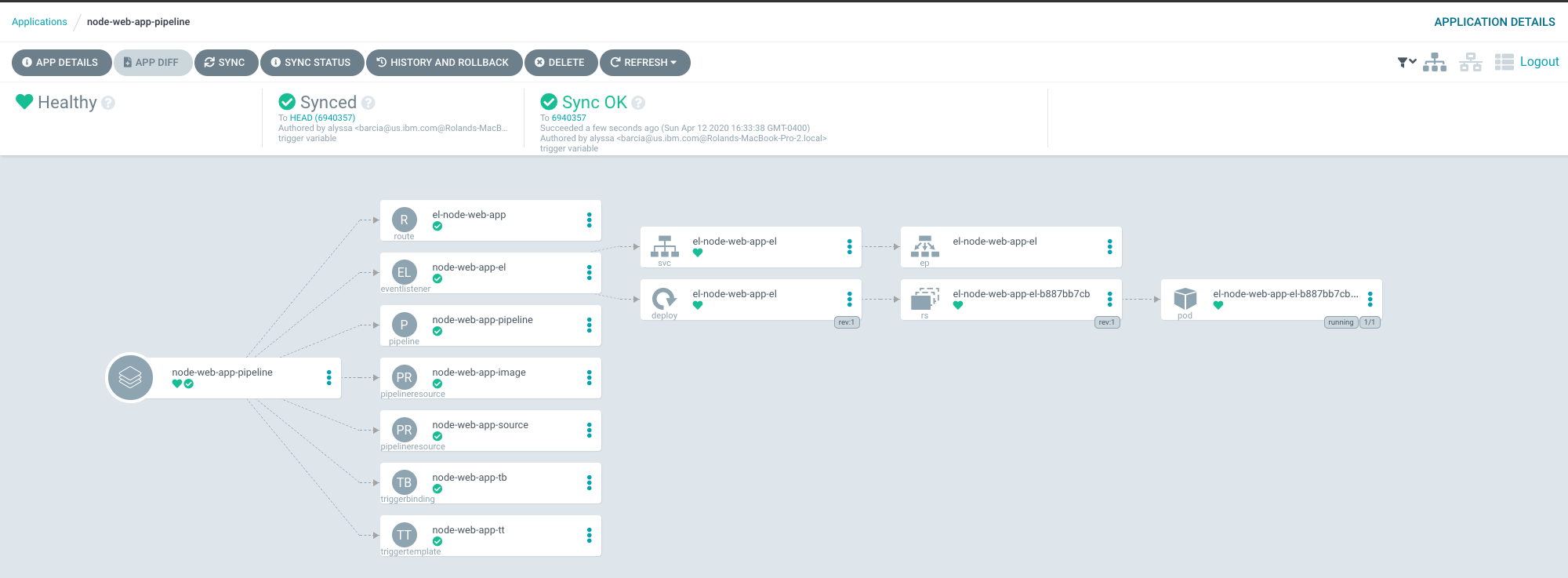
argocd app create node-web-app-project --repo https://github.com/pritidesai/node-web-app --path pipeline --dest-name docker-desktop --dest-namespace node-web-projectOnce you run sync, your pipeline should be deployed, and your screen in ArgoCD should look like below.
