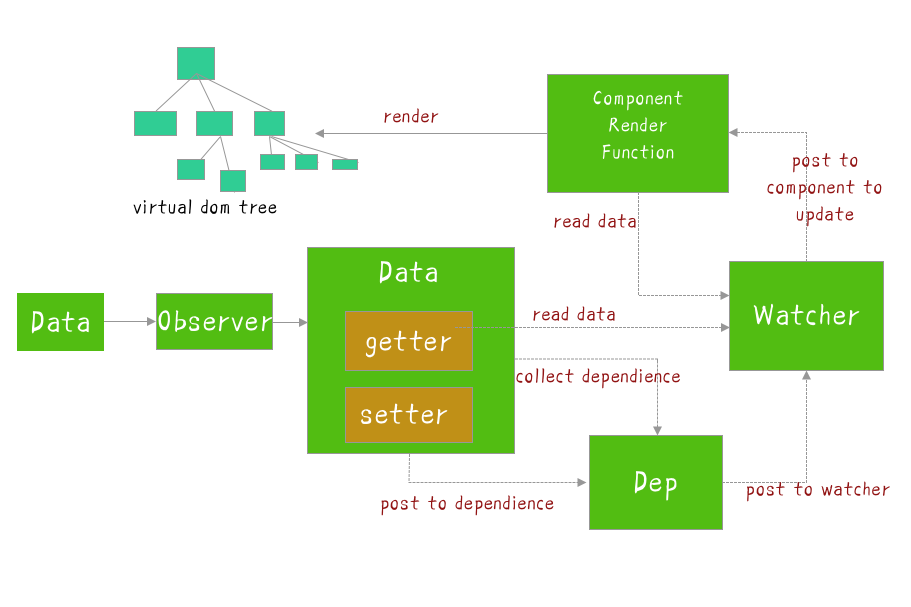
[1]. Vue reactive principle
Add getter and setter to the properties of the object for dependency collection and distribution updates
Collect the dependencies of the current reactive object. Each reactive object including sub-objects has a Dep instance (where subs is an array of Watcher instances). When the data changes, each watcher will be notified through dep.notify().
Instances are divided into three types: rendering watcher (render watcher), calculated attribute watcher (computed watcher), and listener watcher (user watcher)
The watcher instantiates dep and adds subscribers to dep.subs. Dep traverses dep.subs through notify to notify each watcher of updates.
In initState, when the computed attribute is initialized, the computed watcher dependency collection is triggered
In initState, when the listening attribute is initialized, the user watcher dependency collection is triggered
The process of render() triggers the render watcher dependency collection
During re-render, vm.render() is executed again, which will remove the subscription of watcer in all subs and re-assign the value.
The response data is modified in the component to trigger the logic of the setter
Traverse all subs (Watcher instances) and call the update method of each watcher.
When a Vue instance is created, Vue will traverse the properties of the data option, use Object.defineProperty to add getters and setters to the properties to hijack the reading of the data (getters are used for dependency collection, setters are used to distribute updates), and internally track dependencies , Notify changes when properties are accessed and modified.
Each component instance will have a corresponding watcher instance, which will record all dependent data attributes (dependency collection, computed watcher, user watcher instances) during component rendering, and then the setter method will notify when the dependency is changed The watcher instance that relies on this data is recalculated (distributed updates), so that its associated components are re-rendered.
[2]. The realization principle of computed:
The essence of computed is a lazily evaluated observer.
A lazy watcher is implemented inside computed, that is, computed watcher. The computed watcher will not be evaluated immediately and will hold a dep instance.
It uses this.dirty property to mark whether the calculated property needs to be re-evaluated.
When the dependent state of computed changes, this lazy watcher will be notified,
The computed watcher uses this.dep.subs.length to determine whether there are subscribers,
If there is, it will be recalculated and then compared with the old and new values. If it changes, it will be re-rendered. (Vue wants to ensure that not only the value that the calculated attribute depends on changes, but also that the rendering watcher is triggered to re-render when the final calculated value of the calculated attribute changes, which is essentially an optimization.)
