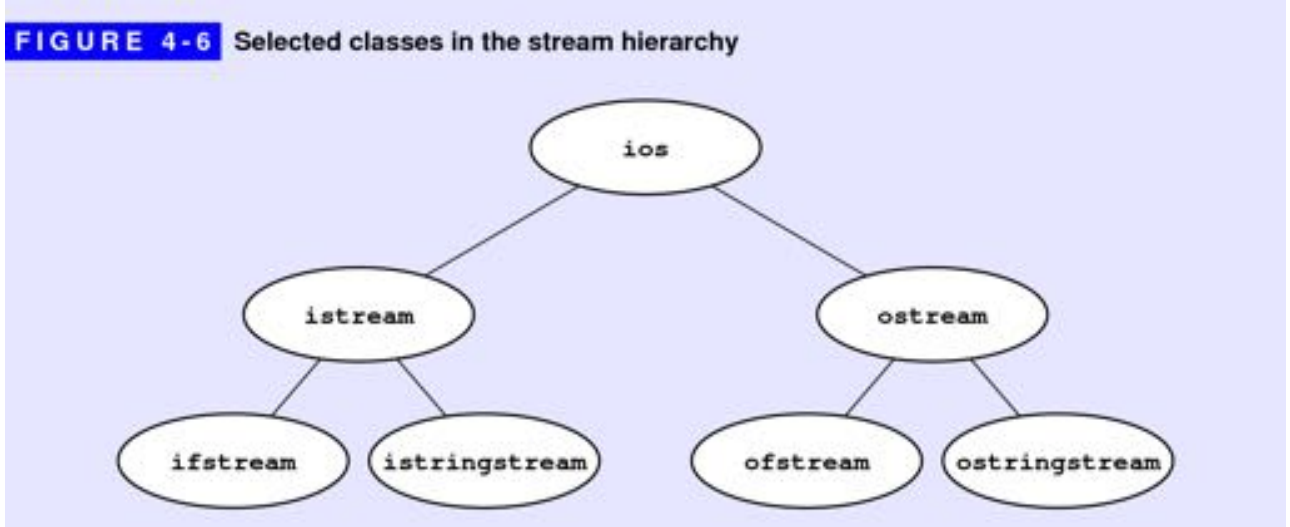
该章节主要是描述字符串处理内容。
探索 C++ 中流(stream)存在那些特征,以及如何利用 stream 去处理文件数据。
<< 被称为插入运算符(insertion operation),左侧为输出流,右侧为需要插入的数据。<< 通过重载操作符使得其可以输出不同类型的数据值。C++ 中利用一系列称为操纵器(manipulator)的东西实现格式化输出。有些操纵器是短暂的,仅仅影响下一个输出的字段,而有些操纵器则是持久的,直到显示调用改变其属性。
| manipulator | message |
|---|---|
| endl | 将换行结束符插入输出流 |
| setw(n) | 设置下一个字段输出为 n 个字符,若不足默认填充空格,该操作是短暂的 |
| setprecision(digits) | 设置数值的精度,该操作是持久的 |
| setfill(ch) | 设置流的填充为字符 ch,该操作是持久的 |
| left | 指定字段左对齐,持久操作 |
| right | 指定字段右对齐,持久操作 |
| intermal | 指定字段居中对齐,持久操作 |
| fixed | 指定浮点数具体显示数值,而不是科学计数法,持久操作 |
| scientific | 以科学计数法显示,持久操作 |
| showpoint/noshowpoint | 显示/不显示小数点,持久操作 |
持久存储数据在存储媒介中的数据集合称为文件。C++ 中头文件 fstream 中包含两个流处理类 ifstream 和 ofstream 用于处理文件的读取和写入。
读写文件的基本步骤:
1. 声明一个流变量引用该文件
ifstream infile;
ofstream outfile;
2. 打开文件
infile.open("file.txt");
由于流库的引入早于string 类,所以需要一个 C 风格的字符串表示
infile.open(filename.c_str());
3. 转换数据
4. 关闭文件
infile.close();| 方法名 | 功能描述 |
|---|---|
| get(var) | 将文件流中的下一个字符以引用的方式存储到 var 变量中,并返回 stream |
| get() | 返回文件流中的下一个字符 |
| clear() | 用于清除文件读写的错误标志 |
| fail() | 若文件读取发生错误,返回 true,否则返回 false |
| close() | 关闭文件 |
| unget() | 撤回最近一个读取的字符,将其重新放回输入流中 |
| eof() | 若到达文件末尾则返回 true, 否则返回false |
| operator>>() | 提取带格式的数据,跳过前导空格 |
| getline(infile, str) | 该函数是自由函数,传入两个引用参数,将读取的一行存储在 str 字符串中 |
| open(filename) | 打开文件 |
头文件 sstream 提供了一些类允许用户关联一个字符串和流,使得可以类似 fstream 中的方式处理字符串。主要是两个类 istringstream 和 ostringstream。
| 成员函数 | 功能说明 |
|---|---|
| str() | 获取流的字符串 |
根据行为而不是表示方式定义的类型称为抽象数据类型(Abstract Data Type)。本章主要介绍五个类别,Vector、Stack、Queue、Map 和 Set。
- 构造函数
explicit vector( const Allocator& alloc );初始化空容器explicit vector( size_type count );构造 count 个默认值的容器explicit vector( size_type count, const T& value = T(), const Allocator& alloc = Allocator() );构造 count 个 元素值为 value 的容器vector( InputIt first, InputIt last, const Allocator& alloc = Allocator() );构造拥有范围[first, last)内容的容器
- push_back(value) 将元素 value 追加到容器末尾
- insert() 将元素插入到容器的指定位置
iterator insert( const_iterator pos, const T& value );将元素 value 插入到容器 pos 之前iterator insert( const_iterator pos, size_type count, const T& value );在容器 pos 之前插入count 个元素 value 的副本iterator insert( const_iterator pos, InputIt first, InputIt last );在容器 pos 之前插入来自范围[first, last)的元素iterator insert( const_iterator pos, std::initializer_list<T> ilist );在容器 pos 之前插入初始化列表的元素vector( const vector& other );拷贝构造函数vector( std::initializer_list<T> init, const Allocator& alloc = Allocator() );使用初始化列表构造容器
- erase 从容器擦除指定元素
iterator erase( iterator pos );移除容器 pos 处的元素iterator erase( iterator first, iterator last );移除容器 [first, last) 区间的元素
- 指定元素的获取
reference at( size_type pos );返回指定位置的元素引用,并且做边界检查reference operator[]( size_type pos );返回指定位置的元素引用,不做边界检查
size_type size() const;返回容器元素个数void clear();清除容器中所有元素