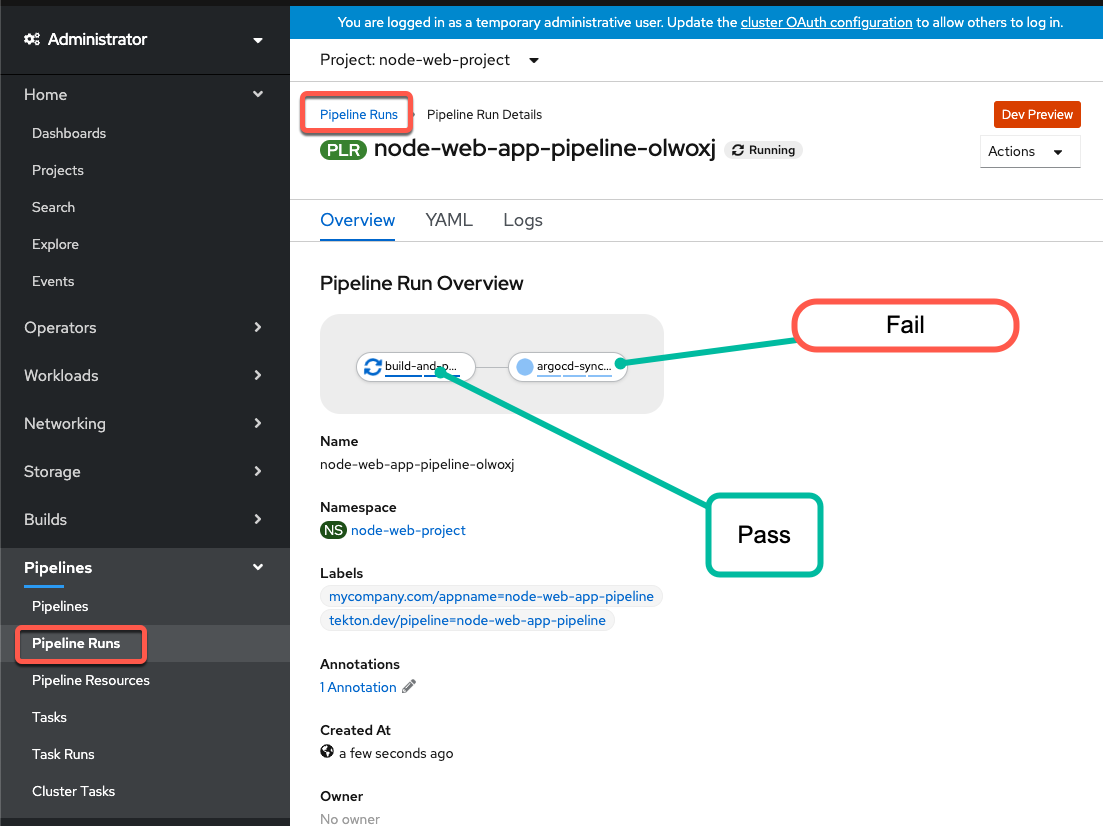
At this point you can run a build. The Build Should succeed, but the deploy should fail. If you configure the deployment first however, deployment will fail to start because the image has not been published.
- You can go into the PipelineRuns section of the Tekton Dashboard and click Create.
- Select the
Pipeline,PipelineResources, andServiceAccount.
- The pipeline should run, the build should pass (Creates the Container Image and publishes it to the Container Registry). The argo-cd sync should fail because we have not configured the argod app for deploying the node-web-project.
Let's look at the OpenShift Configuration for our node application.
-
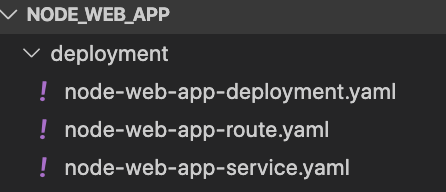
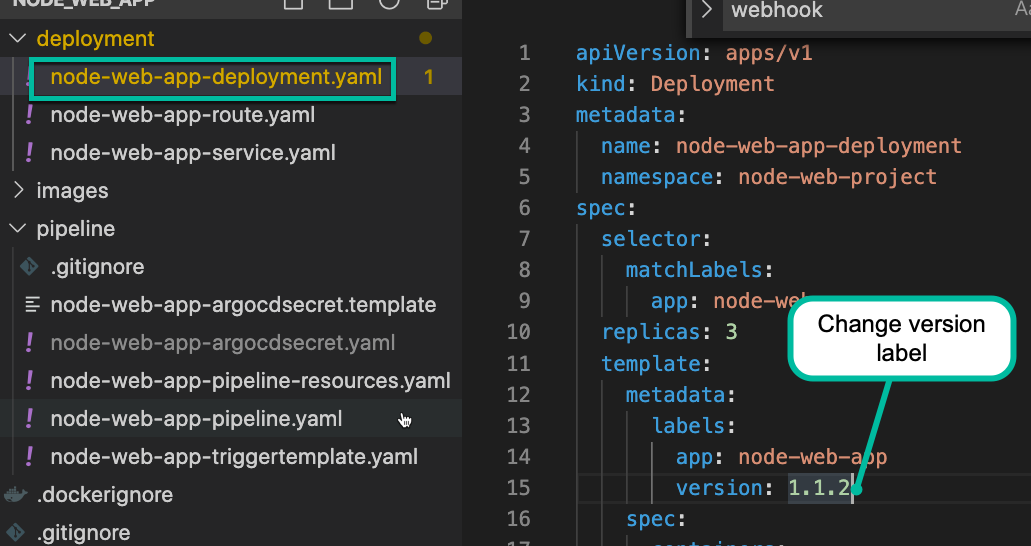
node-web-app-deployment.yaml - This represents our Kubernetes Deployment.