If not, just set this.dirty = true. (When the calculated attribute depends on other data, the attribute will not be recalculated immediately. It will only be calculated when the attribute needs to be read elsewhere, that is, it has the characteristics of lazy (lazy calculation).)
[3]. What is the difference between computed and watch and application scenarios?
the difference computed attribute: depends on other attribute values, and the computed value is cached. Only when the attribute value it depends on changes, the computed value will be recalculated the next time the computed value is obtained.
Watch listener: It is more about the function of "observation", no cache, similar to the monitoring callback of some data, whenever the monitored data changes, the callback will be executed for subsequent operations.
Application scenario Application scenarios:
When we need to perform numerical calculations and rely on other data, we should use computed, because we can use the cache feature of computed to avoid recalculation every time we get a value.
When we need to perform asynchronous or expensive operations when data changes, we should use watch. Using the watch option allows us to perform asynchronous operations (accessing an API), limiting the frequency with which we perform the operation, and before we get the final result ,Set the intermediate state. These are things that calculated properties cannot do.
[4]. Why is Proxy adopted in Vue3.0 and Object.defineProperty is abandoned?
Object.defineProperty itself has a certain ability to monitor the changes of array subscripts, but in Vue, considering the performance/experience cost-effectiveness, this feature is greatly abandoned (why can Vue not detect array changes). In order to solve this problem, the following methods can be used to monitor the array after internal processing in vue
push();
pop();
shift();
unshift();
splice();
sort();
reverse();Since only the above 7 methods have been hacked, the attributes of other arrays are also undetectable, and they still have certain limitations.
Object.defineProperty can only hijack the properties of the object, so we need to traverse each property of each object. In Vue 2.x, data is monitored through recursion + traversal of data objects. If the attribute value is also an object, then deep traversal is required. Obviously, it is better to hijack a complete object.
Proxy can hijack the entire object and return a new object. Proxy can not only proxy objects, but also proxy arrays. It can also proxy dynamically added attributes.
[5]. What is the use of keys in Vue?
The key is the unique id for each vnode. Depending on the key, our diff operation can be more accurate and faster (for simple list page rendering, the diff node is also faster, but it will produce some hidden side effects, such as may not Transition effects, or the state of binding data (form) at some nodes, will cause state dislocation.)
In the process of the diff algorithm, the new and old nodes will be cross-compared first.
More accurate: Because the key is not reused in place, in the sameNode function a.key === b.key comparison can avoid in-situ reuse. So it will be more accurate. If the key is not added, the state of the previous node will be retained, which will cause a series of bugs.
Faster: The uniqueness of the key can be fully utilized by the Map data structure. Compared with the time complexity of traversal search O(n), the time complexity of Map is only O(1). The source code is as follows:
[6]. Talk about the principle of nextTick
JS execution is single-threaded, and it is based on an event loop. The event loop is roughly divided into the following steps:
All synchronization tasks are executed on the main thread, forming an execution context stack.
In addition to the main thread, there is also a "task queue" (task queue). As long as the asynchronous task has a running result, an event is placed in the "task queue".
Once all the synchronization tasks in the "execution stack" are executed, the system will read the "task queue" to see what events are in it. Those corresponding asynchronous tasks end the waiting state, enter the execution stack, and start execution.
The main thread keeps repeating the third step above.
The execution process of the main thread is a tick, and all asynchronous results are scheduled through the "task queue". What is stored in the message queue is a task. The specification stipulates that tasks are divided into two categories, macro tasks and micro tasks, and after each macro task ends, all micro tasks must be cleared.
In the browser environment:
Common macro tasks include setTimeout, MessageChannel, postMessage, setImmediate
Common micro tasks include MutationObsever and Promise.then
You may not have noticed that Vue is executed asynchronously when updating the DOM. As long as it listens to data changes, Vue will open a queue and buffer all data changes that occur in the same event loop.