栈结构中数据遵循先进后出的原则。
void push( const value_type& value );将元素 value 推到栈顶reference top();返回栈顶元素的引用void pop();移除栈顶元素size_type size() const;返回栈中元素个数
数据结构中存储元素使用先进先出(First In, Fisrt Out, FIFO)策略的称为队列。
void push( const value_type& value );将元素 value 入队void pop();移除队列前端元素,无返回值reference front();返回队列前端元素的引用,即最高进入队列的元素reference back();返回最近进入队列的元素引用bool empty() const;检查队列是否为空size_type size() const;返回队列中的元素个数
映射的概念类似于字典,可以通过一个单词找对其对应的解释。Map 提供了称为 Key 和 Value 之间的关联。C++ 中 Map是一种 有序关联容器,它包含唯一键的键值对。
- 构造函数
explicit map( const Allocator& alloc );创建空的容器template< class InputIt > map( InputIt first, InputIt last, const Compare& comp = Compare(),const Allocator& alloc = Allocator() );范围构造容器map( std::initializer_list<value_type> init,const Compare& comp = Compare(),const Allocator& alloc = Allocator() );用初始化列表构造容器
- 修改器
std::pair<iterator, bool> insert( const value_type& value );将元素插入容器,并返回一个std::pairiterator insert( iterator pos, const value_type& value );在 value 插入到 pos 之前的位置template< class InputIt > void insert( InputIt first, InputIt last );插入来自范围 [first, last)范围内的元素
- 元素访问
T& at( const Key& key );返回指定键值的元素的引用,若不存在对应的键值,则抛出std::out_of_range类型异常。T& operator[]( const Key& key );返回指定键值的元素的引用
Set 类抽象了数学中的集合概念,该容器中的元素是无序的且每个元素只能出现一次。但是C++ std库中的set被实现为有序集合。
- 构造函数
set();构造空的集合容器template< class InputIt > set( InputIt first, InputIt last, const Compare& comp = Compare(),const Allocator& alloc = Allocator() );以范围[first, last)内元素构造集合容器set( const set& other );拷贝构造函数set( std::initializer_list<value_type> init, const Compare& comp = Compare(),const Allocator& alloc = Allocator() );以初始化列表元素构造集合容器
- 容量
bool empty() const;检查集合容器是否为空size_type size() const;返回集合容器的元素个数
- 修改器
std::pair<iterator, bool> insert( const value_type& value );将元素插入集合容器iterator insert( iterator pos, const value_type& value );将元素插入到位置 pos 之前iterator insert( iterator pos, const value_type& value );将范围[first, last)元素插入容器void insert( std::initializer_list<value_type> ilist );将初始化列表元素插入容器iterator erase( iterator pos );移除指定位置的元素iterator erase( iterator first, iterator last );移除指定范围内的元素size_type erase( const Key& key );移除键值等于key的元素size_type count( const Key& key ) const;返回容器中键值等于key的元素个数,由于集合容器元素具有唯一性,只能返回0或1template< class C2 > void merge( std::set<Key, C2, Allocator>& source );尝试提取source中的每个元素到当前容器中,并用*this的比较对象插入到*this。若*this存在source中的键值,则不提取该元素。合并过程不复制和移动元素,只会重定向容器结点的内部指针。iterator find( const Key& key );寻找键值等于key的元素并返回其位置,若不存在,则返回尾后迭代器(end()
- 结构体定义
// 使用点运算符访问成员
struct Point{
int x;
int y;
};
Point p;
p.x = 10;
p.y = 2;- 类(class)定义
class Point{
public:
Point(){
};
Point(int cx, int cy){
x = cx;
y = cy;
}
int Getx(){
return x;
}
int Gety(){
return y;
}
void showPoint(){
cout << "(" << x <<", " << y << ")" << endl;
}
private:
int x;
int y;
};class Point{
public:
// ...