-
node-web-app-service.yaml: This expose the node app to the cluster.
-
node-web-app-route.yaml: Exposes an OpenShift Route so you can access Node App from outside the cluster
Just like we used argocd to deploy the tekton pipeline, you will create another argocd app that corresponds to the deployment. You can create an argo cd app via the GUI or commandline.
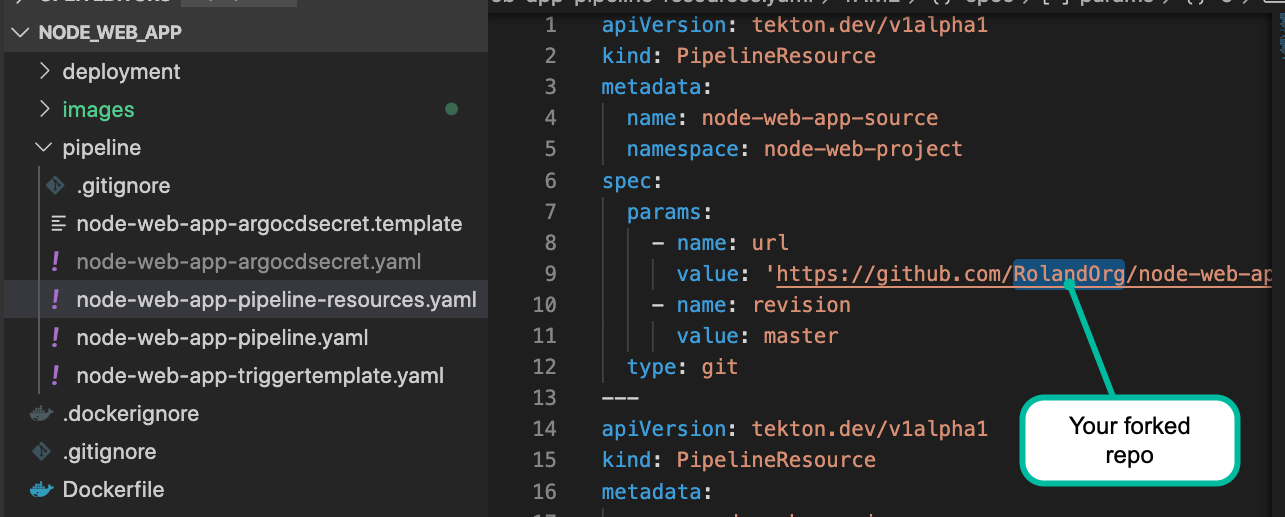
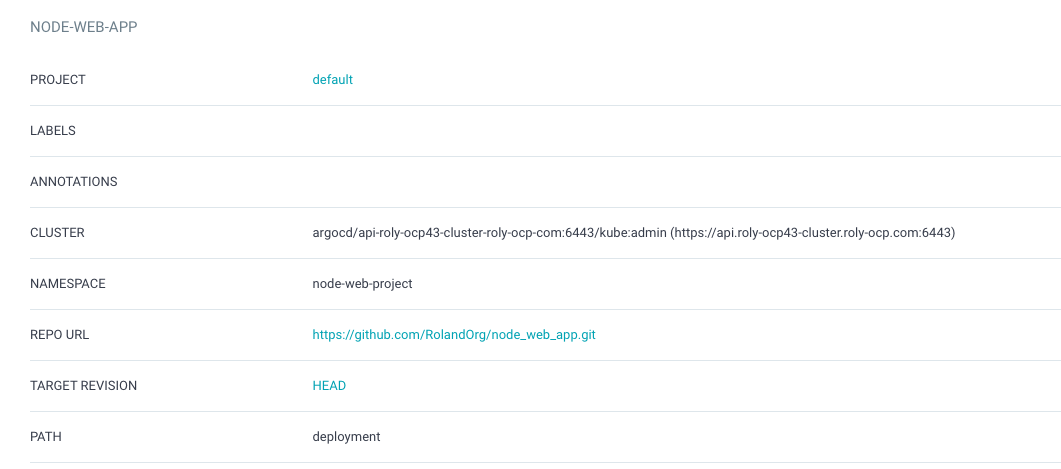
The screenshot below shows the parameters I entered. You need to use your own forked git repo.