If the same watcher is triggered multiple times, it will only be pushed to the queue once. This removal of duplicate data during buffering is very important to avoid unnecessary calculations and DOM operations.
Then, in the next event loop "tick", Vue refreshes the queue and executes the actual (deduplicated) work.
Vue internally tries to use native Promise.then, MutationObserver and setImmediate for asynchronous queues. If the execution environment does not support it, it will use setTimeout(fn, 0) instead
In the source code of vue2.5, the macrotask downgrade scheme is: setImmediate, MessageChannel, setTimeout
The realization principle of vue's nextTick method:
Vue uses asynchronous queues to control DOM updates and nextTick callbacks.
Because of its high-priority feature, microtask can ensure that the microtasks in the queue are executed before an event loop
Considering compatibility issues, vue made a downgrade scheme from microtask to macrotask
[7]. How does vue mutate array methods?
Let's take a look at the source code first
Simply put, Vue rewrites the 7 methods of the array through prototype interception. First, it gets the ob of this array, which is its Observer object. If there is a new value, it calls observeArray to monitor the new value. Then manually call notify, notify the render watcher, and execute update
[8]. Why must the Vue component data be a function?
In the new Vue() instance, data can be directly an object. Why in the vue component, data must be a function?
Because components can be reused, objects in JS are referenced. If the component data is an object, then the data attribute values in the sub-components will pollute each other and cause side effects.
So the data option of a component must be a function, so each instance can maintain an independent copy of the returned object. Instances of new Vue will not be reused, so there is no such problem.
[9]. Talk about the Vue event mechanism, handwriting $on, $off, $emit, $once
The Vue event mechanism is essentially an implementation of a publish-subscribe model.
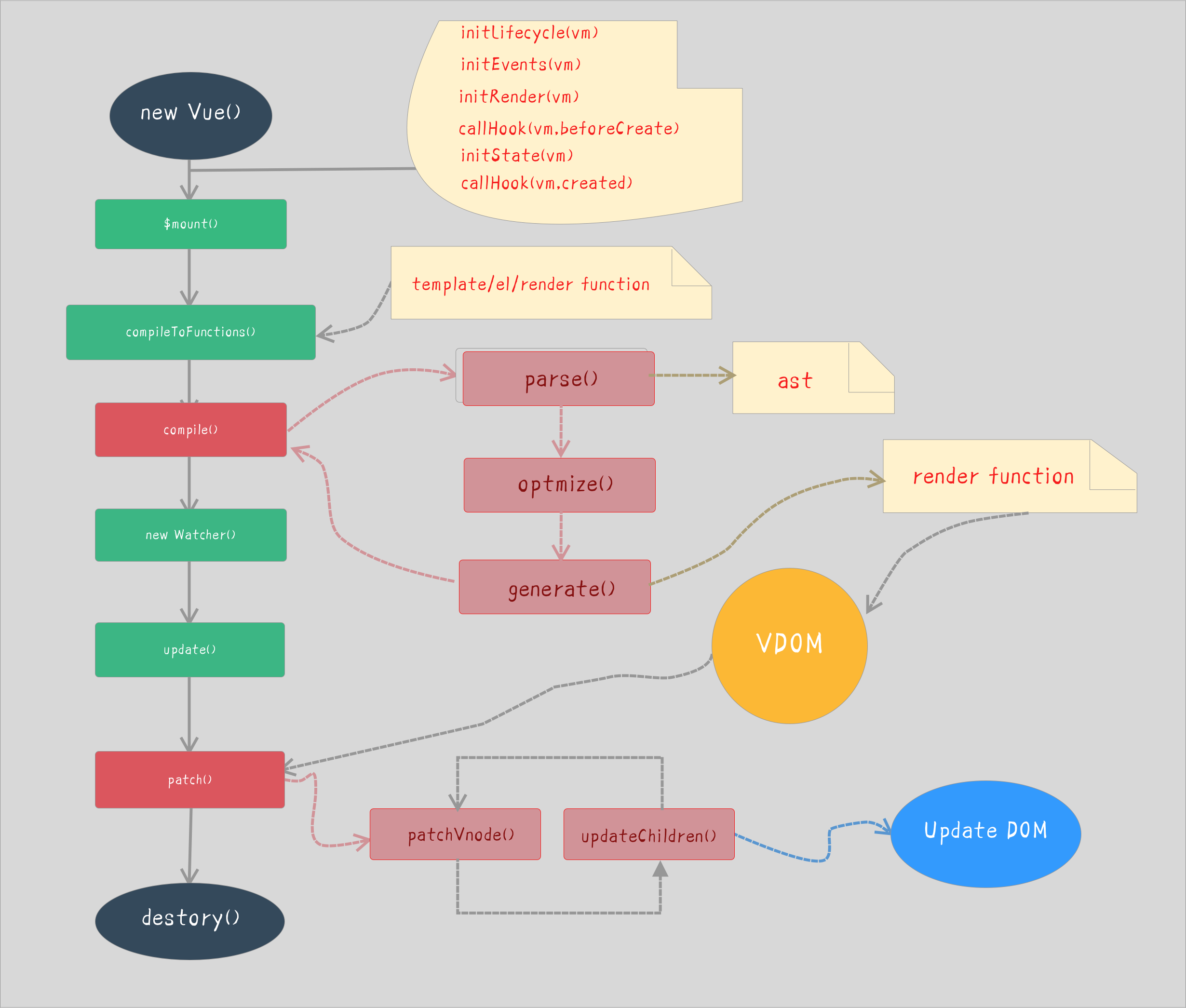
[10]. Talk about the Vue render process.
Call the compile function to generate the render function string. The compilation process is as follows:
The parse function parses the template and generates ast (abstract syntax tree)
The optimize function optimizes static nodes (marking content that does not need to be updated every time, the diff algorithm will directly skip the static nodes, thereby reducing the comparison process and optimizing the performance of the patch)
