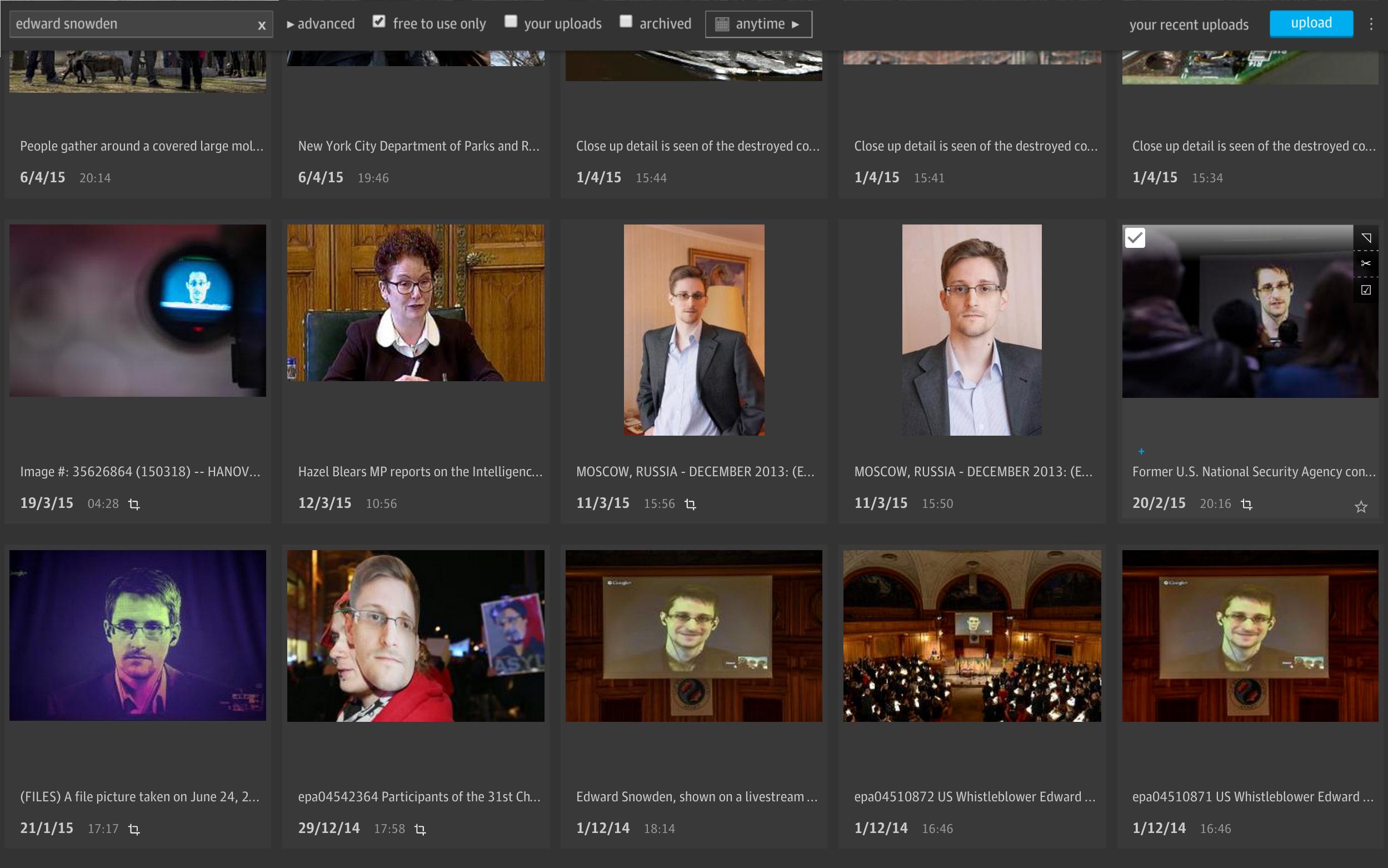
Grid
Grid is the Guardian’s new image management system, which provides a universal and fast experience accessing media that is organised and using it in an affordable way to produce high-quality content.
See the Vision document for more details on the core principles behind this project.
Grid runs as a set of independent micro-services (Scala and Play Framework) exposed as hypermedia APIs (argo) and accessed using a rich Web user interface (AngularJS).
Grid relies on Elasticsearch for blazing-fast searching, and AWS services as additional storage and communication mechanisms.
Running the applications
Requirements
You will need to install:
- sbt
- JDK 8
- Nginx
- GraphicsMagick or ImageMagick (we use
GraphicsMagick on the servers).
sudo apt-get install graphicsorbrew install imagemagick.