- Project: default
- cluster: (URL Of your OpenShift Cluster)
- namespace should be the name of your OpenShift Project
- repo url: should be your forked git repo.
- Targer Revision: Head
- PATH: deployment
- AutoSync Disabled.
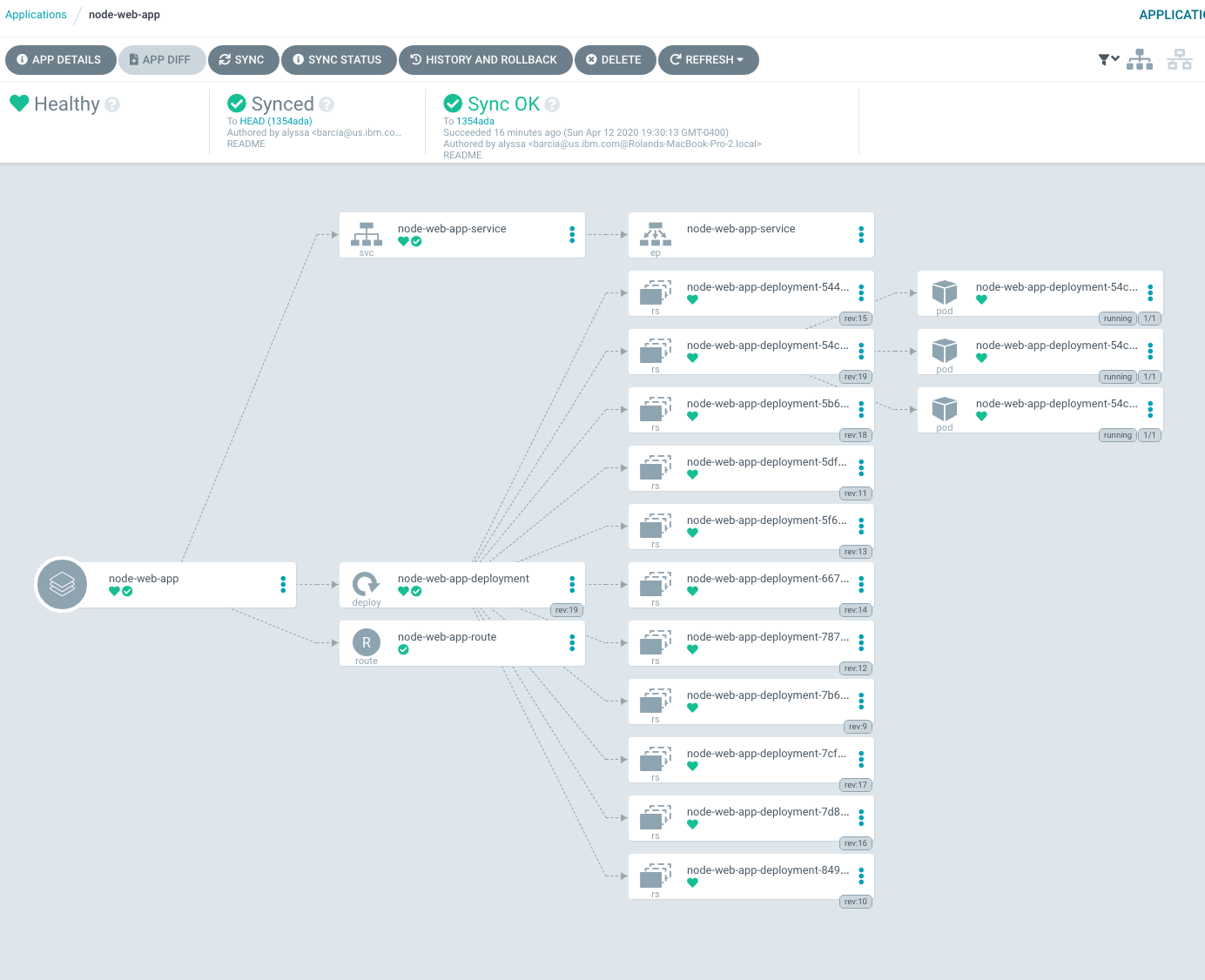
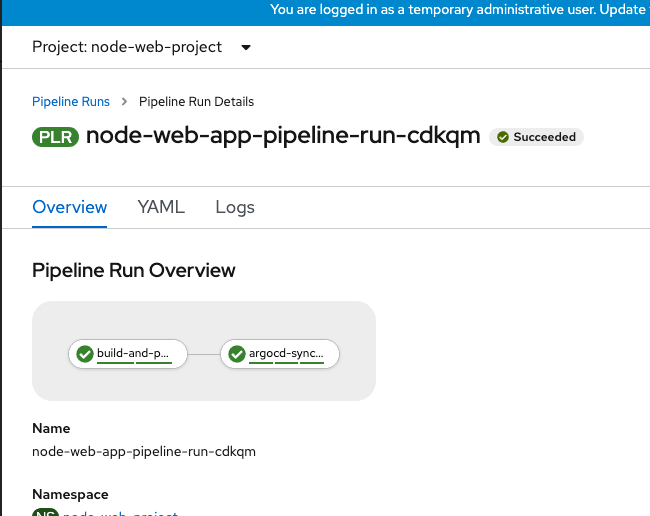
argocd app create node-web-app --repo https://github.com/pritidesai/node-web-app --path