User-Authentication using JWT
User Authentication using Traditional Approach
-
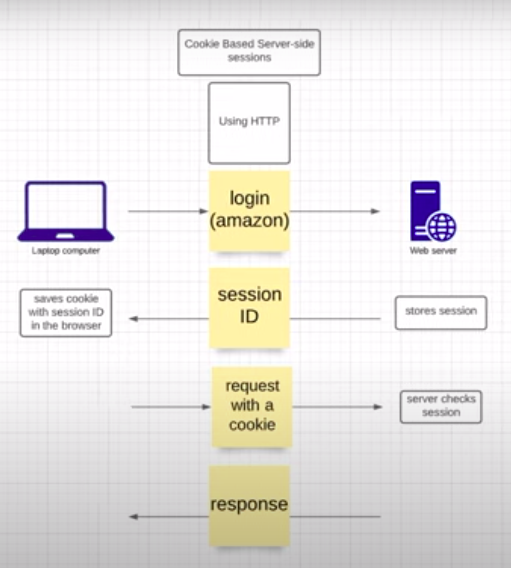
Stores the session in DB and generates
Session IDfor each session of the User (sent to client - browser from server) -
Session ID is saved in Cookie
-
cookie is a text file saved in your local storage in the browser
-
it is in the form of key-value pair
-
-
The cookie is sent to server for every subsequent requests made by the client. This is called STATEFUL protocol between front-end client (browser) and back-end server
-
STATEFUL protocol - saves everything in the back-end
-
STATELESS protocol - saves everything in the front-end client
-
-
Authentication state handled on the server
-
Has security issues. Easy for attackers to point to your account
User Authentication using JSON Web Tokens (JWT)
-
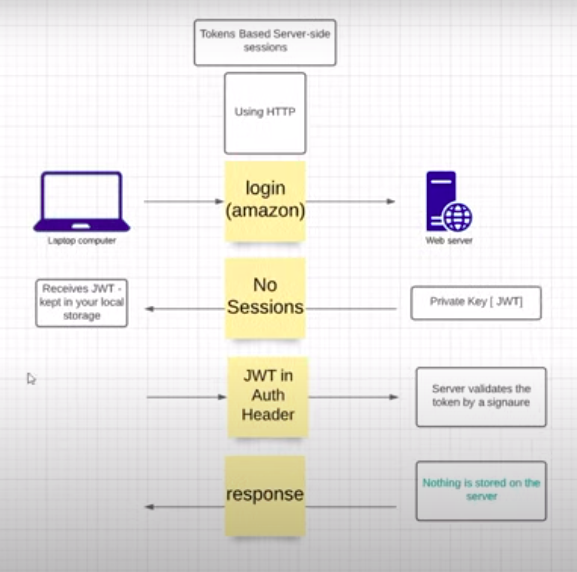
Server generates
JWT(sent to client) -
Stored in the local storage in the browser
-
On subsequent requests, the JWT is placed along with authorization header prefixed by the bearer of the token
-
Server needs to validate the JWT signature
-
JWT handled on the client side
jwt.io
-
allows you to decode, verify and generate JWT
-
password hashing method used : hs256
-
JWT has 3 sections :
-
Header (has algorithm and type of token)
-
Payload (has actual data)
-
Verify Signature (signature along with secret key)
-
Approaches to get a secure secret key
-
random() method in os module
import os os.random(12)
-
uuid4() method in uuid module
import uuid uuid.uuid4().hex
-
secrets module
import secrets secrets.token_urlsafe(12)
Python libraries to be used
-
flask
-
jwt
-
datetime
-
functools
Example of authentication of user via login page
Login Page using Flask and JWT