// 友元函数
friend ostream& operator<<(ostream& out, Point p);
private:
int x;
int y;
};
// 运算符重载
ostream& operator<<(ostream& out, Point p){
out << "(" << p.x <<", " << p.y << ")";
return out;
}- 重载
++运算符,存在前缀++和后缀++两种形式
// 重载前缀++
type operator++(type ..., ){
...
}
// 重载后缀++
type operator++(type ..., int){
...
}- 设计一个新类所需的策略
- 从用户的角度出发考虑
- 确定那些信息应该属于私有变量
- 定义一系列构造函数进行类的创建
- 确定需要暴露的类公开方法
- 代码和代码测试的实现
递归函数必须能够识别可以分解的问题以及递归退出条件。
常见例子:
- 回文串判断
- 二分搜索
-
nullptr 用于区分空指针和0。
-
constexpr 常量表达式,用于在编译期间计算,获取确定值,提供代码性能
-
初始化列表的概念绑定至类型上,称之为 std::initializer_list,允许函数像其它类型参数一样传递
void foo(initializer_list<int> x){
for(auto it = x.begin(); it != x.end(); it++){
cout << *it << endl;
}
}- 结构化绑定
tuple<int, double, string> f(){
return make_tuple(1, 2.3, "hello");
}
int main(){
auto [x, y, z] = f();
cout << x << y << z << endl;
return 0;
}- 类型推导,关键字
auto和decltype实现了类型推导auto无法用于函数传参,且无法用于数组类型推导decltype是为了解决auto只能推导变量,decltype(表达式)- 尾返回类型推导
if constexpr
#include <iostream>
template<typename T>
auto print_type_info(const T& t) {
// 编译期间确定条件判断
if constexpr (std::is_integral<T>::value) {
return t + 1;
} else {
return t + 0.001;
}
}
int main() {
std::cout << print_type_info(5) << std::endl;
std::cout << print_type_info(3.14) << std::endl;
}- 区间 for 迭代
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
int main() {
std::vector<int> vec = {1, 2, 3, 4};
if (auto itr = std::find(vec.begin(), vec.end(), 3); itr != vec.end()) *itr = 4;
for (auto element : vec)
std::cout << element << std::endl; // read only
for (auto &element : vec) {
element += 1; // writeable
}
for (auto element : vec)
std::cout << element << std::endl; // read only
}- 类型别名模板,模板是用来产生类型的。
typedef int (*process)(void *); // 函数指针
using NewProcess = int(*)(void *); // using 定义别名函数指针
// 类型别名模板
template<typename T>
using TrueDarkMagic = MagicType<std::vector<T>, std::string>;
int main() {
TrueDarkMagic<bool> you;
}- 默认模板参数
template<typename T = int, typename U = int>
auto add(T x, U y) -> decltype(x+y) {
return x+y;
}- 变长参数模板,允许任意个数、任意类别的模板参数
// 变长参数模板
template<typename... Ts> class Magic;
// 不定长参数函数
template<typename... Args> void printf(const std::string &str, Args... args);#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
// ... 表示不定长参数
template<typename ...Ts>
void magic(Ts... args){
// sizeof... 计算不定长参数个数
cout << sizeof...(args) << endl;
}
void test01(){
magic();
magic(1, "Hello"); // 可以接收任意数量、任意类型参数
magic(2, 'c', 5.5);
}
int main(){
test01();
return 0;
}- 递归模板函数进行参数解包
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
template<typename T>
void print(T value); // 需要提前声明函数,否则报错
template<typename T, typename ...Ts>
void print(T value, Ts ... args){
cout << value << endl;
print(args...); // 需要存在递归终止条件
}
// 模板函数重载
template<typename T>
void print(T value){
std::cout << value << std::endl;
}
int main(){
print(1, "Hello World", 2.32);
return 0;
}