deployment --dest-name docker-desktop --dest-namespace node-web-projectFrom here, you can trigger a sync manually by clicking sync. Once your resources are deployed, your build from earlier is complete. The screen should look like the figure below.
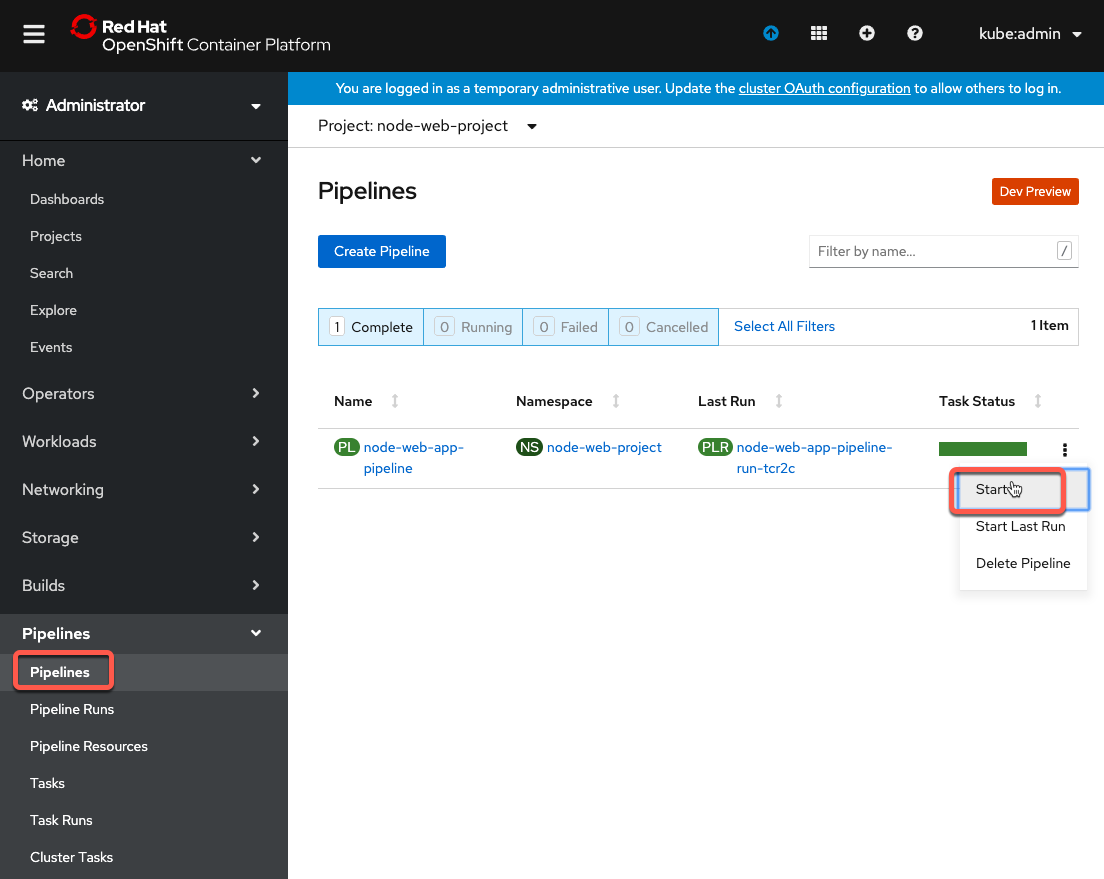
- You can go into the Pipelines section of the OpenShift Console, right click the pipeline and click Start.