The generate function generates the render function string
Call the new Watcher function to monitor the changes in the data. When the data changes, the Render function executes to generate a vnode object
Call the patch method, compare the old and new vnode objects, and add, modify, and delete real DOM elements through the DOM diff algorithm
[11]. Talk about the implementation principle and caching strategy of keep-alive:
Get the first sub-component object and its component name wrapped by keep-alive.
Condition matching is performed according to the set include/exclude (if any),
and it is decided whether to cache.
If there is no match, return the component instance directly.
Generate a cache Key based on the component ID and tag,
and find whether the component instance has been cached in the cache object.
If it exists, directly take out the cached value and update the position of
the key in this.keys .
(update the key position is the key to realize the LRU replacement strategy)
Store the component instance in this.cache object and save the key value,
and then check the cache .
Whether the number of instances exceeds the set value of max,
if it exceeds, the least recently used instance (that is, the key with subscript 0)
will be deleted according to the LRU replacement strategy.
Finally, the keepAlive property of the component instance is set to true,
which is wrapped in rendering and execution .
The hook function of the component will be used, not detailed here.
The implementation of keep-alive uses the LRU strategy to
push the recently accessed component to the end of this.keys,
this.keys[0] is the component that has not been accessed for the longest time.
When the cache instance exceeds the max setting value,
delete this.keys[0]
[12]. What is the principle of implementing vm.$set()?
Due to the limitations of modern JavaScript (and Object.observe has also been deprecated), Vue cannot detect the addition or deletion of object properties.
Since Vue will perform getter/setter conversion on the property when initializing the instance, the property must exist on the data object in order for Vue to convert it to reactive.
For already created instances, Vue does not allow dynamic addition of root-level reactive properties.
However, you can use the Vue.set(object, propertyName, value) method to add responsive properties to nested objects.
So how does Vue internally solve the problem that the new properties of the object cannot respond?