Nginx
To run correctly in standalone mode we run behind nginx, this can be installed as follows:
- Install nginx:
- Linux:
sudo apt-get install nginx - Mac OSX:
brew install nginx
- Make sure you have a sites-enabled folder under your nginx home. This should be
- Linux:
/etc/nginx/sites-enabled - Mac OSX:
/usr/local/etc/nginx/
- Make sure your nginx.conf (found in your nginx home) contains the following line in the http{} block:
include sites-enabled/*;
- you may also want to disable the default server on 8080
-
Get the dev-nginx repo checked out on your machine
-
Set up certs if you've not already done so
-
Configure the app routes in nginx
sudo <path_of_dev-nginx>/setup-app.rb <path_of_media_service_repo>/nginx-mapping.yml
Elasticsearch
You can run setup.sh to install and start Elasticsearch. You can use
the script to start up Elasticsearch even if it's already installed.
Alternatively you can do these steps manually:
Run the Elasticsearch installer from the elasticsearch directory:
$ cd elasticsearch/
$ ./dev-install.sh
Start Elasticsearch from the elasticsearch directory:
$ cd elasticsearch/
$ ./dev-start.sh
Create CloudFormation Stack
First you need to create some dev credentials and resources in AWS.
Log into the AWS Console (ask your friendly system administrator for a link and credentials) and change to the EU (Ireland) availability zone.
Go to the CloudFormation console and add a new stack, call it
media-service-DEV-{your-username}, upload the template file from
cloud-formation/dev-template.json and create the stack.
.properties files
Generate your .properties files for the various media-service services using the dot-properties generator
This will also create a panda.properties file that configures the
pan-domain authentication
This file will be used by the different applications to share auth config, so that CORS is enabled across APIs.
Make sure you put the generated .properties files in
/etc/gu/ instead of ~/.gu/ as many apps do.
Run Media API
From the project root, run via sbt:
$ sbt
> project media-api
> run
You may pass an argument to run to define which port to attach to, e.g.:
> run 9001
The media api should be up at http://localhost:9001/.
Run Thrall
From the project root, run via sbt:
$ sbt
> project thrall
> run 9002
The thrall should be up at http://localhost:9002/.
Run the Image Loader
From the project root, run via sbt:
$ sbt
> project image-loader
> run 9003
The image loader should be up at http://localhost:9003/.
You can upload a test image to it using curl:
curl -X POST --data-binary @integration/src/test/resources/images/honeybee.jpg http://localhost:9003/images
It should then appear in the Media API at http://localhost:9001/images.
Run the FTP Watcher
From the project root, run via sbt:
$ sbt -Dftp.active=true
> project ftp-watcher
> run 9004
The FTP watcher should be up at http://localhost:9004/.
Images should appear in the Media API at http://localhost:9001/images.
Run Kahuna
Run the setup.sh script from the kahuna directory to get started:
$ cd kahuna
$ ./setup.sh
Then, from the project root, run via sbt:
$ sbt
> project kahuna
> run 9005
The user interface should be up at http://localhost:9005/.
Run Cropper
Add an API key for cropper to your key bucket:
# Create key file
$ CROPPER_KEY=cropper-`head -c 1024 /dev/urandom | md5sum | awk '{ print $1 }'`
$ echo Cropper > $CROPPER_KEY
# Upload to S3
# note: see `aws --profile media s3 ls | grep keybucket` output to find your bucket name
$ aws s3 cp $CROPPER_KEY s3://...YOUR_BUCKET_NAME.../
From the project root, run via sbt:
$ sbt
> project cropper
> run 9006
The user interface should be up at http://localhost:9006/.
Run Metadata Editor
From the project root, run via sbt:
$ sbt
> project metadata-editor
> run 9007
The user interface should be up at http://localhost:9007/.
Run ImgOps
Troubleshooting
Nginx returns "413 Request Entity Too Large"
Make sure you bump the maximum allowed body size in your nginx config (defaults to 1MB):
client_max_body_size 20m;
Crops fail with a 500 HTTP error and an SSL error in the cropper logs
Make sure you install any certificate authority file needed in the Java runtime for the cropper service to talk to the media-api.
You can do so with the keytool command:
$ sudo keytool -import \
-trustcacerts \
-alias internalrootca \
-file rootcafile.cer \
-keystore /path/to/global/jre/lib/security/cacerts
where internalrootca is the name you want to give the certificate in
your keystore, rootcafile.cer is the certificate file you want to
install, and /path/to/global/jre/lib/security/cacerts the location
of the cacerts file for the JRE you're using.
On Mac OS X, it may be something like
/Library/Java/JavaVirtualMachines/jdk1.8.0_25.jdk/Contents/Home/jre/lib/security/cacerts;
on GNU Linux, it may be something like
/usr/lib/jvm/java-1.8.0-openjdk-amd64/jre/lib/security/cacerts.