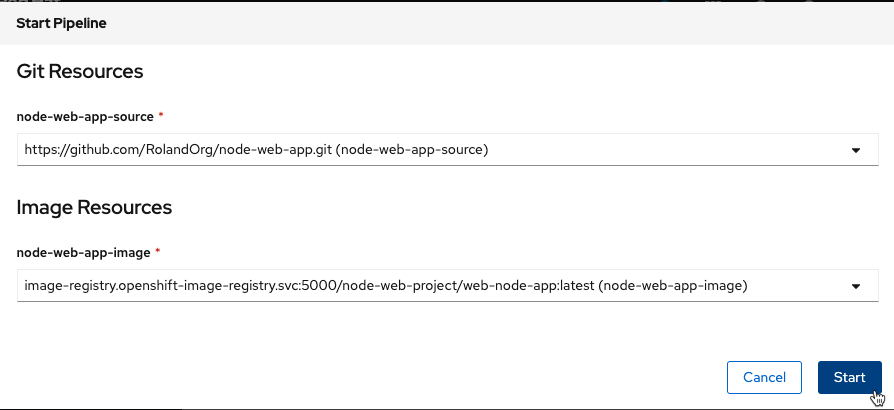
- You will see that the values are prepopulated with default PipelineResources as shown below.
- The pipeline should run, should now complete.
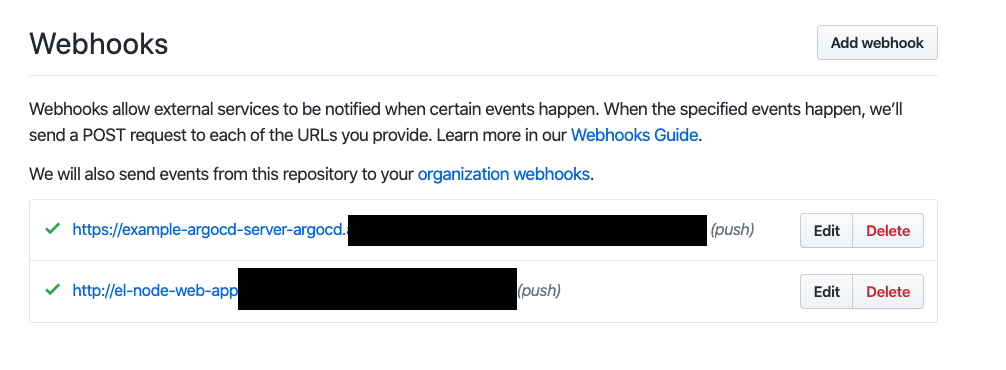
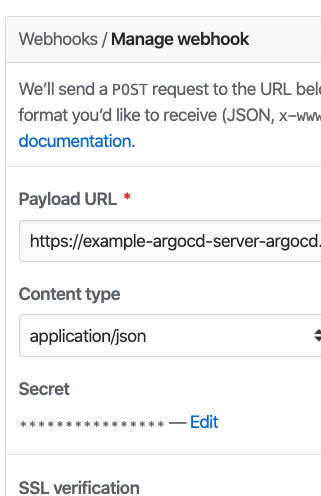
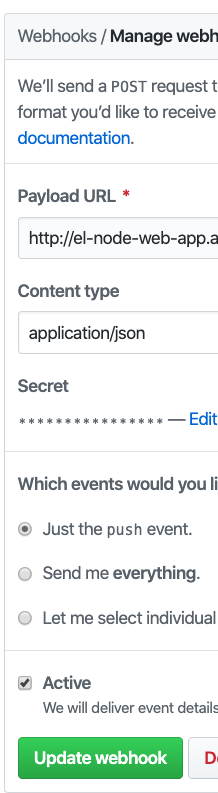
You will now need to configure 2 WebHooks.