[13] . Realize shallow copy and deep copy
[14] . think about setTimeout()
[15] . parseInt and map()
[16] . What is anti-shake and throttling? What's the difference? How to achieve?
- Anti-shake function will only be executed once within n seconds after triggering the high-frequency event. If the high-frequency event is triggered again within n seconds, the time will be recalculated;
[17] . Introduce the difference between Set, Map, WeakSet and WeakMap?
Setmembers are unique, unordered, and non-repetitive;[value, value], the key value is consistent with the key name (or only the key value, no key name); It can be traversed, the methods are:add,delete,has.- The members of
WeakSetare all objects; the members are all weak references, which can be recycled by garbage collection mechanism, and can be used to saveDOMnodes, which are not easy to cause memory leaks; they cannot be traversed. The methods includeadd,delete, andhas. Mapis essentially a collection of key-value pairs, similar to a collection; it can be traversed, with many methods, and can be converted with various data formats.WeakMaponly accepts the object as the key name (except null), and does not accept other types of values as the key name; the key name is a weak reference, the key value can be arbitrary, and the object pointed to by the key name can be garbage collected. The name is invalid; it cannot be traversed. The methods areget,set,has, anddelete.
[18] . Handwriting EventEmitter
[19] . Flatten the array and remove duplicate data, and finally get an ascending and non-repetitive array
[20] . Count the number of occurrences of each element in the array
[21] . When importing styles on a page, what is the difference between using link and @import
Difference in affiliation.
@import can only import style sheets, link can also define RSS, rel connection attributes, and introduce website icons;
the loading order is different; when the page is loaded, the CSS introduced by the link tag is loaded at the same time; the CSS imported by @import will be loaded after the page is loaded
After being loaded; Compatibility difference;
[22]. The rendering principle of the browser
First parse the received document and construct a DOM tree according to the document definition. The DOM tree is composed of DOM elements and attribute nodes; then the CSS is parsed to generate a CSSOM rule tree; and a Render Tree is constructed based on the DOM tree and CSSOM rule tree.
The node of the rendering tree is called the rendering object. The rendering object is a rectangle containing attributes such as color and size. The rendering object corresponds to the DOM object, but this correspondence is not one-to-one. Invisible DOM elements will not
Is inserted into the render tree.
When rendering objects are created and added to the tree, they have no position or size, so when the browser generates the render tree, it will be laid out according to the render tree (also called reflow).
What the browser has to do at this stage is to figure out the exact position and size of each node on the page.
Usually this behavior is also called "automatic rearrangement".
After the layout phase is over, it is the drawing phase, where the tree is rendered and the paint method of the object is called to display their content on the screen, and the UI basic components are used for drawing.
For a better user experience, the rendering engine will render the content on the screen as early as possible, and will not wait until all html parsing is completed before constructing and laying out the render tree.
It displays part of the content after parsing part of the content, and may download the rest of the content on the Internet.
[23] . What is the auto-completion function of HTML5 form?
The autocomplete attribute specifies whether the input field should enable the auto-complete function, the default is enabled, set to autocomplete=off to turn off the function. Auto-complete allows the browser to predict the input to the field. When the user starts typing in the field, the browser should display the options filled in the field based on the previously typed value.
[24] . How to realize the communication between multiple tabs in the browser?
The communication between multiple tabs is essentially achieved through the intermediary model.
Because there is no way to communicate directly between tabs, we can find an intermediary to let the tabs communicate with the intermediary, and then let this intermediary forward the message.
