Morse Talk is a Python library which deals with Morse code. The documentation is available at http://morse-talk.readthedocs.org/en/latest
pip install morse-talkgit clone https://github.com/OrkoHunter/morse-talk.git
cd morse-talk/
python setup.py install>>> import morse_talk as mtalk
# Encoding in morse
>>> mtalk.encode('Alpha Ranger 45 departed')
'.- .-.. .--. .... .- .-. .- -. --. . .-. ....- .....
-.. . .--. .- .-. - . -..'
# Encoding using binary pattern
>>> mtalk.encode('Alpha Ranger 45 knocked down', encoding='binary')
'1111000111111000111111110001111000111100000001111100011110001111000111111100010001111
10000000111111100011111000000011111110001111000111111111000111111110001111111000100011
11100000001111100011111111100011111110001111'
# Decoding a code encoded in morse
>>> code = '-... --- -- -... -..- .--. --'
>>> mtalk.decode(code)
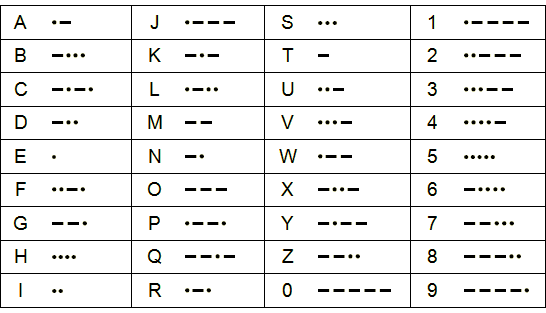
'bomb x pm'Morse code is a method of transmitting text information as a series of on-off tones, lights, or clicks that can be directly understood by a skilled listener or observer without special equipment. The International Morse Code encodes the ISO basic Latin alphabet, some extra Latin letters, the Arabic numerals and a small set of punctuation and procedural signals as standardized sequences of short and long signals called "dots" and "dashes", or "dits" and "dahs". Because many non-English natural languages use more than the 26 Roman letters, extensions to the Morse alphabet exist for those languages.
International Morse code is composed of five elements:
- short mark, dot or "dit" (·) : "dot duration" is one time unit long
- longer mark, dash or "dah" (–) : three time units long
- inter-element gap between the dots and dashes within a character : one dot duration or one unit long
- short gap (between letters) : three time units long
- medium gap (between words) : seven time units long