-
One WebHook will be configured to our argocd pipeline app. This will enable us to push changes to our pipeline plus for argocd to detect changes for our app (though autosync is not on)
-
One webhook will go to your Tekton Event Listener to start a tekton build from git push
kubectl get eventlistener -n node-web-project
kubectl get svc -n node-web-project
kubectl port-forward svc/el-node-web-app-el -n node-web-project 8080
ngrok http 8080curl -v \
-H 'X-GitHub-Event: push' \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
-d '{"repository":{"url": "https://github.com/pritidesai/node-web-app", "name": "node-web-app"}, "head_commit":{"id": "b20de767cf9799a23d8cb6bbd795c3c5e0b4b95a"}}' \
http://localhost:8080
- Push the changes to your repo
git add .
git commit -m "First Deployment"
git push
In a real deployment, you might have many webhooks. git push can be build to dev while a git tag can be a build for test.
-
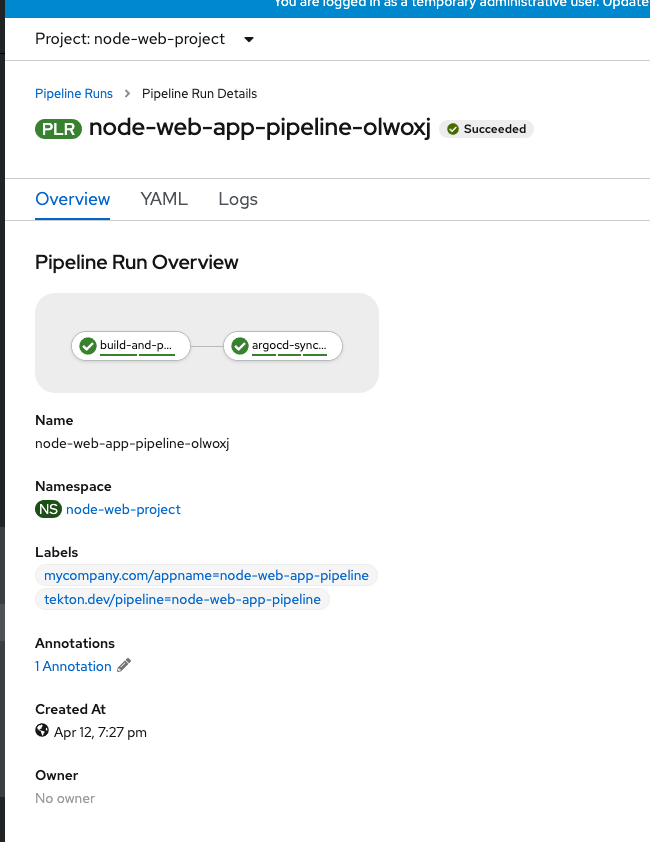
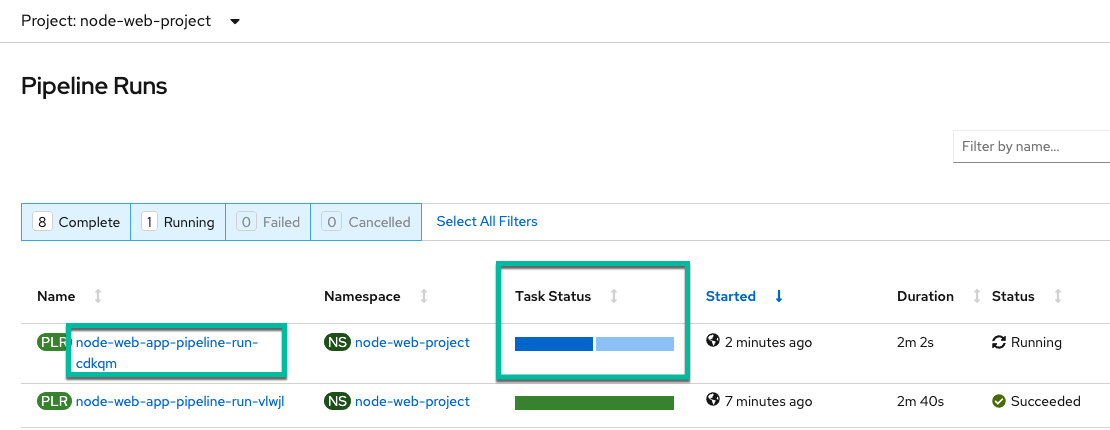
Go to the OpenShift Console and you should see a pipleine run kickoff. Wait till it is complete. Notice the name of the pipleine run matches that in the trigger template.