Using Websocket, the communication tab is connected to the same server. After sending a message to the server, the server pushes the message to all connected clients; you can call localStorage. When localStorage is added, modified or deleted in another browsing context, it will
To trigger a storage event, we can communicate with the page information by listening to the storage event and controlling its value; if we can get a reference to the corresponding tab, multiple tabs can also be communicated through the postMessage method;
[25]. Briefly describe the front-end performance optimization
In terms of page content,
the number of HTTP requests is reduced through file merging, css sprite, base64, etc.,
to avoid excessive requests causing waiting; DNS cache and other mechanisms are used to reduce the number of DNS queries;
Unchanged resources are cached;
through lazy loading, to reduce the resources that need to be requested when the first screen of the page is loaded,
and the delayed-loaded resources are requested to be loaded when the user needs to access them;
through user behavior, some resources are pre-used
The way of loading is to improve the response speed when users need to access resources;
the server uses CDN service to improve the response speed of users to resource requests;
the server uses Gzip, Deflate and other methods to compress the transmitted resources to reduce the transmission of files
Reduce the size of the cookie as much as possible, and allocate static resources to other domain names
to avoid carrying unnecessary cookies when requesting static resources;
[26] . What is webp?
WebP is a new image format developed by Google. It is a bitmap with direct color that supports both lossy and lossless compression methods.
The biggest advantage of using the webp format is that it has a smaller file size under the same quality files.
Therefore, it is very suitable for the transmission of network pictures, because the reduction of the picture volume means the reduction of the request time, which will improve the user experience.
This is a new image format developed by Google.
By creating an Image object, set its src attribute to a webp format picture,
and then get the width and height of the picture in the onload event. If it can be obtained,
it means that the browser supports webp format pictures.
If the onerror function cannot be obtained or triggered, it means that the browser does not support images in webp format.
[27] . Introduce BFC and its applications
BFC (Block Format Context) block-level formatting context is a CSS rendering mode in the page box model,
which is equivalent to an independent container, and the elements inside and outside elements do not affect each other.
The ways to create BFC are: html root element ,float, floating absolute positioning ,overflow not visible display for table layout or flexible layout;
the main function of BFC is to: clear floating and prevent overlapping of margins between adjacent elements in the same BFC container
[28] . How to center a div horizontally and vertically?
[29] . Introduce Repaint & Reflow, and how to optimize it?
The browser uses the Flow Based Layout;
the browser parses HTML into DOM, and parses CSS into CSSOM.
The DOM and CSSOM merge to produce a Render Tree; with RenderTree,
We know the styles of all the nodes, and then calculate their size and position on the page,
and finally draw the nodes on the page; because the browser uses a stream layout,
the calculation of the Render Tree usually only needs to be traversed once.
But with the exception of table and its internal elements, they may need to be calculated multiple times,
which usually takes 3 times the time of the same element,
which is one of the reasons why you should avoid using table layout;
Redrawing will not affect the layout due to changes in the collection properties of nodes or changes in styles, and which is called redrawing,
such as outline, visibility, color, background-color, etc.
The cost of redrawing is high, so the browser must verify the DOM ,
The visibility of other node elements on the tree.
Reflow means that the layout or geometric properties need to be changed, which is called reflow.
Reflow is a key factor affecting browser performance,
because its changes involve the layout update of part of the page (or the entire page).
The reflow of an element may result in the subsequent reflow of all child elements,
nodes and ancestor nodes that follow it in the DOM.
Most of the reflow will cause the page to be re-rendered.
Redrawing will definitely cause redrawing, and redrawing will not necessarily cause reflowing.
Most modern browsers use the queue mechanism to update the layout in batches.
The browser will put the modification operation in the queue. At least one browser refresh (ie 16.6ms) will clear the queue, but when you get the layout information, the queue is
There may be operations that affect the return value of these properties or methods.
Even if there is no operation, the browser will forcefully clear the queue,
trigger reflow and redraw to ensure that the correct value is returned.
For example, offsetTop, clientTop, scrollTop, getComputedStyle(), width, height, getBoundingClientRect().
Frequent use of these properties should be avoided. They will all force the rendering to refresh the queue.