-
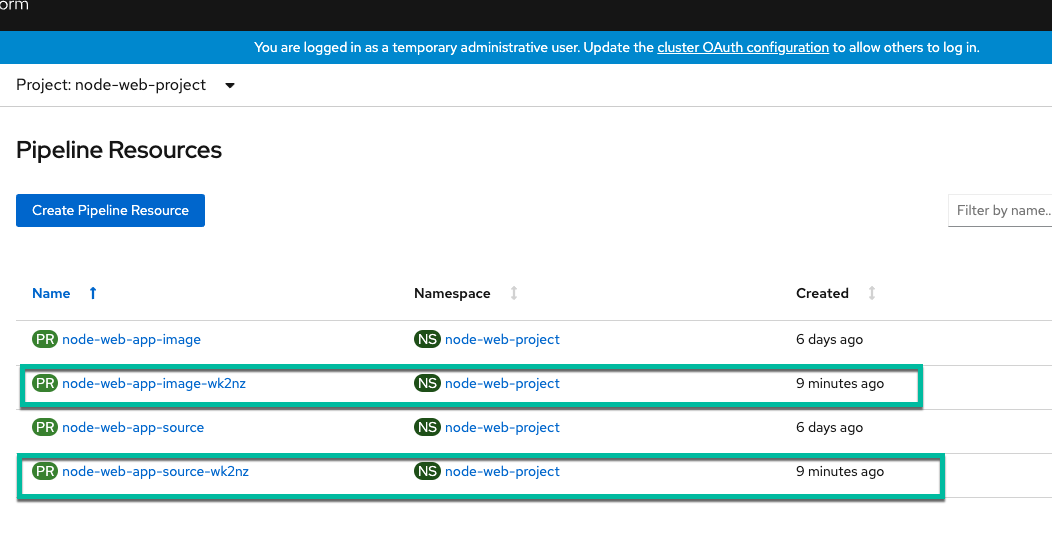
While waiting for the build, go to pipeline resources section and look to see new pipeline resources created for the webhook build. It will dynamically create a resource for build so you know what parameters were used to run the build.
-
Go back to the Pipeline Runs and check that the build is complete.
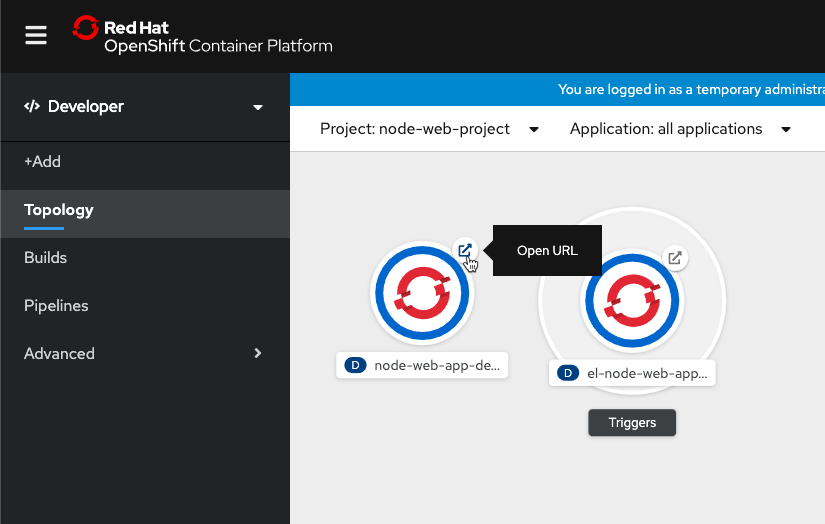
- Go to the Topology view on the Developer Side and launch the app as shown.
- If it all works out, your app should look like this
This completes loading the solution.
-
argocd runs in an argocd namespace. Your tekton pipleine runs in your app namespace.
-
using tkn log instance to see tekton activity
-
oc logs for various pods
-
Redeploying TriggerTemplate does not cause the Event App to restart. Delete pod to run new instance.