- Use
transforminstead oftop; - use
visibilityto replacedisplay: none, the former causesredrawing, and the latter causesreflow; - Avoid using
tablelayout; try to change the class at the end oftheDOM tree as much as possible; - Avoid setting multiple
inline styles, CSS selectors - Match and search from right to left to avoid excessive node levels; apply animation effects to elements whose position attribute is absolute or fixed to avoid affecting the layout of other elements; avoid using CSS expressions, which may cause reflow; CSS hardware acceleration;
- Avoid frequent manipulation of
stylesandmodifythe class; - Avoid frequent manipulation of the
DOMand merge multiple modifications into one; - Avoid frequent reading of attributes that will cause
reflow/redraw, and cache the results; - Use
absolutepositioning for elements with complex animations, so it is out of the document flow;
[30] . Analyze and compare the pros and cons of opacity: 0, visibility: hidden, display: none and applicable scenarios
display: none- it does not occupy space, can not be clicked, would cause reflow, do not affect child elementsvisibility: hidden-occupy space, can not be clicked, cause redrawing, child elements can be set visible for displayopacity: 0-occupy space, clickable, causes redrawing, do not affect child elements
[31] . Brief description of the CSS box model
The box is composed of margin, border, padding, and content;
standard box model: box-sizing: content-box;
IE box model: box-sizing: border-box;
[32] . Briefly describe Rem and its conversion principle
rem is a new relative length unit of CSS3,
which refers to the size of the calculated value relative to the font-size of the root element html.
By default, the font-size of the root element is 16px.
If you want to set the font size of 12px, then 12px/16px = 0.75rem.
Because px is a relatively fixed unit, the font size is directly fixed and cannot be scaled with the browser;
rem is directly relative to the root element html, avoiding the hierarchical relationship,
and it is better supported by new mobile browsers; vw + for personal use
Percentage layout is used more, you can use webpack's postcss-loader plug-in postcss-px-to-viewport to realize automatic conversion from px to vw, which is very suitable for development.
[33] . Mobile viewport configuration
[34] . Briefly describe pseudo-classes and pseudo-elements
Pseudo-classes are used to add corresponding styles to existing elements when they are in a certain state.
This state changes according to changes in user behavior.
For example: hover.
It can add styles to elements only in a state that the dom tree cannot describe, so it is called a pseudo-class.
Pseudo-elements are used to create elements that are not originally in the document tree and add styles to them,
such as ::before.
Although the user can see these contents, he is not in the document tree.
The operation object of the pseudo-class is the existing element in the document tree, and the pseudo-element is to create an element outside the document tree.
In the css specification, a double colon :: represents a pseudo element, and a colon : represents a pseudo class.
[35] . Margin and padding of inline elements
- Horizontal direction: both are valid in the horizontal direction;
- Vertical direction: both are invalid in the vertical direction; (padding-top and padding-bottom will show the effect, but the height will not be stretched and will not affect the surrounding elements)
[36] . Which properties in CSS can be inherited?
-
font-family
-
font-size
-
font-weight
-
font-style
-
text-indent
-
text-align
-
line-hight
-
word-spacing
-
letter-spacing
-
color
-
cursor
-
visibility
[37] . What are the new pseudo-classes in CSS3?
(E.g. nth-child)
-
elem:nth-child(n): select the nth element whose label is elem under the parent element; -
elem:nth-last-child(n): Same as above, search from the back; -
elem:last-child: the last child element -
elem:only-child: If elem is the only child element under the parent element, select it; -
elem:nth-of-type(n): select the nthelemtype element under the parent element; -
elem:empty: Selectelemtype elements that do not contain child elements and content; -
:not(elem): select each element that isnotanelemelement; -
:enabled: the form component in theenabledstate
[38] . Create a triangle with pure CSS
[39] . The coverage rule between min-width/max-width and min-height/max-height attributes?
max-width will override width, even if width is inline style or !important is set.
min-width will override max-width, this rule occurs when min-width and max-width conflict
[40] . Simply talk about the types of memory leaks in js
Unexpected global variables;
closures;
timers that have not been emptied;
event listeners that have not been destroyed;
DOM references;
[41] . Simulate the implementation of new
[42] . try to handwrite render function in vue.